Brandon M. Stewart
AutoPersuade: A Framework for Evaluating and Explaining Persuasive Arguments
Oct 11, 2024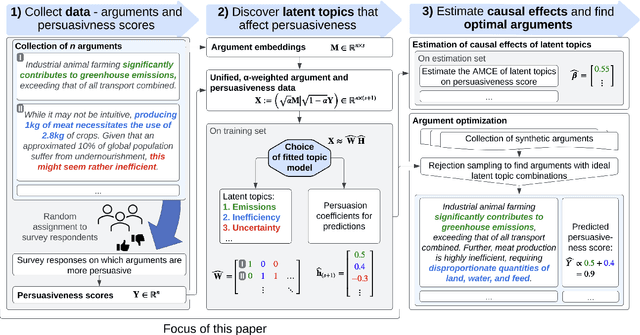

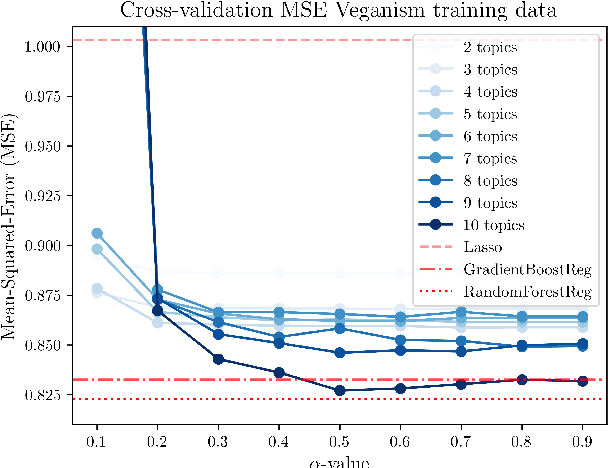
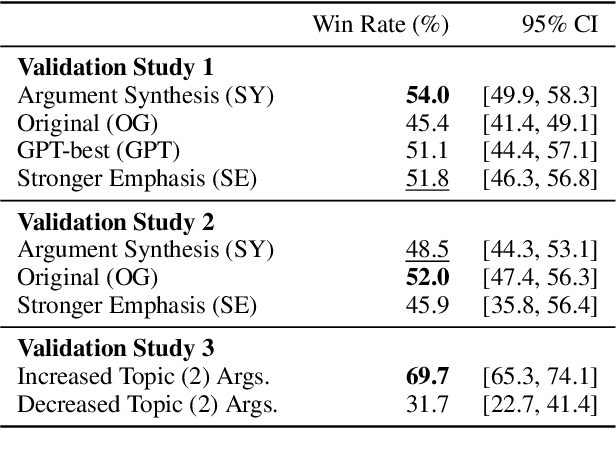
Abstract:We introduce AutoPersuade, a three-part framework for constructing persuasive messages. First, we curate a large dataset of arguments with human evaluations. Next, we develop a novel topic model to identify argument features that influence persuasiveness. Finally, we use this model to predict the effectiveness of new arguments and assess the causal impact of different components to provide explanations. We validate AutoPersuade through an experimental study on arguments for veganism, demonstrating its effectiveness with human studies and out-of-sample predictions.
GPT Deciphering Fedspeak: Quantifying Dissent Among Hawks and Doves
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:Markets and policymakers around the world hang on the consequential monetary policy decisions made by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). Publicly available textual documentation of their meetings provides insight into members' attitudes about the economy. We use GPT-4 to quantify dissent among members on the topic of inflation. We find that transcripts and minutes reflect the diversity of member views about the macroeconomic outlook in a way that is lost or omitted from the public statements. In fact, diverging opinions that shed light upon the committee's "true" attitudes are almost entirely omitted from the final statements. Hence, we argue that forecasting FOMC sentiment based solely on statements will not sufficiently reflect dissent among the hawks and doves.
More Victories, Less Cooperation: Assessing Cicero's Diplomacy Play
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:The boardgame Diplomacy is a challenging setting for communicative and cooperative artificial intelligence. The most prominent communicative Diplomacy AI, Cicero, has excellent strategic abilities, exceeding human players. However, the best Diplomacy players master communication, not just tactics, which is why the game has received attention as an AI challenge. This work seeks to understand the degree to which Cicero succeeds at communication. First, we annotate in-game communication with abstract meaning representation to separate in-game tactics from general language. Second, we run two dozen games with humans and Cicero, totaling over 200 human-player hours of competition. While AI can consistently outplay human players, AI-Human communication is still limited because of AI's difficulty with deception and persuasion. This shows that Cicero relies on strategy and has not yet reached the full promise of communicative and cooperative AI.
REFORMS: Reporting Standards for Machine Learning Based Science
Aug 15, 2023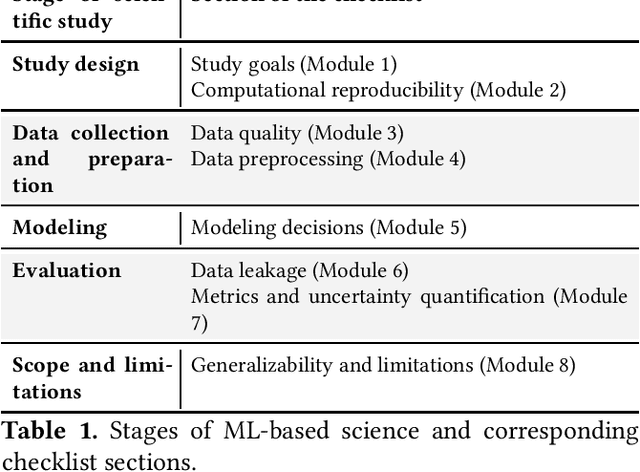
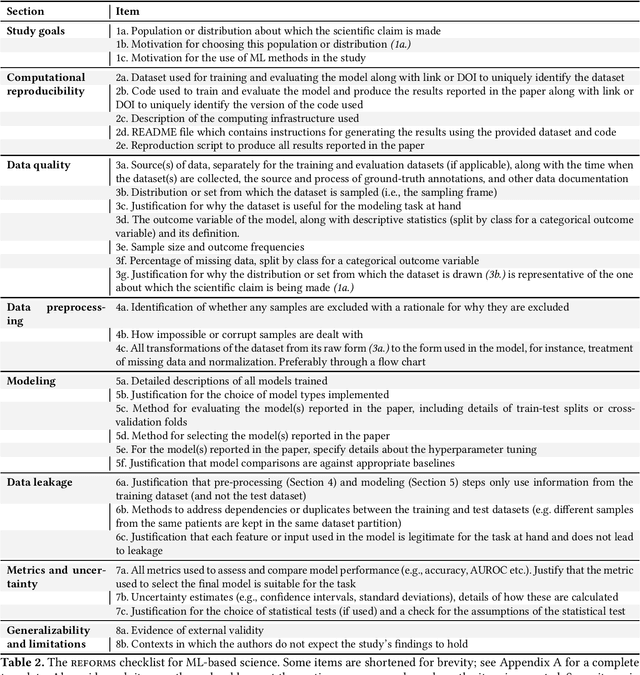
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) methods are proliferating in scientific research. However, the adoption of these methods has been accompanied by failures of validity, reproducibility, and generalizability. These failures can hinder scientific progress, lead to false consensus around invalid claims, and undermine the credibility of ML-based science. ML methods are often applied and fail in similar ways across disciplines. Motivated by this observation, our goal is to provide clear reporting standards for ML-based science. Drawing from an extensive review of past literature, we present the REFORMS checklist ($\textbf{Re}$porting Standards $\textbf{For}$ $\textbf{M}$achine Learning Based $\textbf{S}$cience). It consists of 32 questions and a paired set of guidelines. REFORMS was developed based on a consensus of 19 researchers across computer science, data science, mathematics, social sciences, and biomedical sciences. REFORMS can serve as a resource for researchers when designing and implementing a study, for referees when reviewing papers, and for journals when enforcing standards for transparency and reproducibility.
Using Large Language Model Annotations for Valid Downstream Statistical Inference in Social Science: Design-Based Semi-Supervised Learning
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:In computational social science (CSS), researchers analyze documents to explain social and political phenomena. In most scenarios, CSS researchers first obtain labels for documents and then explain labels using interpretable regression analyses in the second step. The recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) can lower costs for CSS research by annotating documents cheaply at scale, but such surrogate labels are often imperfect and biased. We present a new algorithm for using outputs from LLMs for downstream statistical analyses while guaranteeing statistical properties -- like asymptotic unbiasedness and proper uncertainty quantification -- which are fundamental to CSS research. We show that direct use of LLM-predicted surrogate labels in downstream statistical analyses leads to substantial bias and invalid confidence intervals, even with high surrogate accuracy of 80--90\%. To address this, we build on debiased machine learning to propose the design-based semi-supervised learning (DSL) estimator. DSL employs a doubly-robust procedure to combine surrogate labels with a smaller number of gold-standard labels. Our approach guarantees valid inference for downstream statistical analyses, even when surrogates are arbitrarily biased, without requiring stringent assumptions, by controlling the probability of sampling documents for gold-standard labeling. Both our theoretical analysis and experimental results show that DSL provides valid statistical inference while achieving root mean squared errors comparable to existing alternatives that focus only on prediction without statistical guarantees.
Causal Inference in Natural Language Processing: Estimation, Prediction, Interpretation and Beyond
Sep 02, 2021
Abstract:A fundamental goal of scientific research is to learn about causal relationships. However, despite its critical role in the life and social sciences, causality has not had the same importance in Natural Language Processing (NLP), which has traditionally placed more emphasis on predictive tasks. This distinction is beginning to fade, with an emerging area of interdisciplinary research at the convergence of causal inference and language processing. Still, research on causality in NLP remains scattered across domains without unified definitions, benchmark datasets and clear articulations of the remaining challenges. In this survey, we consolidate research across academic areas and situate it in the broader NLP landscape. We introduce the statistical challenge of estimating causal effects, encompassing settings where text is used as an outcome, treatment, or as a means to address confounding. In addition, we explore potential uses of causal inference to improve the performance, robustness, fairness, and interpretability of NLP models. We thus provide a unified overview of causal inference for the computational linguistics community.
Naïve regression requires weaker assumptions than factor models to adjust for multiple cause confounding
Jul 24, 2020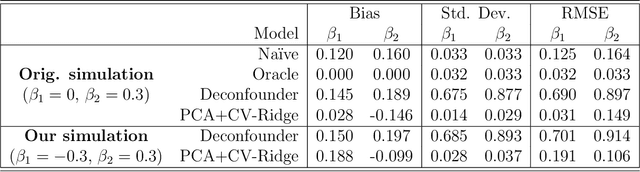
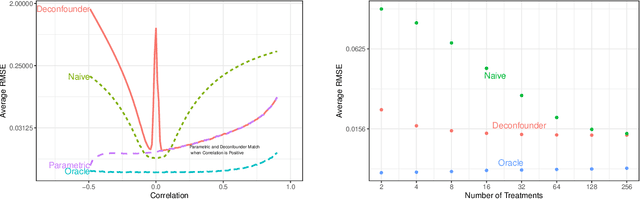
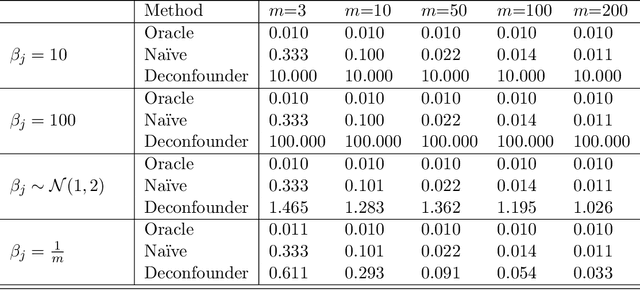

Abstract:The empirical practice of using factor models to adjust for shared, unobserved confounders, $\mathbf{Z}$, in observational settings with multiple treatments, $\mathbf{A}$, is widespread in fields including genetics, networks, medicine, and politics. Wang and Blei (2019, WB) formalizes these procedures and develops the "deconfounder," a causal inference method using factor models of $\mathbf{A}$ to estimate "substitute confounders," $\hat{\mathbf{Z}}$, then estimating treatment effects by regressing the outcome, $\mathbf{Y}$, on part of $\mathbf{A}$ while adjusting for $\hat{\mathbf{Z}}$. WB claim the deconfounder is unbiased when there are no single-cause confounders and $\hat{\mathbf{Z}}$ is "pinpointed." We clarify pinpointing requires each confounder to affect infinitely many treatments. We prove under these assumptions, a na\"ive semiparametric regression of $\mathbf{Y}$ on $\mathbf{A}$ is asymptotically unbiased. Deconfounder variants nesting this regression are therefore also asymptotically unbiased, but variants using $\hat{\mathbf{Z}}$ and subsets of causes require further untestable assumptions. We replicate every deconfounder analysis with available data and find it fails to consistently outperform na\"ive regression. In practice, the deconfounder produces implausible estimates in WB's case study to movie earnings: estimates suggest comic author Stan Lee's cameo appearances causally contributed \$15.5 billion, most of Marvel movie revenue. We conclude neither approach is a viable substitute for careful research design in real-world applications.
How to Make Causal Inferences Using Texts
Feb 06, 2018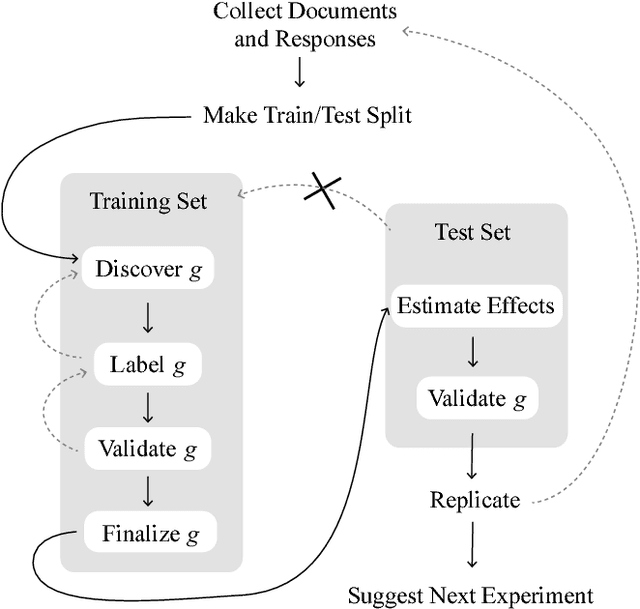
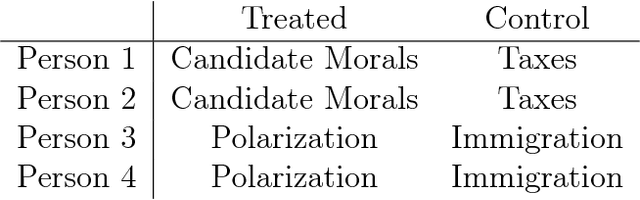
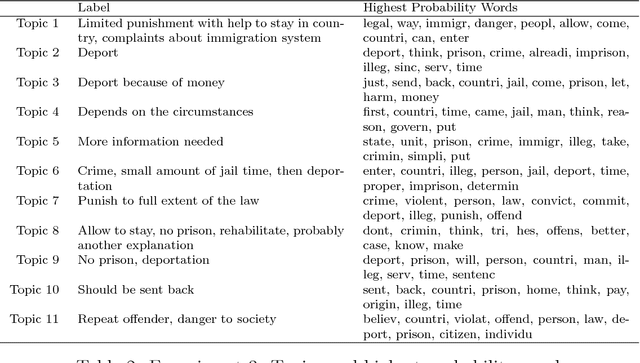
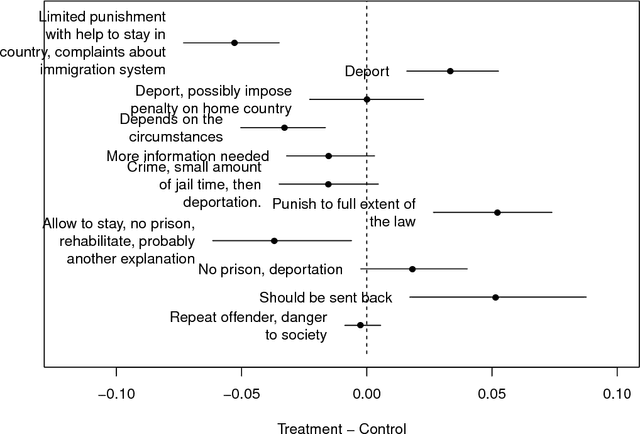
Abstract:New text as data techniques offer a great promise: the ability to inductively discover measures that are useful for testing social science theories of interest from large collections of text. We introduce a conceptual framework for making causal inferences with discovered measures as a treatment or outcome. Our framework enables researchers to discover high-dimensional textual interventions and estimate the ways that observed treatments affect text-based outcomes. We argue that nearly all text-based causal inferences depend upon a latent representation of the text and we provide a framework to learn the latent representation. But estimating this latent representation, we show, creates new risks: we may introduce an identification problem or overfit. To address these risks we describe a split-sample framework and apply it to estimate causal effects from an experiment on immigration attitudes and a study on bureaucratic response. Our work provides a rigorous foundation for text-based causal inferences.
How Algorithmic Confounding in Recommendation Systems Increases Homogeneity and Decreases Utility
Oct 30, 2017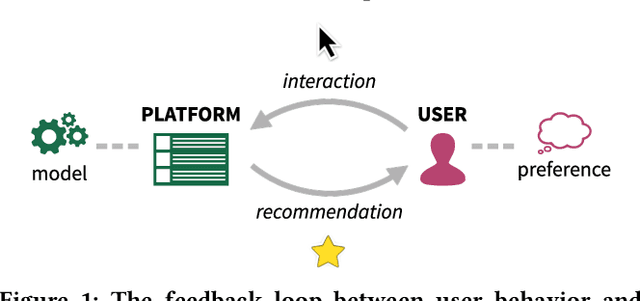
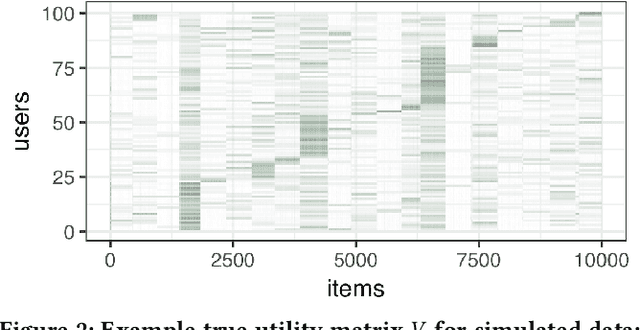
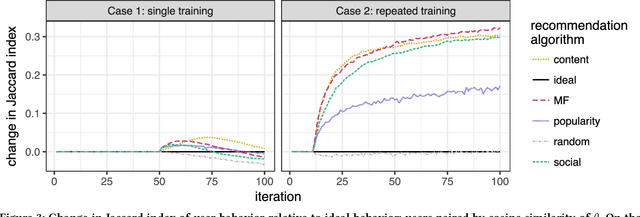
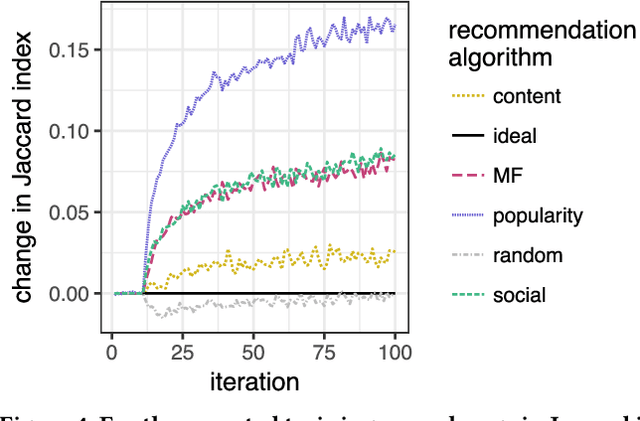
Abstract:Recommendation systems occupy an expanding role in everyday decision making, from choice of movies and household goods to consequential medical and legal decisions. The data used to train and test these systems is algorithmically confounded in that it is the result of a feedback loop between human choices and an existing algorithmic recommendation system. Using simulations, we demonstrate that algorithmic confounding can disadvantage algorithms in training, bias held-out evaluation, and amplify homogenization of user behavior without gains in utility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge