Mengze Hong
Orchestration-Free Customer Service Automation: A Privacy-Preserving and Flowchart-Guided Framework
Feb 17, 2026Abstract:Customer service automation has seen growing demand within digital transformation. Existing approaches either rely on modular system designs with extensive agent orchestration or employ over-simplified instruction schemas, providing limited guidance and poor generalizability. This paper introduces an orchestration-free framework using Task-Oriented Flowcharts (TOFs) to enable end-to-end automation without manual intervention. We first define the components and evaluation metrics for TOFs, then formalize a cost-efficient flowchart construction algorithm to abstract procedural knowledge from service dialogues. We emphasize local deployment of small language models and propose decentralized distillation with flowcharts to mitigate data scarcity and privacy issues in model training. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness in various service tasks, with superior quantitative and application performance compared to strong baselines and market products. By releasing a web-based system demonstration with case studies, we aim to promote streamlined creation of future service automation.
RAL2M: Retrieval Augmented Learning-To-Match Against Hallucination in Compliance-Guaranteed Service Systems
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Hallucination is a major concern in LLM-driven service systems, necessitating explicit knowledge grounding for compliance-guaranteed responses. In this paper, we introduce Retrieval-Augmented Learning-to-Match (RAL2M), a novel framework that eliminates generation hallucination by repositioning LLMs as query-response matching judges within a retrieval-based system, providing a robust alternative to purely generative approaches. To further mitigate judgment hallucination, we propose a query-adaptive latent ensemble strategy that explicitly models heterogeneous model competence and interdependencies among LLMs, deriving a calibrated consensus decision. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method effectively leverages the "wisdom of the crowd" and significantly outperforms strong baselines. Finally, we discuss best practices and promising directions for further exploiting latent representations in future work.
Multimodal Peer Review Simulation with Actionable To-Do Recommendations for Community-Aware Manuscript Revisions
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) offer promising capabilities for automating academic workflows, existing systems for academic peer review remain constrained by text-only inputs, limited contextual grounding, and a lack of actionable feedback. In this work, we present an interactive web-based system for multimodal, community-aware peer review simulation to enable effective manuscript revisions before paper submission. Our framework integrates textual and visual information through multimodal LLMs, enhances review quality via retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) grounded in web-scale OpenReview data, and converts generated reviews into actionable to-do lists using the proposed Action:Objective[\#] format, providing structured and traceable guidance. The system integrates seamlessly into existing academic writing platforms, providing interactive interfaces for real-time feedback and revision tracking. Experimental results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed system in generating more comprehensive and useful reviews aligned with expert standards, surpassing ablated baselines and advancing transparent, human-centered scholarly assistance.
Contextualized Token Discrimination for Speech Search Query Correction
Sep 04, 2025



Abstract:Query spelling correction is an important function of modern search engines since it effectively helps users express their intentions clearly. With the growing popularity of speech search driven by Automated Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, this paper introduces a novel method named Contextualized Token Discrimination (CTD) to conduct effective speech query correction. In CTD, we first employ BERT to generate token-level contextualized representations and then construct a composition layer to enhance semantic information. Finally, we produce the correct query according to the aggregated token representation, correcting the incorrect tokens by comparing the original token representations and the contextualized representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method across all metrics, and we further present a new benchmark dataset with erroneous ASR transcriptions to offer comprehensive evaluations for audio query correction.
Technical Report: A Practical Guide to Kaldi ASR Optimization
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:This technical report introduces innovative optimizations for Kaldi-based Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems, focusing on acoustic model enhancement, hyperparameter tuning, and language model efficiency. We developed a custom Conformer block integrated with a multistream TDNN-F structure, enabling superior feature extraction and temporal modeling. Our approach includes advanced data augmentation techniques and dynamic hyperparameter optimization to boost performance and reduce overfitting. Additionally, we propose robust strategies for language model management, employing Bayesian optimization and $n$-gram pruning to ensure relevance and computational efficiency. These systematic improvements significantly elevate ASR accuracy and robustness, outperforming existing methods and offering a scalable solution for diverse speech recognition scenarios. This report underscores the importance of strategic optimizations in maintaining Kaldi's adaptability and competitiveness in rapidly evolving technological landscapes.
QualBench: Benchmarking Chinese LLMs with Localized Professional Qualifications for Vertical Domain Evaluation
May 08, 2025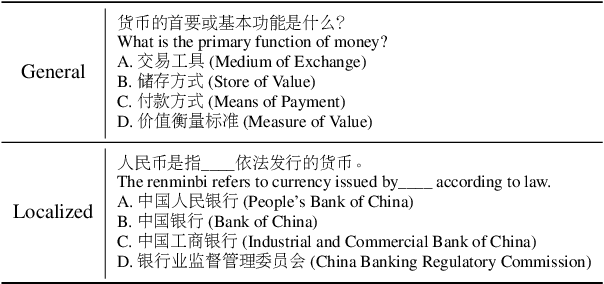
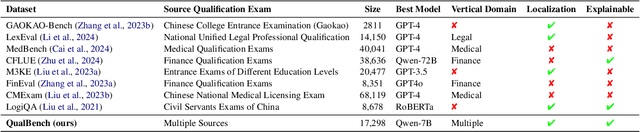
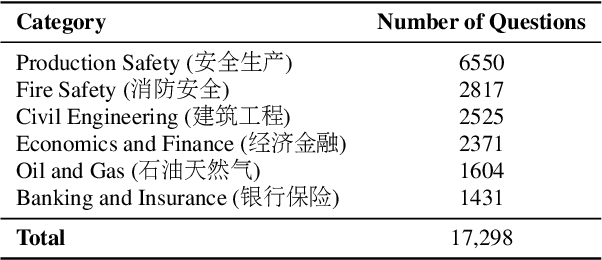
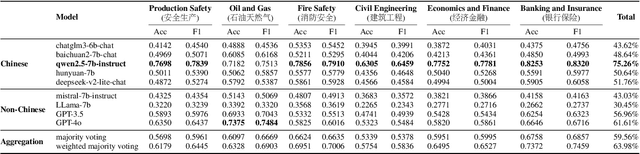
Abstract:The rapid advancement of Chinese large language models (LLMs) underscores the need for domain-specific evaluations to ensure reliable applications. However, existing benchmarks often lack coverage in vertical domains and offer limited insights into the Chinese working context. Leveraging qualification exams as a unified framework for human expertise evaluation, we introduce QualBench, the first multi-domain Chinese QA benchmark dedicated to localized assessment of Chinese LLMs. The dataset includes over 17,000 questions across six vertical domains, with data selections grounded in 24 Chinese qualifications to closely align with national policies and working standards. Through comprehensive evaluation, the Qwen2.5 model outperformed the more advanced GPT-4o, with Chinese LLMs consistently surpassing non-Chinese models, highlighting the importance of localized domain knowledge in meeting qualification requirements. The best performance of 75.26% reveals the current gaps in domain coverage within model capabilities. Furthermore, we present the failure of LLM collaboration with crowdsourcing mechanisms and suggest the opportunities for multi-domain RAG knowledge enhancement and vertical domain LLM training with Federated Learning.
Dial-In LLM: Human-Aligned Dialogue Intent Clustering with LLM-in-the-loop
Dec 12, 2024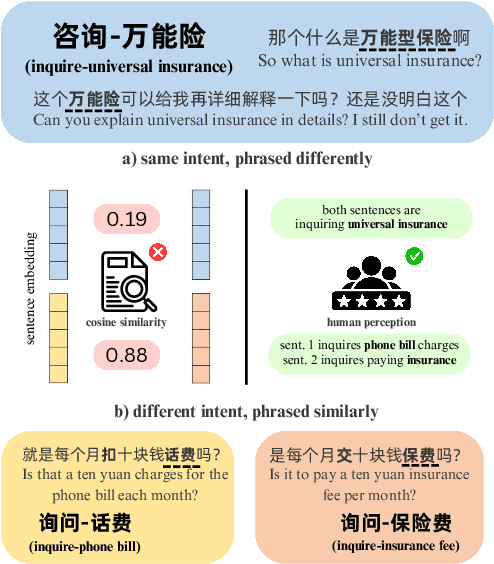
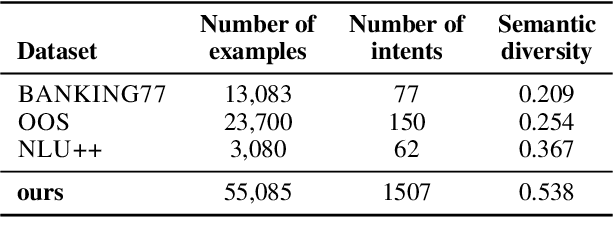
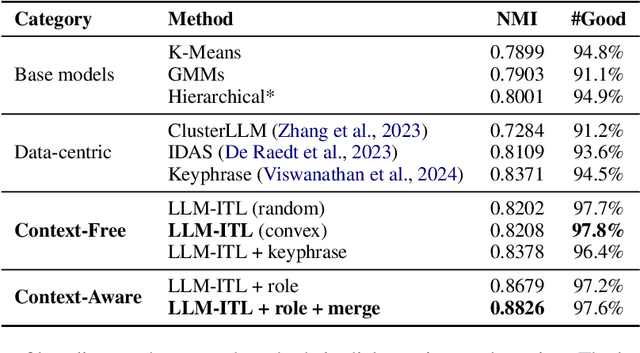
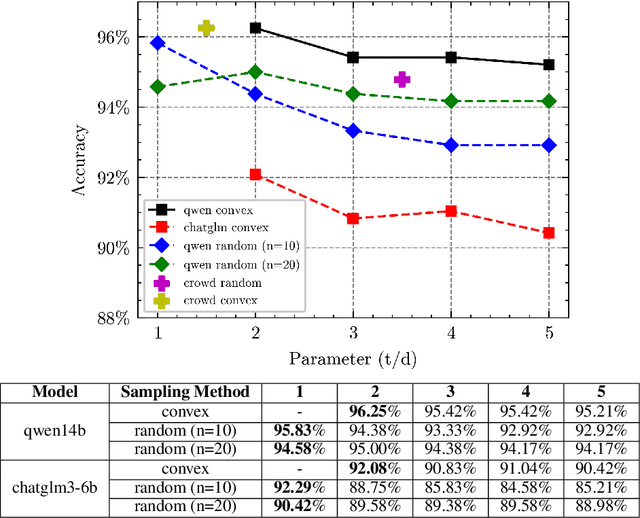
Abstract:The discovery of customer intention from dialogue plays an important role in automated support system. However, traditional text clustering methods are poorly aligned with human perceptions due to the shift from embedding distance to semantic distance, and existing quantitative metrics for text clustering may not accurately reflect the true quality of intent clusters. In this paper, we leverage the superior language understanding capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) for designing better-calibrated intent clustering algorithms. We first establish the foundation by verifying the robustness of fine-tuned LLM utility in semantic coherence evaluation and cluster naming, resulting in an accuracy of 97.50% and 94.40%, respectively, when compared to the human-labeled ground truth. Then, we propose an iterative clustering algorithm that facilitates cluster-level refinement and the continuous discovery of high-quality intent clusters. Furthermore, we present several LLM-in-the-loop semi-supervised clustering techniques tailored for intent discovery from customer service dialogue. Experiments on a large-scale industrial dataset comprising 1,507 intent clusters demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed techniques. The methods outperformed existing counterparts, achieving 6.25% improvement in quantitative metrics and 12% enhancement in application-level performance when constructing an intent classifier.
Dialogue Language Model with Large-Scale Persona Data Engineering
Dec 12, 2024

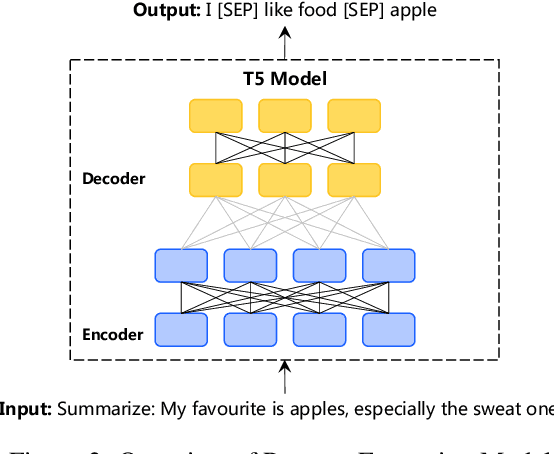
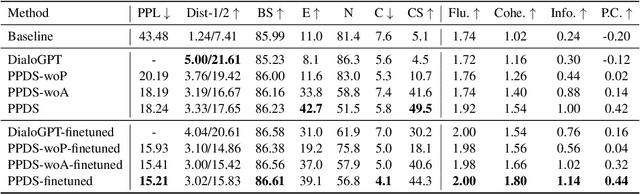
Abstract:Maintaining persona consistency is paramount in the application of open-domain dialogue systems, as exemplified by models like ChatGPT. Despite significant advancements, the limited scale and diversity of current persona dialogue datasets remain challenges to achieving robust persona-consistent dialogue models. In this study, drawing inspiration from the success of large-scale pre-training, we introduce PPDS, an open-domain persona dialogue system that employs extensive generative pre-training on a persona dialogue dataset to enhance persona consistency. Specifically, we present a persona extraction model designed to autonomously and precisely generate vast persona dialogue datasets. Additionally, we unveil a pioneering persona augmentation technique to address the invalid persona bias inherent in the constructed dataset. Both quantitative and human evaluations consistently highlight the superior response quality and persona consistency of our proposed model, underscoring its effectiveness.
Deconfounding Time Series Forecasting
Oct 27, 2024



Abstract:Time series forecasting is a critical task in various domains, where accurate predictions can drive informed decision-making. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on current observations of variables to predict future outcomes, typically overlooking the influence of latent confounders, unobserved variables that simultaneously affect both the predictors and the target outcomes. This oversight can introduce bias and degrade the performance of predictive models. In this study, we address this challenge by proposing an enhanced forecasting approach that incorporates representations of latent confounders derived from historical data. By integrating these confounders into the predictive process, our method aims to improve the accuracy and robustness of time series forecasts. The proposed approach is demonstrated through its application to climate science data, showing significant improvements over traditional methods that do not account for confounders.
Expanding Chatbot Knowledge in Customer Service: Context-Aware Similar Question Generation Using Large Language Models
Oct 16, 2024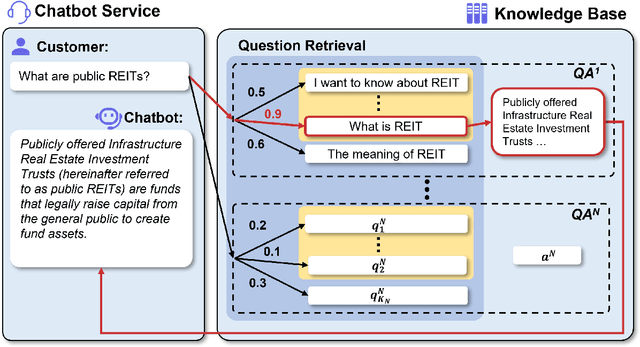

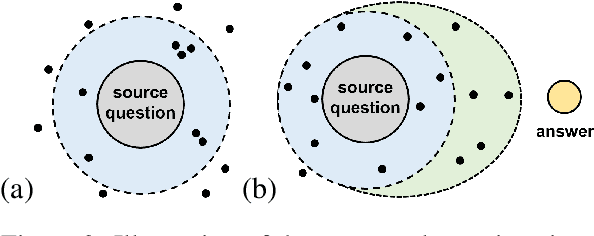
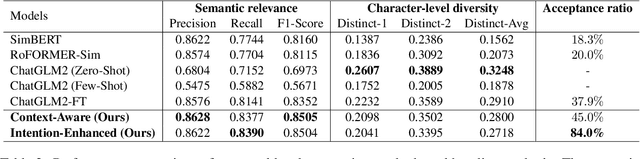
Abstract:Reliable responses of service chatbots are often achieved by employing retrieval-based methods that restrict answers to a knowledge base comprising predefined question-answer pairs (QA pairs). To accommodate potential variations in how a customer's query may be expressed, it emerges as the favored solution to augment these QA pairs with similar questions that are possibly diverse while remaining semantic consistency. This augmentation task is known as Similar Question Generation (SQG). Traditional methods that heavily rely on human efforts or rule-based techniques suffer from limited diversity or significant semantic deviation from the source question, only capable of producing a finite number of useful questions. To address these limitations, we propose an SQG approach based on Large Language Models (LLMs), capable of producing a substantial number of diverse questions while maintaining semantic consistency to the source QA pair. This is achieved by leveraging LLMs' natural language understanding capability through fine-tuning with specially designed prompts. The experiments conducted on a real customer-service dataset demonstrate that our method surpasses baseline methods by a significant margin in terms of semantic diversity. Human evaluation further confirms that integrating the answer that reflects the customer's intention is crucial for increasing the number of generated questions that meet business requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge