Wengyu Zhang
Removal of Hallucination on Hallucination: Debate-Augmented RAG
May 24, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances factual accuracy by integrating external knowledge, yet it introduces a critical issue: erroneous or biased retrieval can mislead generation, compounding hallucinations, a phenomenon we term Hallucination on Hallucination. To address this, we propose Debate-Augmented RAG (DRAG), a training-free framework that integrates Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) mechanisms into both retrieval and generation stages. In retrieval, DRAG employs structured debates among proponents, opponents, and judges to refine retrieval quality and ensure factual reliability. In generation, DRAG introduces asymmetric information roles and adversarial debates, enhancing reasoning robustness and mitigating factual inconsistencies. Evaluations across multiple tasks demonstrate that DRAG improves retrieval reliability, reduces RAG-induced hallucinations, and significantly enhances overall factual accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/Huenao/Debate-Augmented-RAG.
MolGround: A Benchmark for Molecular Grounding
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Current molecular understanding approaches predominantly focus on the descriptive aspect of human perception, providing broad, topic-level insights. However, the referential aspect -- linking molecular concepts to specific structural components -- remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we propose a molecular grounding benchmark designed to evaluate a model's referential abilities. We align molecular grounding with established conventions in NLP, cheminformatics, and molecular science, showcasing the potential of NLP techniques to advance molecular understanding within the AI for Science movement. Furthermore, we constructed the largest molecular understanding benchmark to date, comprising 79k QA pairs, and developed a multi-agent grounding prototype as proof of concept. This system outperforms existing models, including GPT-4o, and its grounding outputs have been integrated to enhance traditional tasks such as molecular captioning and ATC (Anatomical, Therapeutic, Chemical) classification.
Mean of Means: Human Localization with Calibration-free and Unconstrained Camera Settings (extended version)
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Accurate human localization is crucial for various applications, especially in the Metaverse era. Existing high precision solutions rely on expensive, tag-dependent hardware, while vision-based methods offer a cheaper, tag-free alternative. However, current vision solutions based on stereo vision face limitations due to rigid perspective transformation principles and error propagation in multi-stage SVD solvers. These solutions also require multiple high-resolution cameras with strict setup constraints.To address these limitations, we propose a probabilistic approach that considers all points on the human body as observations generated by a distribution centered around the body's geometric center. This enables us to improve sampling significantly, increasing the number of samples for each point of interest from hundreds to billions. By modeling the relation between the means of the distributions of world coordinates and pixel coordinates, leveraging the Central Limit Theorem, we ensure normality and facilitate the learning process. Experimental results demonstrate human localization accuracy of 96\% within a 0.3$m$ range and nearly 100\% accuracy within a 0.5$m$ range, achieved at a low cost of only 10 USD using two web cameras with a resolution of 640$\times$480 pixels.
PolySmart @ TRECVid 2024 Video-To-Text
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present our methods and results for the Video-To-Text (VTT) task at TRECVid 2024, exploring the capabilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) like LLaVA and LLaVA-NeXT-Video in generating natural language descriptions for video content. We investigate the impact of fine-tuning VLMs on VTT datasets to enhance description accuracy, contextual relevance, and linguistic consistency. Our analysis reveals that fine-tuning substantially improves the model's ability to produce more detailed and domain-aligned text, bridging the gap between generic VLM tasks and the specialized needs of VTT. Experimental results demonstrate that our fine-tuned model outperforms baseline VLMs across various evaluation metrics, underscoring the importance of domain-specific tuning for complex VTT tasks.
Mean of Means: A 10-dollar Solution for Human Localization with Calibration-free and Unconstrained Camera Settings
Jul 30, 2024



Abstract:Accurate human localization is crucial for various applications, especially in the Metaverse era. Existing high precision solutions rely on expensive, tag-dependent hardware, while vision-based methods offer a cheaper, tag-free alternative. However, current vision solutions based on stereo vision face limitations due to rigid perspective transformation principles and error propagation in multi-stage SVD solvers. These solutions also require multiple high-resolution cameras with strict setup constraints. To address these limitations, we propose a probabilistic approach that considers all points on the human body as observations generated by a distribution centered around the body's geometric center. This enables us to improve sampling significantly, increasing the number of samples for each point of interest from hundreds to billions. By modeling the relation between the means of the distributions of world coordinates and pixel coordinates, leveraging the Central Limit Theorem, we ensure normality and facilitate the learning process. Experimental results demonstrate human localization accuracy of 95% within a 0.3m range and nearly 100% accuracy within a 0.5m range, achieved at a low cost of only 10 USD using two web cameras with a resolution of 640x480 pixels.
Prior Knowledge Integration via LLM Encoding and Pseudo Event Regulation for Video Moment Retrieval
Jul 23, 2024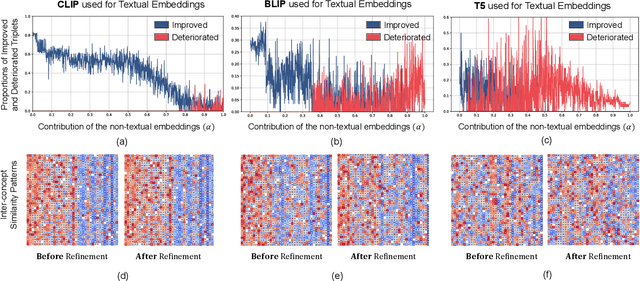
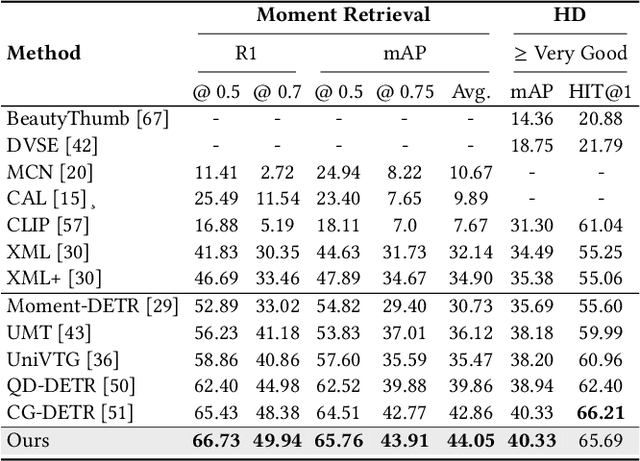
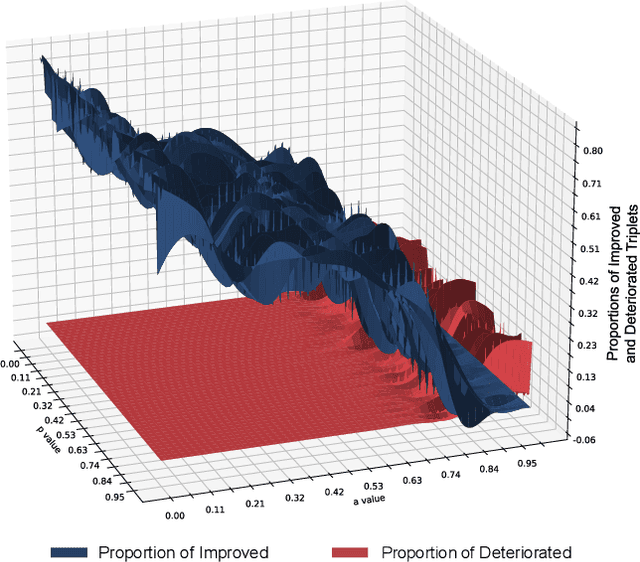
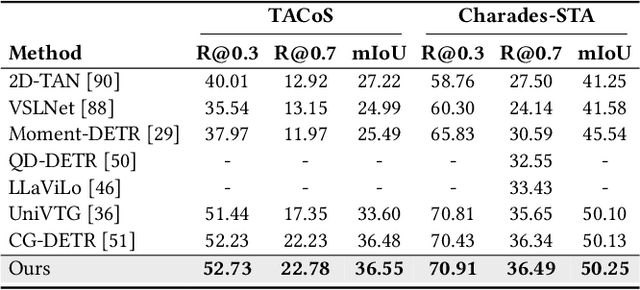
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the feasibility of leveraging large language models (LLMs) for integrating general knowledge and incorporating pseudo-events as priors for temporal content distribution in video moment retrieval (VMR) models. The motivation behind this study arises from the limitations of using LLMs as decoders for generating discrete textual descriptions, which hinders their direct application to continuous outputs like salience scores and inter-frame embeddings that capture inter-frame relations. To overcome these limitations, we propose utilizing LLM encoders instead of decoders. Through a feasibility study, we demonstrate that LLM encoders effectively refine inter-concept relations in multimodal embeddings, even without being trained on textual embeddings. We also show that the refinement capability of LLM encoders can be transferred to other embeddings, such as BLIP and T5, as long as these embeddings exhibit similar inter-concept similarity patterns to CLIP embeddings. We present a general framework for integrating LLM encoders into existing VMR architectures, specifically within the fusion module. Through experimental validation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods by achieving state-of-the-art performance in VMR. The source code can be accessed at https://github.com/fletcherjiang/LLMEPET.
A Survey on Personalized Content Synthesis with Diffusion Models
May 09, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have significantly impacted content creation, leading to the emergence of Personalized Content Synthesis (PCS). With a small set of user-provided examples, PCS aims to customize the subject of interest to specific user-defined prompts. Over the past two years, more than 150 methods have been proposed. However, existing surveys mainly focus on text-to-image generation, with few providing up-to-date summaries on PCS. This paper offers a comprehensive survey of PCS, with a particular focus on the diffusion models. Specifically, we introduce the generic frameworks of PCS research, which can be broadly classified into optimization-based and learning-based approaches. We further categorize and analyze these methodologies, discussing their strengths, limitations, and key techniques. Additionally, we delve into specialized tasks within the field, such as personalized object generation, face synthesis, and style personalization, highlighting their unique challenges and innovations. Despite encouraging progress, we also present an analysis of the challenges such as overfitting and the trade-off between subject fidelity and text alignment. Through this detailed overview and analysis, we propose future directions to advance the development of PCS.
A Picture Is Worth a Graph: Blueprint Debate on Graph for Multimodal Reasoning
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a pilot study aimed at introducing multi-agent debate into multimodal reasoning. The study addresses two key challenges: the trivialization of opinions resulting from excessive summarization and the diversion of focus caused by distractor concepts introduced from images. These challenges stem from the inductive (bottom-up) nature of existing debating schemes. To address the issue, we propose a deductive (top-down) debating approach called Blueprint Debate on Graphs (BDoG). In BDoG, debates are confined to a blueprint graph to prevent opinion trivialization through world-level summarization. Moreover, by storing evidence in branches within the graph, BDoG mitigates distractions caused by frequent but irrelevant concepts. Extensive experiments validate BDoG, achieving state-of-the-art results in Science QA and MMBench with significant improvements over previous methods.
Generative Active Learning for Image Synthesis Personalization
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a pilot study that explores the application of active learning, traditionally studied in the context of discriminative models, to generative models. We specifically focus on image synthesis personalization tasks. The primary challenge in conducting active learning on generative models lies in the open-ended nature of querying, which differs from the closed form of querying in discriminative models that typically target a single concept. We introduce the concept of anchor directions to transform the querying process into a semi-open problem. We propose a direction-based uncertainty sampling strategy to enable generative active learning and tackle the exploitation-exploration dilemma. Extensive experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating that an open-source model can achieve superior performance compared to closed-source models developed by large companies, such as Google's StyleDrop. The source code is available at https://github.com/zhangxulu1996/GAL4Personalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge