Chaochao Yan
MaskConver: Revisiting Pure Convolution Model for Panoptic Segmentation
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:In recent years, transformer-based models have dominated panoptic segmentation, thanks to their strong modeling capabilities and their unified representation for both semantic and instance classes as global binary masks. In this paper, we revisit pure convolution model and propose a novel panoptic architecture named MaskConver. MaskConver proposes to fully unify things and stuff representation by predicting their centers. To that extent, it creates a lightweight class embedding module that can break the ties when multiple centers co-exist in the same location. Furthermore, our study shows that the decoder design is critical in ensuring that the model has sufficient context for accurate detection and segmentation. We introduce a powerful ConvNeXt-UNet decoder that closes the performance gap between convolution- and transformerbased models. With ResNet50 backbone, our MaskConver achieves 53.6% PQ on the COCO panoptic val set, outperforming the modern convolution-based model, Panoptic FCN, by 9.3% as well as transformer-based models such as Mask2Former (+1.7% PQ) and kMaX-DeepLab (+0.6% PQ). Additionally, MaskConver with a MobileNet backbone reaches 37.2% PQ, improving over Panoptic-DeepLab by +6.4% under the same FLOPs/latency constraints. A further optimized version of MaskConver achieves 29.7% PQ, while running in real-time on mobile devices. The code and model weights will be publicly available
MARS: A Motif-based Autoregressive Model for Retrosynthesis Prediction
Sep 27, 2022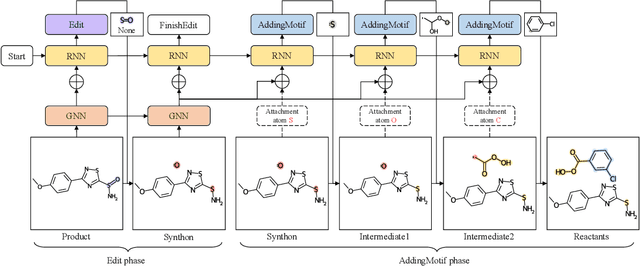
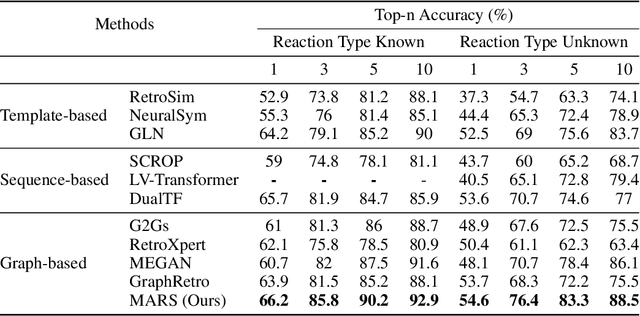
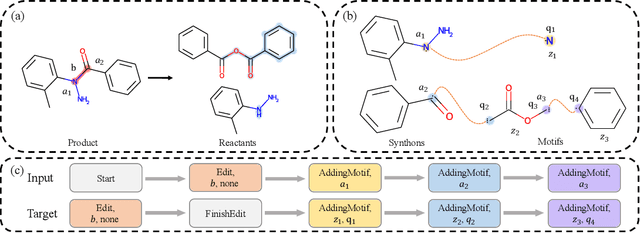
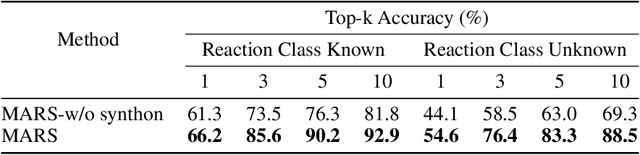
Abstract:Retrosynthesis is a major task for drug discovery. It is formulated as a graph-generating problem by many existing approaches. Specifically, these methods firstly identify the reaction center, and break target molecule accordingly to generate synthons. Reactants are generated by either adding atoms sequentially to synthon graphs or directly adding proper leaving groups. However, both two strategies suffer since adding atoms results in a long prediction sequence which increases generation difficulty, while adding leaving groups can only consider the ones in the training set which results in poor generalization. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end graph generation model for retrosynthesis prediction, which sequentially identifies the reaction center, generates the synthons, and adds motifs to the synthons to generate reactants. Since chemically meaningful motifs are bigger than atoms and smaller than leaving groups, our method enjoys lower prediction complexity than adding atoms and better generalization than adding leaving groups. Experiments on a benchmark dataset show that the proposed model significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art algorithms.
RetroComposer: Discovering Novel Reactions by Composing Templates for Retrosynthesis Prediction
Dec 20, 2021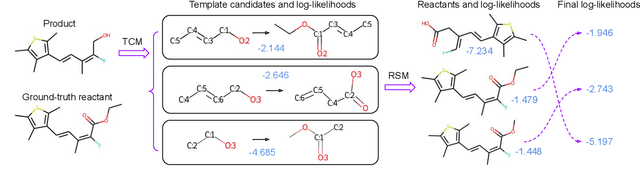
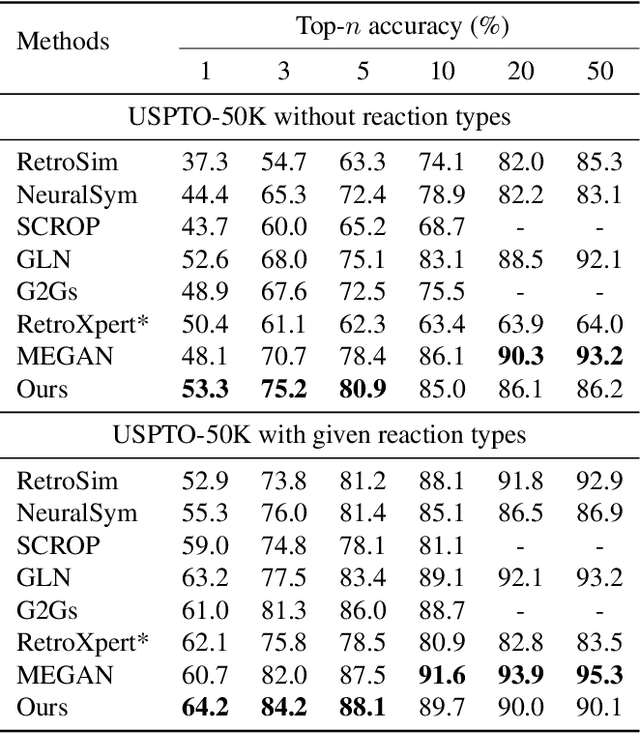
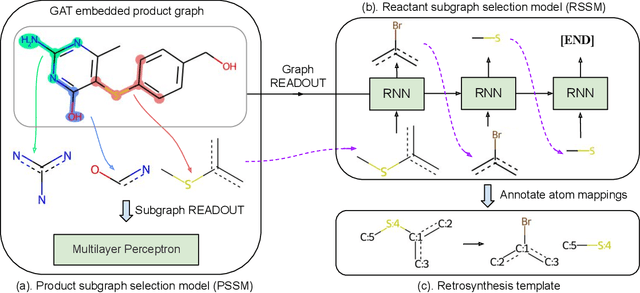
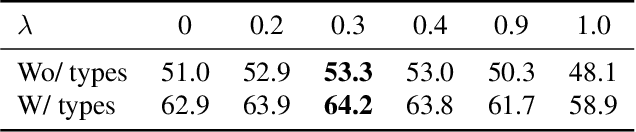
Abstract:The main target of retrosynthesis is to recursively decompose desired molecules into available building blocks. Existing template-based retrosynthesis methods follow a template selection stereotype and suffer from the limited training templates, which prevents them from discovering novel reactions. To overcome the limitation, we propose an innovative retrosynthesis prediction framework that can compose novel templates beyond training templates. So far as we know, this is the first method that can find novel templates for retrosynthesis prediction. Besides, we propose an effective reactant candidates scoring model that can capture atom-level transformation information, and it helps our method outperform existing methods by a large margin. Experimental results show that our method can produce novel templates for 328 test reactions in the USPTO-50K dataset, including 21 test reactions that are not covered by the training templates.
Bridging the Gap Between Object Detection and User Intent via Query-Modulation
Jun 18, 2021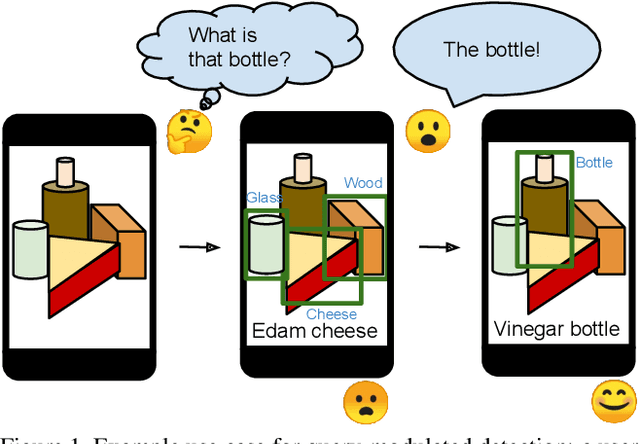
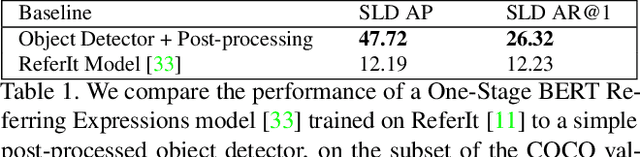
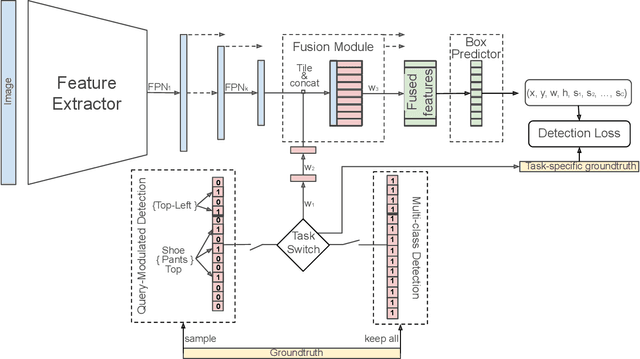
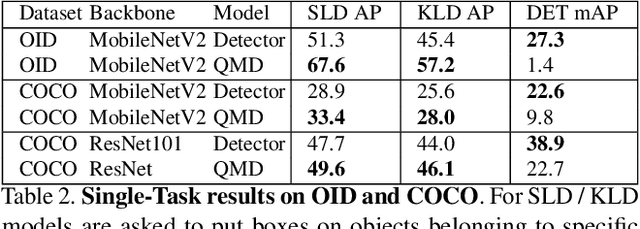
Abstract:When interacting with objects through cameras, or pictures, users often have a specific intent. For example, they may want to perform a visual search. However, most object detection models ignore the user intent, relying on image pixels as their only input. This often leads to incorrect results, such as lack of a high-confidence detection on the object of interest, or detection with a wrong class label. In this paper we investigate techniques to modulate standard object detectors to explicitly account for the user intent, expressed as an embedding of a simple query. Compared to standard object detectors, query-modulated detectors show superior performance at detecting objects for a given label of interest. Thanks to large-scale training data synthesized from standard object detection annotations, query-modulated detectors can also outperform specialized referring expression recognition systems. Furthermore, they can be simultaneously trained to solve for both query-modulated detection and standard object detection.
Hierarchical Graph Capsule Network
Dec 16, 2020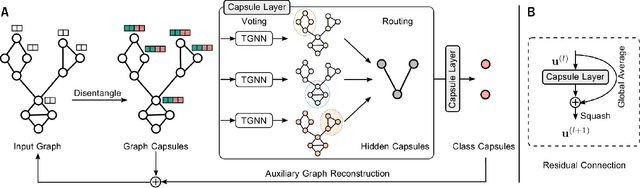
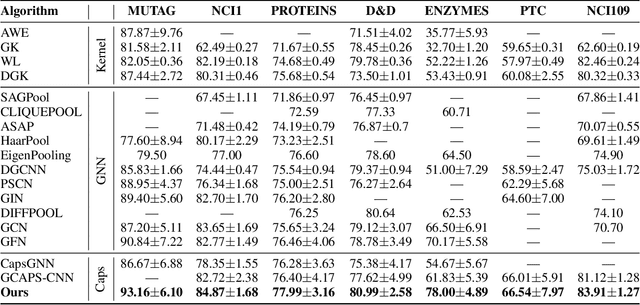
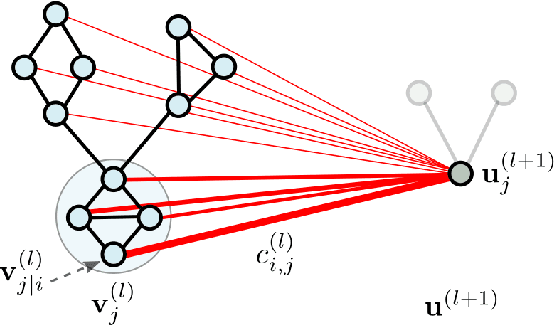
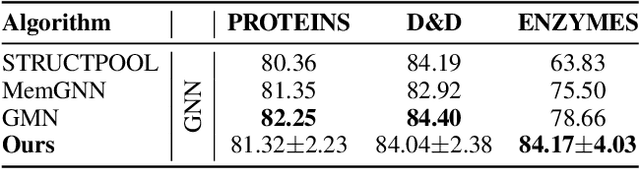
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) draw their strength from explicitly modeling the topological information of structured data. However, existing GNNs suffer from limited capability in capturing the hierarchical graph representation which plays an important role in graph classification. In this paper, we innovatively propose hierarchical graph capsule network (HGCN) that can jointly learn node embeddings and extract graph hierarchies. Specifically, disentangled graph capsules are established by identifying heterogeneous factors underlying each node, such that their instantiation parameters represent different properties of the same entity. To learn the hierarchical representation, HGCN characterizes the part-whole relationship between lower-level capsules (part) and higher-level capsules (whole) by explicitly considering the structure information among the parts. Experimental studies demonstrate the effectiveness of HGCN and the contribution of each component.
RetroXpert: Decompose Retrosynthesis Prediction like a Chemist
Nov 04, 2020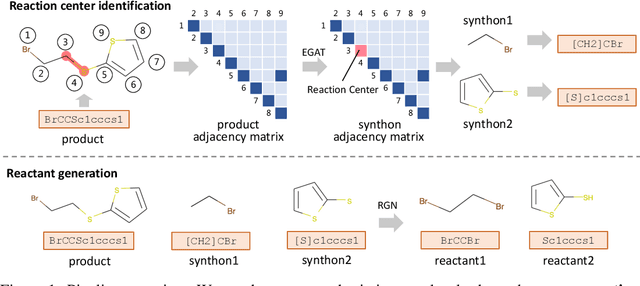
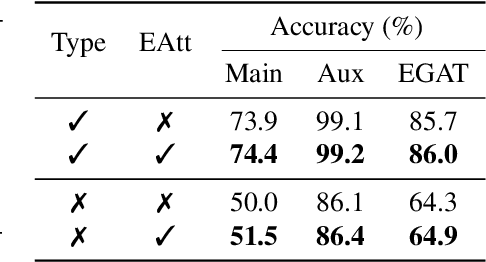
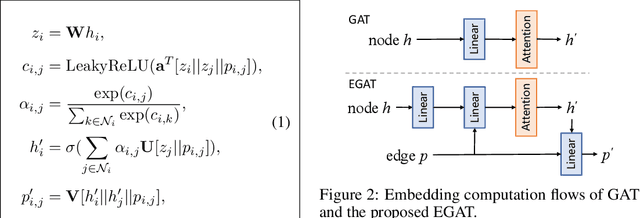
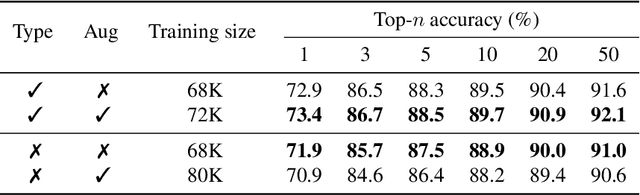
Abstract:Retrosynthesis is the process of recursively decomposing target molecules into available building blocks. It plays an important role in solving problems in organic synthesis planning. To automate or assist in the retrosynthesis analysis, various retrosynthesis prediction algorithms have been proposed. However, most of them are cumbersome and lack interpretability about their predictions. In this paper, we devise a novel template-free algorithm for automatic retrosynthetic expansion inspired by how chemists approach retrosynthesis prediction. Our method disassembles retrosynthesis into two steps: i) identify the potential reaction center of the target molecule through a novel graph neural network and generate intermediate synthons, and ii) generate the reactants associated with synthons via a robust reactant generation model. While outperforming the state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin, our model also provides chemically reasonable interpretation.
Label-Driven Reconstruction for Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
Mar 10, 2020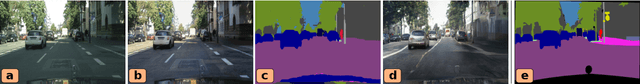
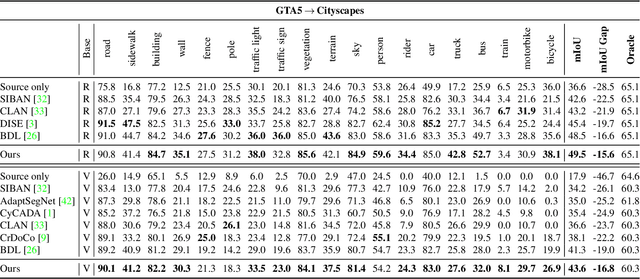
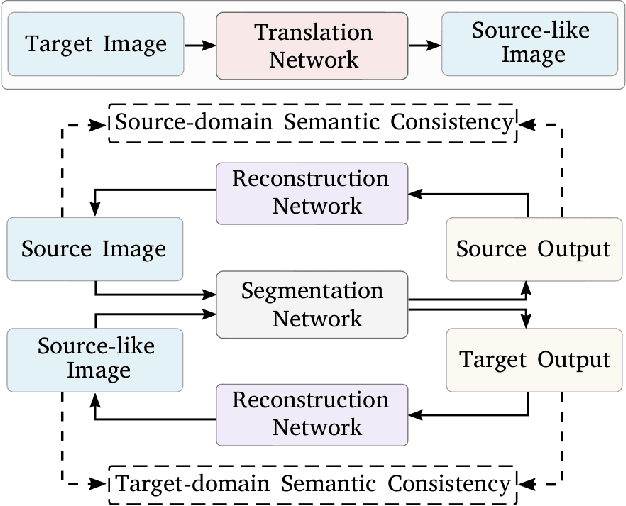
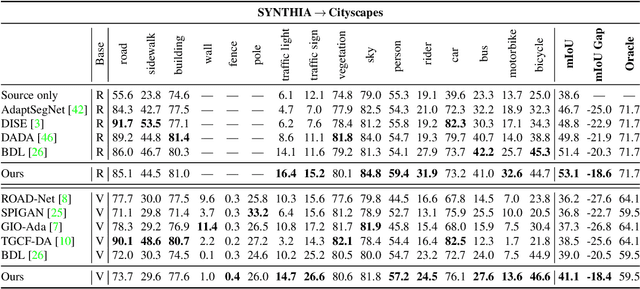
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation enables to alleviate the need for pixel-wise annotation in the semantic segmentation. One of the most common strategies is to translate images from the source domain to the target domain and then align their marginal distributions in the feature space using adversarial learning. However, source-to-target translation enlarges the bias in translated images, owing to the dominant data size of the source domain. Furthermore, consistency of the joint distribution in source and target domains cannot be guaranteed through global feature alignment. Here, we present an innovative framework, designed to mitigate the image translation bias and align cross-domain features with the same category. This is achieved by 1) performing the target-to-source translation and 2) reconstructing both source and target images from their predicted labels. Extensive experiments on adapting from synthetic to real urban scene understanding demonstrate that our framework competes favorably against existing state-of-the-art methods.
Context-Aware Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation
Mar 09, 2020
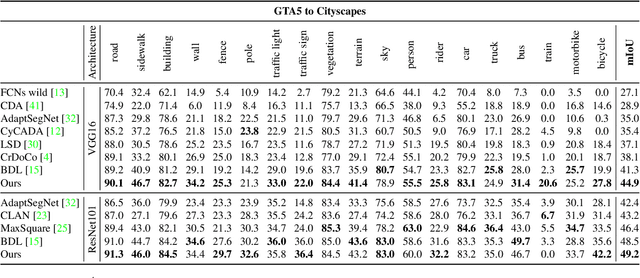
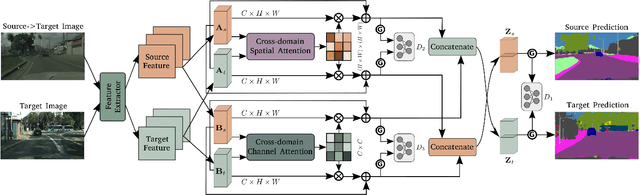
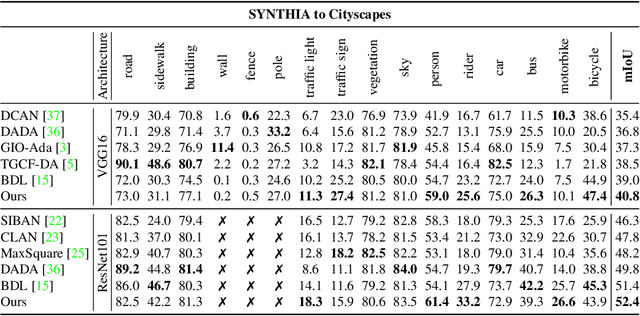
Abstract:In this paper, we consider the problem of unsupervised domain adaptation in the semantic segmentation. There are two primary issues in this field, i.e., what and how to transfer domain knowledge across two domains. Existing methods mainly focus on adapting domain-invariant features (what to transfer) through adversarial learning (how to transfer). Context dependency is essential for semantic segmentation, however, its transferability is still not well understood. Furthermore, how to transfer contextual information across two domains remains unexplored. Motivated by this, we propose a cross-attention mechanism based on self-attention to capture context dependencies between two domains and adapt transferable context. To achieve this goal, we design two cross-domain attention modules to adapt context dependencies from both spatial and channel views. Specifically, the spatial attention module captures local feature dependencies between each position in the source and target image. The channel attention module models semantic dependencies between each pair of cross-domain channel maps. To adapt context dependencies, we further selectively aggregate the context information from two domains. The superiority of our method over existing state-of-the-art methods is empirically proved on "GTA5 to Cityscapes" and "SYNTHIA to Cityscapes".
Re-balancing Variational Autoencoder Loss for Molecule Sequence Generation
Oct 01, 2019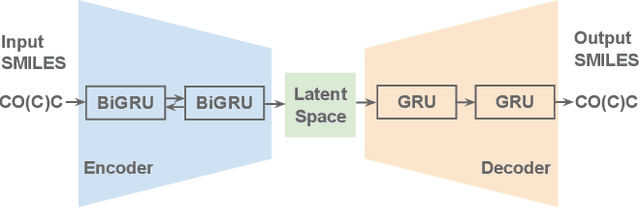
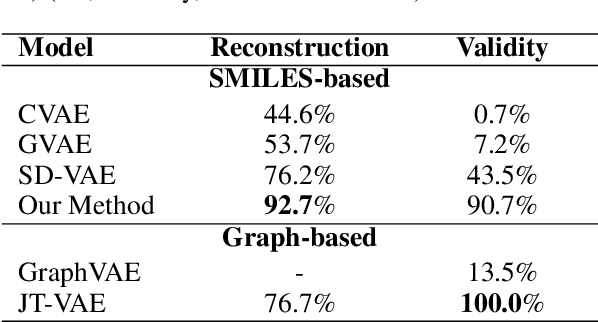
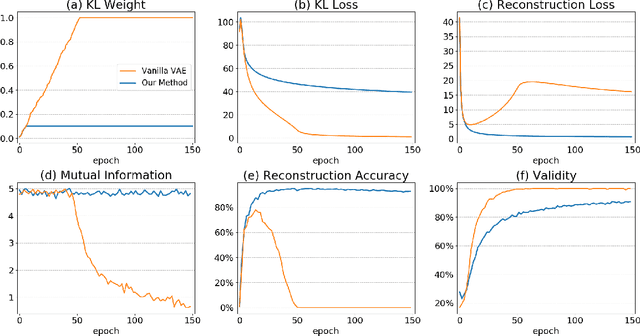
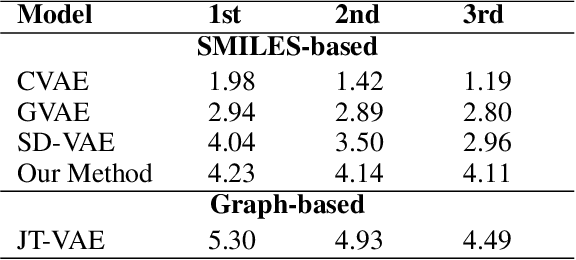
Abstract:Molecule generation is to design new molecules with specific chemical properties and further to optimize the desired chemical properties. Following previous work, we encode molecules into continuous vectors in the latent space and then decode the vectors into molecules under the variational autoencoder (VAE) framework. We investigate the posterior collapse problem of current RNN-based VAEs for molecule sequence generation. For the first time, we find that underestimated reconstruction loss leads to posterior collapse, and provide both theoretical and experimental evidence. We propose an effective and efficient solution to fix the problem and avoid posterior collapse. Without bells and whistles, our method achieves SOTA reconstruction accuracy and competitive validity on the ZINC 250K dataset. When generating 10,000 unique valid SMILES from random prior sampling, it costs JT-VAE1450s while our method only needs 9s. Our implementation is at https://github.com/chaoyan1037/Re-balanced-VAE.
Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for Thoracic Disease Classification and Localization on Chest X-rays
Jul 16, 2018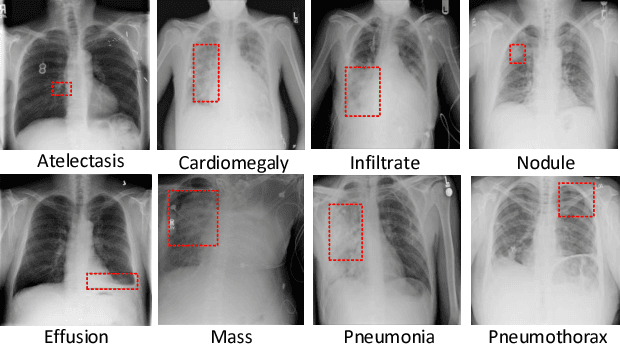
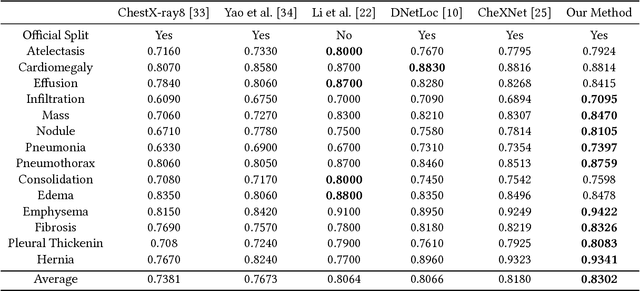
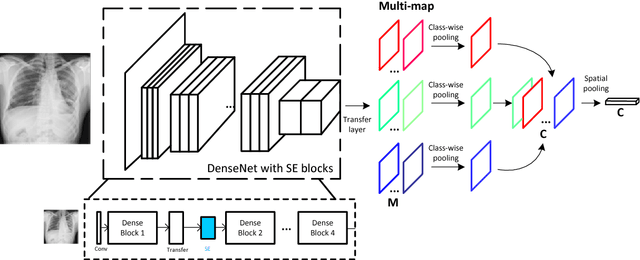
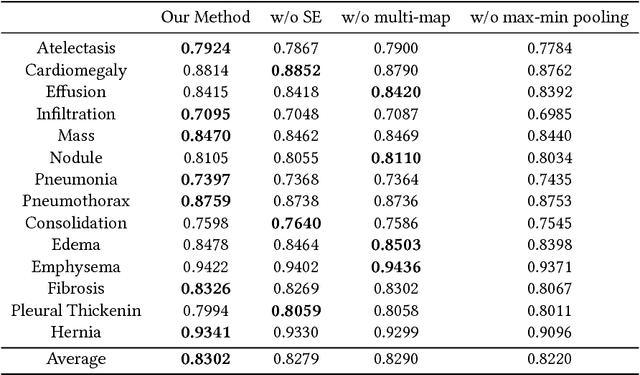
Abstract:Chest X-rays is one of the most commonly available and affordable radiological examinations in clinical practice. While detecting thoracic diseases on chest X-rays is still a challenging task for machine intelligence, due to 1) the highly varied appearance of lesion areas on X-rays from patients of different thoracic disease and 2) the shortage of accurate pixel-level annotations by radiologists for model training. Existing machine learning methods are unable to deal with the challenge that thoracic diseases usually happen in localized disease-specific areas. In this article, we propose a weakly supervised deep learning framework equipped with squeeze-and-excitation blocks, multi-map transfer, and max-min pooling for classifying thoracic diseases as well as localizing suspicious lesion regions. The comprehensive experiments and discussions are performed on the ChestX-ray14 dataset. Both numerical and visual results have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed model and its better performance against the state-of-the-art pipelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge