Chen Jason Zhang
RAL2M: Retrieval Augmented Learning-To-Match Against Hallucination in Compliance-Guaranteed Service Systems
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Hallucination is a major concern in LLM-driven service systems, necessitating explicit knowledge grounding for compliance-guaranteed responses. In this paper, we introduce Retrieval-Augmented Learning-to-Match (RAL2M), a novel framework that eliminates generation hallucination by repositioning LLMs as query-response matching judges within a retrieval-based system, providing a robust alternative to purely generative approaches. To further mitigate judgment hallucination, we propose a query-adaptive latent ensemble strategy that explicitly models heterogeneous model competence and interdependencies among LLMs, deriving a calibrated consensus decision. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method effectively leverages the "wisdom of the crowd" and significantly outperforms strong baselines. Finally, we discuss best practices and promising directions for further exploiting latent representations in future work.
Multimodal Peer Review Simulation with Actionable To-Do Recommendations for Community-Aware Manuscript Revisions
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) offer promising capabilities for automating academic workflows, existing systems for academic peer review remain constrained by text-only inputs, limited contextual grounding, and a lack of actionable feedback. In this work, we present an interactive web-based system for multimodal, community-aware peer review simulation to enable effective manuscript revisions before paper submission. Our framework integrates textual and visual information through multimodal LLMs, enhances review quality via retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) grounded in web-scale OpenReview data, and converts generated reviews into actionable to-do lists using the proposed Action:Objective[\#] format, providing structured and traceable guidance. The system integrates seamlessly into existing academic writing platforms, providing interactive interfaces for real-time feedback and revision tracking. Experimental results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed system in generating more comprehensive and useful reviews aligned with expert standards, surpassing ablated baselines and advancing transparent, human-centered scholarly assistance.
Removal of Hallucination on Hallucination: Debate-Augmented RAG
May 24, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances factual accuracy by integrating external knowledge, yet it introduces a critical issue: erroneous or biased retrieval can mislead generation, compounding hallucinations, a phenomenon we term Hallucination on Hallucination. To address this, we propose Debate-Augmented RAG (DRAG), a training-free framework that integrates Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) mechanisms into both retrieval and generation stages. In retrieval, DRAG employs structured debates among proponents, opponents, and judges to refine retrieval quality and ensure factual reliability. In generation, DRAG introduces asymmetric information roles and adversarial debates, enhancing reasoning robustness and mitigating factual inconsistencies. Evaluations across multiple tasks demonstrate that DRAG improves retrieval reliability, reduces RAG-induced hallucinations, and significantly enhances overall factual accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/Huenao/Debate-Augmented-RAG.
QualBench: Benchmarking Chinese LLMs with Localized Professional Qualifications for Vertical Domain Evaluation
May 08, 2025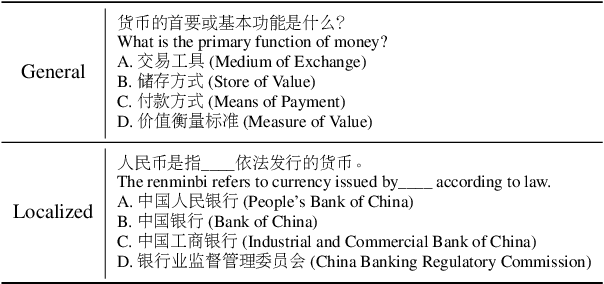
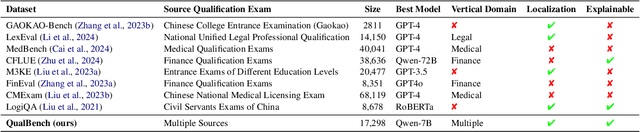
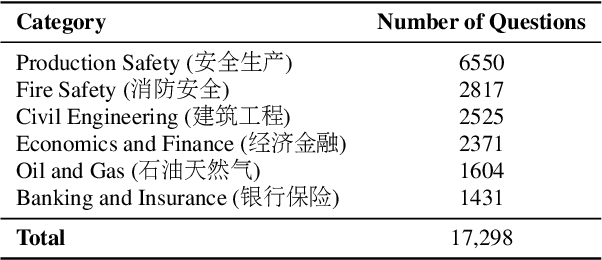
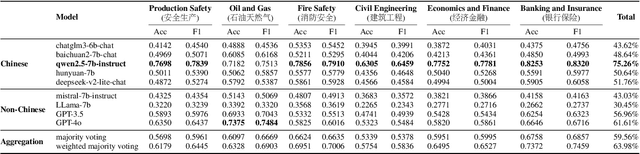
Abstract:The rapid advancement of Chinese large language models (LLMs) underscores the need for domain-specific evaluations to ensure reliable applications. However, existing benchmarks often lack coverage in vertical domains and offer limited insights into the Chinese working context. Leveraging qualification exams as a unified framework for human expertise evaluation, we introduce QualBench, the first multi-domain Chinese QA benchmark dedicated to localized assessment of Chinese LLMs. The dataset includes over 17,000 questions across six vertical domains, with data selections grounded in 24 Chinese qualifications to closely align with national policies and working standards. Through comprehensive evaluation, the Qwen2.5 model outperformed the more advanced GPT-4o, with Chinese LLMs consistently surpassing non-Chinese models, highlighting the importance of localized domain knowledge in meeting qualification requirements. The best performance of 75.26% reveals the current gaps in domain coverage within model capabilities. Furthermore, we present the failure of LLM collaboration with crowdsourcing mechanisms and suggest the opportunities for multi-domain RAG knowledge enhancement and vertical domain LLM training with Federated Learning.
MolGround: A Benchmark for Molecular Grounding
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Current molecular understanding approaches predominantly focus on the descriptive aspect of human perception, providing broad, topic-level insights. However, the referential aspect -- linking molecular concepts to specific structural components -- remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we propose a molecular grounding benchmark designed to evaluate a model's referential abilities. We align molecular grounding with established conventions in NLP, cheminformatics, and molecular science, showcasing the potential of NLP techniques to advance molecular understanding within the AI for Science movement. Furthermore, we constructed the largest molecular understanding benchmark to date, comprising 79k QA pairs, and developed a multi-agent grounding prototype as proof of concept. This system outperforms existing models, including GPT-4o, and its grounding outputs have been integrated to enhance traditional tasks such as molecular captioning and ATC (Anatomical, Therapeutic, Chemical) classification.
Revisiting Graph Neural Networks on Graph-level Tasks: Comprehensive Experiments, Analysis, and Improvements
Jan 01, 2025Abstract:Graphs are essential data structures for modeling complex interactions in domains such as social networks, molecular structures, and biological systems. Graph-level tasks, which predict properties or classes for the entire graph, are critical for applications, such as molecular property prediction and subgraph counting. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown promise in these tasks, but their evaluations are often limited to narrow datasets, tasks, and inconsistent experimental setups, restricting their generalizability. To address these limitations, we propose a unified evaluation framework for graph-level GNNs. This framework provides a standardized setting to evaluate GNNs across diverse datasets, various graph tasks (e.g., graph classification and regression), and challenging scenarios, including noisy, imbalanced, and few-shot graphs. Additionally, we propose a novel GNN model with enhanced expressivity and generalization capabilities. Specifically, we enhance the expressivity of GNNs through a $k$-path rooted subgraph approach, enabling the model to effectively count subgraphs (e.g., paths and cycles). Moreover, we introduce a unified graph contrastive learning algorithm for graphs across diverse domains, which adaptively removes unimportant edges to augment graphs, thereby significantly improving generalization performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves superior performance against fourteen effective baselines across twenty-seven graph datasets, establishing it as a robust and generalizable model for graph-level tasks.
MegaPairs: Massive Data Synthesis For Universal Multimodal Retrieval
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:Despite the rapidly growing demand for multimodal retrieval, progress in this field remains severely constrained by a lack of training data. In this paper, we introduce MegaPairs, a novel data synthesis method that leverages vision language models (VLMs) and open-domain images, together with a massive synthetic dataset generated from this method. Our empirical analysis shows that MegaPairs generates high-quality data, enabling the multimodal retriever to significantly outperform the baseline model trained on 70$\times$ more data from existing datasets. Moreover, since MegaPairs solely relies on general image corpora and open-source VLMs, it can be easily scaled up, enabling continuous improvements in retrieval performance. In this stage, we produced more than 26 million training instances and trained several models of varying sizes using this data. These new models achieve state-of-the-art zero-shot performance across 4 popular composed image retrieval (CIR) benchmarks and the highest overall performance on the 36 datasets provided by MMEB. They also demonstrate notable performance improvements with additional downstream fine-tuning. Our produced dataset, well-trained models, and data synthesis pipeline will be made publicly available to facilitate the future development of this field.
Dial-In LLM: Human-Aligned Dialogue Intent Clustering with LLM-in-the-loop
Dec 12, 2024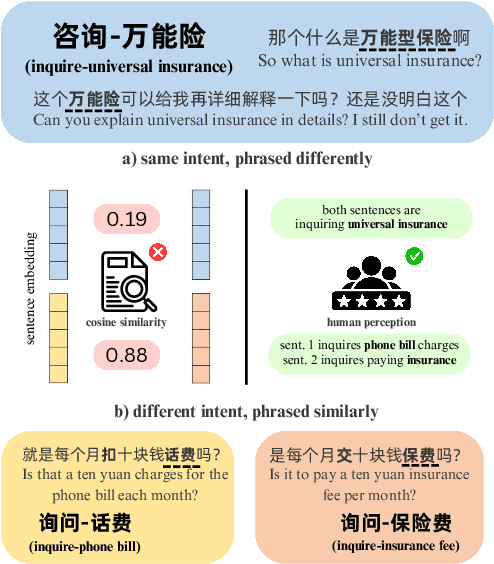
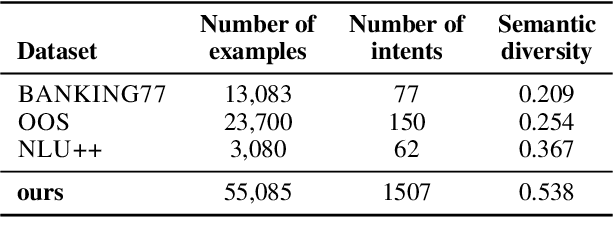
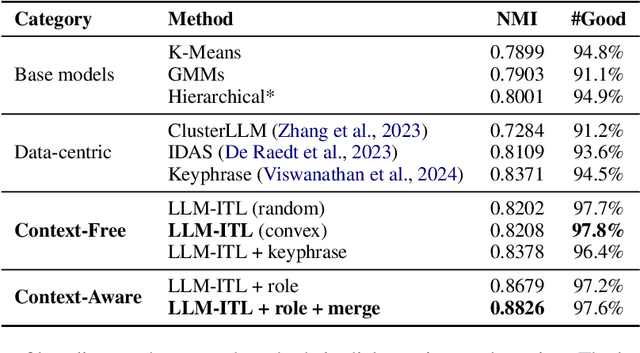
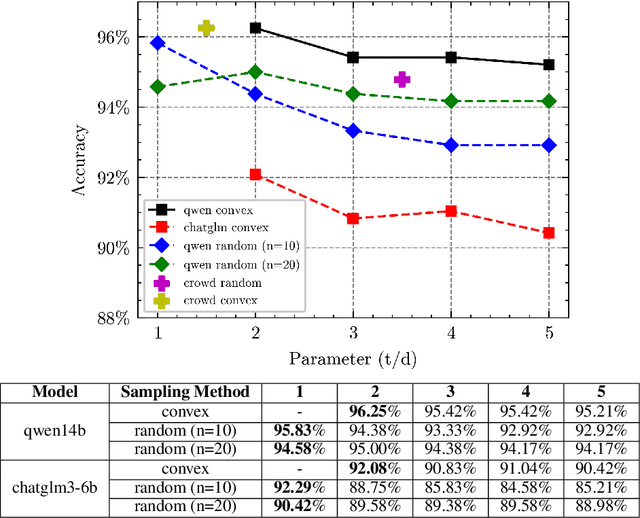
Abstract:The discovery of customer intention from dialogue plays an important role in automated support system. However, traditional text clustering methods are poorly aligned with human perceptions due to the shift from embedding distance to semantic distance, and existing quantitative metrics for text clustering may not accurately reflect the true quality of intent clusters. In this paper, we leverage the superior language understanding capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) for designing better-calibrated intent clustering algorithms. We first establish the foundation by verifying the robustness of fine-tuned LLM utility in semantic coherence evaluation and cluster naming, resulting in an accuracy of 97.50% and 94.40%, respectively, when compared to the human-labeled ground truth. Then, we propose an iterative clustering algorithm that facilitates cluster-level refinement and the continuous discovery of high-quality intent clusters. Furthermore, we present several LLM-in-the-loop semi-supervised clustering techniques tailored for intent discovery from customer service dialogue. Experiments on a large-scale industrial dataset comprising 1,507 intent clusters demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques. The methods outperformed existing counterparts, achieving 6.25% improvement in quantitative metrics and 12% enhancement in application-level performance when constructing an intent classifier.
RingFormer: A Ring-Enhanced Graph Transformer for Organic Solar Cell Property Prediction
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Organic Solar Cells (OSCs) are a promising technology for sustainable energy production. However, the identification of molecules with desired OSC properties typically involves laborious experimental research. To accelerate progress in the field, it is crucial to develop machine learning models capable of accurately predicting the properties of OSC molecules. While graph representation learning has demonstrated success in molecular property prediction, it remains underexplored for OSC-specific tasks. Existing methods fail to capture the unique structural features of OSC molecules, particularly the intricate ring systems that critically influence OSC properties, leading to suboptimal performance. To fill the gap, we present RingFormer, a novel graph transformer framework specially designed to capture both atom and ring level structural patterns in OSC molecules. RingFormer constructs a hierarchical graph that integrates atomic and ring structures and employs a combination of local message passing and global attention mechanisms to generate expressive graph representations for accurate OSC property prediction. We evaluate RingFormer's effectiveness on five curated OSC molecule datasets through extensive experiments. The results demonstrate that RingFormer consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving a 22.77% relative improvement over the nearest competitor on the CEPDB dataset.
Expanding Chatbot Knowledge in Customer Service: Context-Aware Similar Question Generation Using Large Language Models
Oct 16, 2024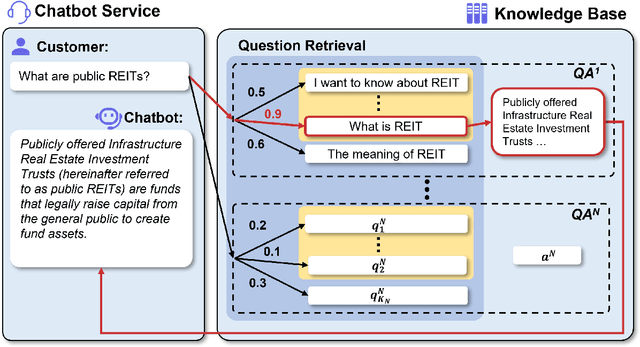

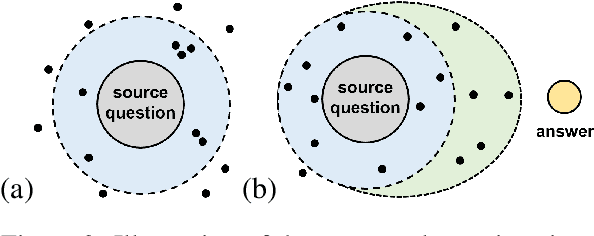
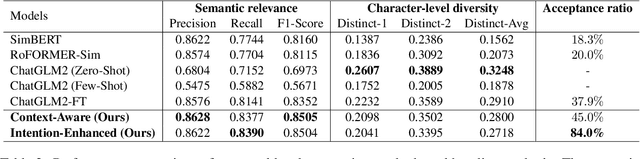
Abstract:Reliable responses of service chatbots are often achieved by employing retrieval-based methods that restrict answers to a knowledge base comprising predefined question-answer pairs (QA pairs). To accommodate potential variations in how a customer's query may be expressed, it emerges as the favored solution to augment these QA pairs with similar questions that are possibly diverse while remaining semantic consistency. This augmentation task is known as Similar Question Generation (SQG). Traditional methods that heavily rely on human efforts or rule-based techniques suffer from limited diversity or significant semantic deviation from the source question, only capable of producing a finite number of useful questions. To address these limitations, we propose an SQG approach based on Large Language Models (LLMs), capable of producing a substantial number of diverse questions while maintaining semantic consistency to the source QA pair. This is achieved by leveraging LLMs' natural language understanding capability through fine-tuning with specially designed prompts. The experiments conducted on a real customer-service dataset demonstrate that our method surpasses baseline methods by a significant margin in terms of semantic diversity. Human evaluation further confirms that integrating the answer that reflects the customer's intention is crucial for increasing the number of generated questions that meet business requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge