Chih-Chung Hsu
GTATrack: Winner Solution to SoccerTrack 2025 with Deep-EIoU and Global Tracklet Association
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Multi-object tracking (MOT) in sports is highly challenging due to irregular player motion, uniform appearances, and frequent occlusions. These difficulties are further exacerbated by the geometric distortion and extreme scale variation introduced by static fisheye cameras. In this work, we present GTATrack, a hierarchical tracking framework that win first place in the SoccerTrack Challenge 2025. GTATrack integrates two core components: Deep Expansion IoU (Deep-EIoU) for motion-agnostic online association and Global Tracklet Association (GTA) for trajectory-level refinement. This two-stage design enables both robust short-term matching and long-term identity consistency. Additionally, a pseudo-labeling strategy is used to boost detector recall on small and distorted targets. The synergy between local association and global reasoning effectively addresses identity switches, occlusions, and tracking fragmentation. Our method achieved a winning HOTA score of 0.60 and significantly reduced false positives to 982, demonstrating state-of-the-art accuracy in fisheye-based soccer tracking. Our code is available at https://github.com/ron941/GTATrack-STC2025.
HSSDCT: Factorized Spatial-Spectral Correlation for Hyperspectral Image Fusion
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Hyperspectral image (HSI) fusion aims to reconstruct a high-resolution HSI (HR-HSI) by combining the rich spectral information of a low-resolution HSI (LR-HSI) with the fine spatial details of a high-resolution multispectral image (HR-MSI). Although recent deep learning methods have achieved notable progress, they still suffer from limited receptive fields, redundant spectral bands, and the quadratic complexity of self-attention, which restrict both efficiency and robustness. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Hierarchical Spatial-Spectral Dense Correlation Network (HSSDCT). The framework introduces two key modules: (i) a Hierarchical Dense-Residue Transformer Block (HDRTB) that progressively enlarges windows and employs dense-residue connections for multi-scale feature aggregation, and (ii) a Spatial-Spectral Correlation Layer (SSCL) that explicitly factorizes spatial and spectral dependencies, reducing self-attention to linear complexity while mitigating spectral redundancy. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that HSSDCT delivers superior reconstruction quality with significantly lower computational costs, achieving new state-of-the-art performance in HSI fusion. Our code is available at https://github.com/jemmyleee/HSSDCT.
PhaSR: Generalized Image Shadow Removal with Physically Aligned Priors
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Shadow removal under diverse lighting conditions requires disentangling illumination from intrinsic reflectance, a challenge compounded when physical priors are not properly aligned. We propose PhaSR (Physically Aligned Shadow Removal), addressing this through dual-level prior alignment to enable robust performance from single-light shadows to multi-source ambient lighting. First, Physically Aligned Normalization (PAN) performs closed-form illumination correction via Gray-world normalization, log-domain Retinex decomposition, and dynamic range recombination, suppressing chromatic bias. Second, Geometric-Semantic Rectification Attention (GSRA) extends differential attention to cross-modal alignment, harmonizing depth-derived geometry with DINO-v2 semantic embeddings to resolve modal conflicts under varying illumination. Experiments show competitive performance in shadow removal with lower complexity and generalization to ambient lighting where traditional methods fail under multi-source illumination. Our source code is available at https://github.com/ming053l/PhaSR.
ReflexSplit: Single Image Reflection Separation via Layer Fusion-Separation
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Single Image Reflection Separation (SIRS) disentangles mixed images into transmission and reflection layers. Existing methods suffer from transmission-reflection confusion under nonlinear mixing, particularly in deep decoder layers, due to implicit fusion mechanisms and inadequate multi-scale coordination. We propose ReflexSplit, a dual-stream framework with three key innovations. (1) Cross-scale Gated Fusion (CrGF) adaptively aggregates semantic priors, texture details, and decoder context across hierarchical depths, stabilizing gradient flow and maintaining feature consistency. (2) Layer Fusion-Separation Blocks (LFSB) alternate between fusion for shared structure extraction and differential separation for layer-specific disentanglement. Inspired by Differential Transformer, we extend attention cancellation to dual-stream separation via cross-stream subtraction. (3) Curriculum training progressively strengthens differential separation through depth-dependent initialization and epoch-wise warmup. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance with superior perceptual quality and robust generalization. Our code is available at https://github.com/wuw2135/ReflexSplit.
VReID-XFD: Video-based Person Re-identification at Extreme Far Distance Challenge Results
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) across aerial and ground views at extreme far distances introduces a distinct operating regime where severe resolution degradation, extreme viewpoint changes, unstable motion cues, and clothing variation jointly undermine the appearance-based assumptions of existing ReID systems. To study this regime, we introduce VReID-XFD, a video-based benchmark and community challenge for extreme far-distance (XFD) aerial-to-ground person re-identification. VReID-XFD is derived from the DetReIDX dataset and comprises 371 identities, 11,288 tracklets, and 11.75 million frames, captured across altitudes from 5.8 m to 120 m, viewing angles from oblique (30 degrees) to nadir (90 degrees), and horizontal distances up to 120 m. The benchmark supports aerial-to-aerial, aerial-to-ground, and ground-to-aerial evaluation under strict identity-disjoint splits, with rich physical metadata. The VReID-XFD-25 Challenge attracted 10 teams with hundreds of submissions. Systematic analysis reveals monotonic performance degradation with altitude and distance, a universal disadvantage of nadir views, and a trade-off between peak performance and robustness. Even the best-performing SAS-PReID method achieves only 43.93 percent mAP in the aerial-to-ground setting. The dataset, annotations, and official evaluation protocols are publicly available at https://www.it.ubi.pt/DetReIDX/ .
Towards Robust DeepFake Detection under Unstable Face Sequences: Adaptive Sparse Graph Embedding with Order-Free Representation and Explicit Laplacian Spectral Prior
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Ensuring the authenticity of video content remains challenging as DeepFake generation becomes increasingly realistic and robust against detection. Most existing detectors implicitly assume temporally consistent and clean facial sequences, an assumption that rarely holds in real-world scenarios where compression artifacts, occlusions, and adversarial attacks destabilize face detection and often lead to invalid or misdetected faces. To address these challenges, we propose a Laplacian-Regularized Graph Convolutional Network (LR-GCN) that robustly detects DeepFakes from noisy or unordered face sequences, while being trained only on clean facial data. Our method constructs an Order-Free Temporal Graph Embedding (OF-TGE) that organizes frame-wise CNN features into an adaptive sparse graph based on semantic affinities. Unlike traditional methods constrained by strict temporal continuity, OF-TGE captures intrinsic feature consistency across frames, making it resilient to shuffled, missing, or heavily corrupted inputs. We further impose a dual-level sparsity mechanism on both graph structure and node features to suppress the influence of invalid faces. Crucially, we introduce an explicit Graph Laplacian Spectral Prior that acts as a high-pass operator in the graph spectral domain, highlighting structural anomalies and forgery artifacts, which are then consolidated by a low-pass GCN aggregation. This sequential design effectively realizes a task-driven spectral band-pass mechanism that suppresses background information and random noise while preserving manipulation cues. Extensive experiments on FF++, Celeb-DFv2, and DFDC demonstrate that LR-GCN achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly improved robustness under severe global and local disruptions, including missing faces, occlusions, and adversarially perturbed face detections.
DenseSR: Image Shadow Removal as Dense Prediction
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Shadows are a common factor degrading image quality. Single-image shadow removal (SR), particularly under challenging indirect illumination, is hampered by non-uniform content degradation and inherent ambiguity. Consequently, traditional methods often fail to simultaneously recover intra-shadow details and maintain sharp boundaries, resulting in inconsistent restoration and blurring that negatively affect both downstream applications and the overall viewing experience. To overcome these limitations, we propose the DenseSR, approaching the problem from a dense prediction perspective to emphasize restoration quality. This framework uniquely synergizes two key strategies: (1) deep scene understanding guided by geometric-semantic priors to resolve ambiguity and implicitly localize shadows, and (2) high-fidelity restoration via a novel Dense Fusion Block (DFB) in the decoder. The DFB employs adaptive component processing-using an Adaptive Content Smoothing Module (ACSM) for consistent appearance and a Texture-Boundary Recuperation Module (TBRM) for fine textures and sharp boundaries-thereby directly tackling the inconsistent restoration and blurring issues. These purposefully processed components are effectively fused, yielding an optimized feature representation preserving both consistency and fidelity. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the merits of our approach over existing methods. Our code can be available on https://github$.$com/VanLinLin/DenseSR
Multi Source COVID-19 Detection via Kernel-Density-based Slice Sampling
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We present our solution for the Multi-Source COVID-19 Detection Challenge, which classifies chest CT scans from four distinct medical centers. To address multi-source variability, we employ the Spatial-Slice Feature Learning (SSFL) framework with Kernel-Density-based Slice Sampling (KDS). Our preprocessing pipeline combines lung region extraction, quality control, and adaptive slice sampling to select eight representative slices per scan. We compare EfficientNet and Swin Transformer architectures on the validation set. The EfficientNet model achieves an F1-score of 94.68%, compared to the Swin Transformer's 93.34%. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our KDS-based pipeline on multi-source data and highlight the importance of dataset balance in multi-institutional medical imaging evaluation.
NTIRE 2025 Image Shadow Removal Challenge Report
Jun 18, 2025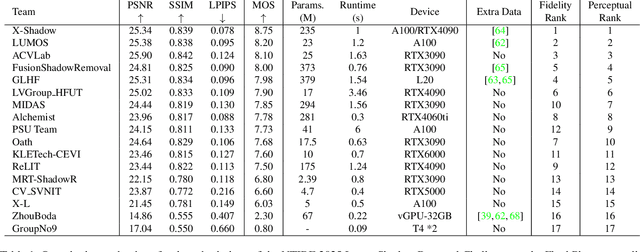

Abstract:This work examines the findings of the NTIRE 2025 Shadow Removal Challenge. A total of 306 participants have registered, with 17 teams successfully submitting their solutions during the final evaluation phase. Following the last two editions, this challenge had two evaluation tracks: one focusing on reconstruction fidelity and the other on visual perception through a user study. Both tracks were evaluated with images from the WSRD+ dataset, simulating interactions between self- and cast-shadows with a large number of diverse objects, textures, and materials.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge