Weakly Supervised Deep Learning for Thoracic Disease Classification and Localization on Chest X-rays
Paper and Code
Jul 16, 2018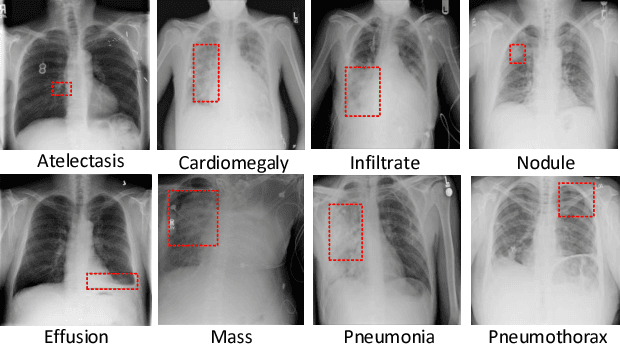
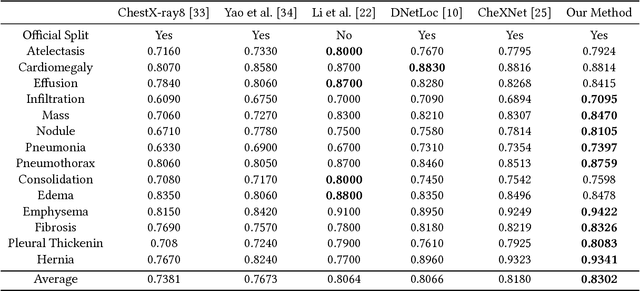
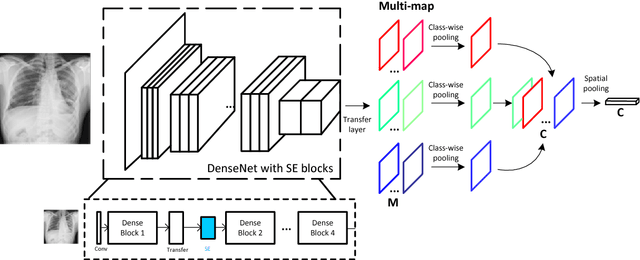
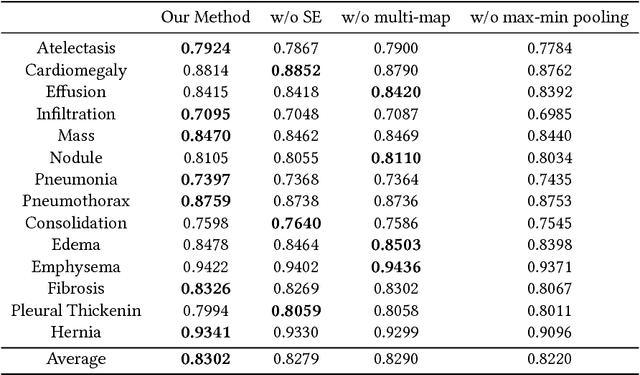
Chest X-rays is one of the most commonly available and affordable radiological examinations in clinical practice. While detecting thoracic diseases on chest X-rays is still a challenging task for machine intelligence, due to 1) the highly varied appearance of lesion areas on X-rays from patients of different thoracic disease and 2) the shortage of accurate pixel-level annotations by radiologists for model training. Existing machine learning methods are unable to deal with the challenge that thoracic diseases usually happen in localized disease-specific areas. In this article, we propose a weakly supervised deep learning framework equipped with squeeze-and-excitation blocks, multi-map transfer, and max-min pooling for classifying thoracic diseases as well as localizing suspicious lesion regions. The comprehensive experiments and discussions are performed on the ChestX-ray14 dataset. Both numerical and visual results have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed model and its better performance against the state-of-the-art pipelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge