Longyu Feng
Auto-Demo Prompting: Leveraging Generated Outputs as Demonstrations for Enhanced Batch Prompting
Oct 02, 2024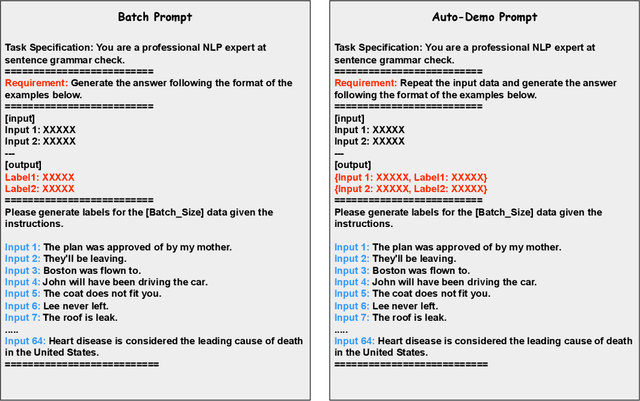
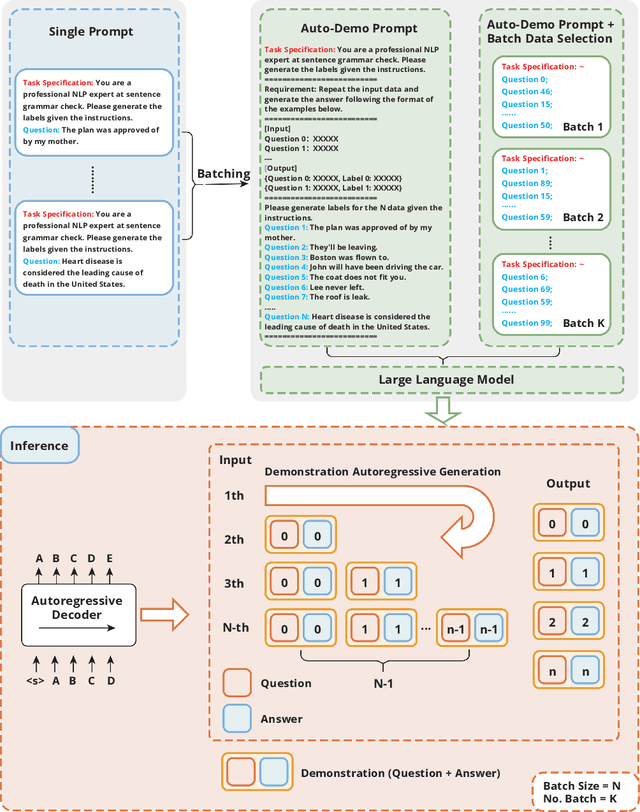
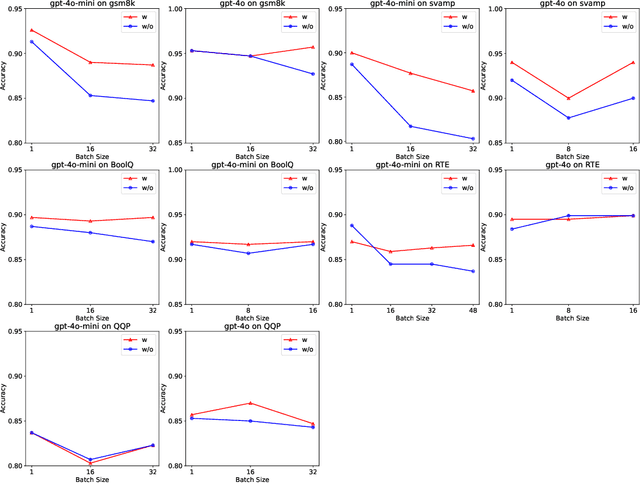
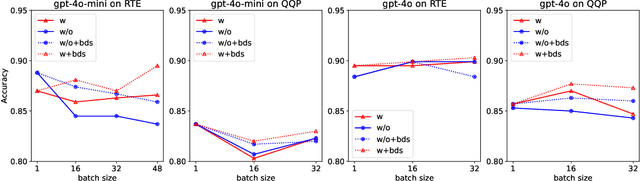
Abstract:Batch prompting is a common technique in large language models (LLMs) used to process multiple inputs simultaneously, aiming to improve computational efficiency. However, as batch sizes increase, performance degradation often occurs due to the model's difficulty in handling lengthy context inputs. Existing methods that attempt to mitigate these issues rely solely on batch data arrangement and majority voting rather than improving the design of the batch prompt itself. In this paper, we address these limitations by proposing "Auto-Demo Prompting," a novel approach that leverages the question-output pairs from earlier questions within a batch as demonstrations for subsequent answer inference. We provide a formal theoretical analysis of how Auto-Demo Prompting functions within the autoregressive generation process of LLMs, illustrating how it utilizes prior outputs to optimize the model's internal representations. Our method effectively bridges the gap between batch prompting and few-shot prompting, enhancing performance with only a slight compromise in token usage. Experimental results across five NLP tasks demonstrate its effectiveness in mitigating performance degradation and occasionally outperforming single prompts. Furthermore, it opens new avenues for applying few-shot learning techniques, such as demonstration selection, within batch prompting, making it a robust solution for real-world applications.
Cost-Aware Uncertainty Reduction in Schema Matching with GPT-4: The Prompt-Matcher Framework
Aug 24, 2024



Abstract:Schema matching is the process of identifying correspondences between the elements of two given schemata, essential for database management systems, data integration, and data warehousing. The inherent uncertainty of current schema matching algorithms leads to the generation of a set of candidate matches. Storing these results necessitates the use of databases and systems capable of handling probabilistic queries. This complicates the querying process and increases the associated storage costs. Motivated by GPT-4 outstanding performance, we explore its potential to reduce uncertainty. Our proposal is to supplant the role of crowdworkers with GPT-4 for querying the set of candidate matches. To get more precise correspondence verification responses from GPT-4, We have crafted Semantic-match and Abbreviation-match prompt for GPT-4, achieving state-of-the-art results on two benchmark datasets DeepMDatasets 100% (+0.0) and Fabricated-Datasets 91.8% (+2.2) recall rate. To optimise budget utilisation, we have devised a cost-aware solution. Within the constraints of the budget, our solution delivers favourable outcomes with minimal time expenditure. We introduce a novel framework, Prompt-Matcher, to reduce the uncertainty in the process of integration of multiple automatic schema matching algorithms and the selection of complex parameterization. It assists users in diminishing the uncertainty associated with candidate schema match results and in optimally ranking the most promising matches. We formally define the Correspondence Selection Problem, aiming to optimise the revenue within the confines of the GPT-4 budget. We demonstrate that CSP is NP-Hard and propose an approximation algorithm with minimal time expenditure. Ultimately, we demonstrate the efficacy of Prompt-Matcher through rigorous experiments.
On Leveraging Large Language Models for Enhancing Entity Resolution
Jan 07, 2024



Abstract:Entity resolution, the task of identifying and consolidating records that pertain to the same real-world entity, plays a pivotal role in various sectors such as e-commerce, healthcare, and law enforcement. The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 has introduced a new dimension to this task, leveraging their advanced linguistic capabilities. This paper explores the potential of LLMs in the entity resolution process, shedding light on both their advantages and the computational complexities associated with large-scale matching. We introduce strategies for the efficient utilization of LLMs, including the selection of an optimal set of matching questions, namely MQsSP, which is proved to be a NP-hard problem. Our approach optimally chooses the most effective matching questions while keep consumption limited to your budget . Additionally, we propose a method to adjust the distribution of possible partitions after receiving responses from LLMs, with the goal of reducing the uncertainty of entity resolution. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach using entropy as a metric, and our experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our proposed methods, offering promising prospects for real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge