Wichayaporn Wongkamjan
Should I Trust You? Detecting Deception in Negotiations using Counterfactual RL
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:An increasingly prevalent socio-technical problem is people being taken in by offers that sound ``too good to be true'', where persuasion and trust shape decision-making. This paper investigates how \abr{ai} can help detect these deceptive scenarios. We analyze how humans strategically deceive each other in \textit{Diplomacy}, a board game that requires both natural language communication and strategic reasoning. This requires extracting logical forms of proposed agreements in player communications and computing the relative rewards of the proposal using agents' value functions. Combined with text-based features, this can improve our deception detection. Our method detects human deception with a high precision when compared to a Large Language Model approach that flags many true messages as deceptive. Future human-\abr{ai} interaction tools can build on our methods for deception detection by triggering \textit{friction} to give users a chance of interrogating suspicious proposals.
Personalized Help for Optimizing Low-Skilled Users' Strategy
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:AIs can beat humans in game environments; however, how helpful those agents are to human remains understudied. We augment CICERO, a natural language agent that demonstrates superhuman performance in Diplomacy, to generate both move and message advice based on player intentions. A dozen Diplomacy games with novice and experienced players, with varying advice settings, show that some of the generated advice is beneficial. It helps novices compete with experienced players and in some instances even surpass them. The mere presence of advice can be advantageous, even if players do not follow it.
What if Red Can Talk? Dynamic Dialogue Generation Using Large Language Models
Jul 29, 2024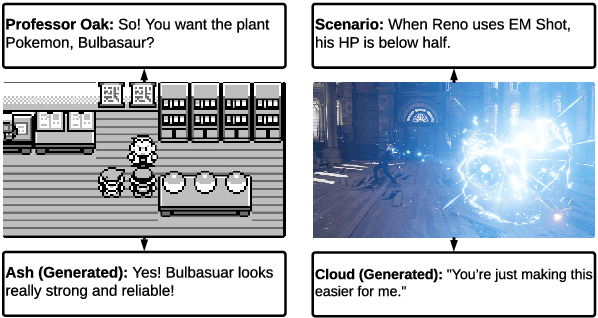
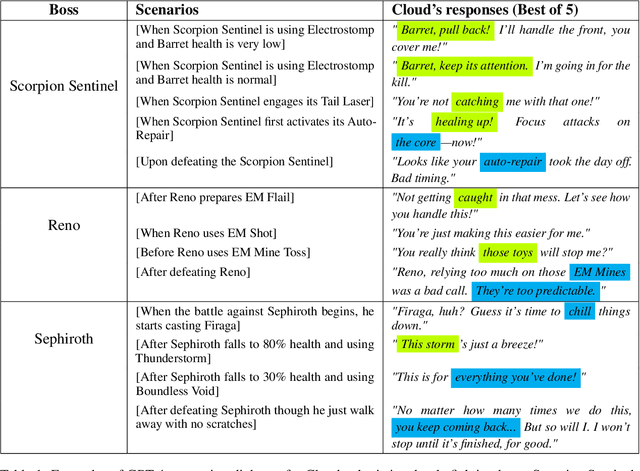
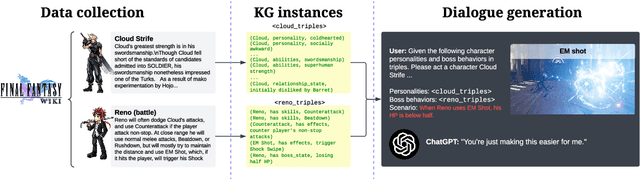
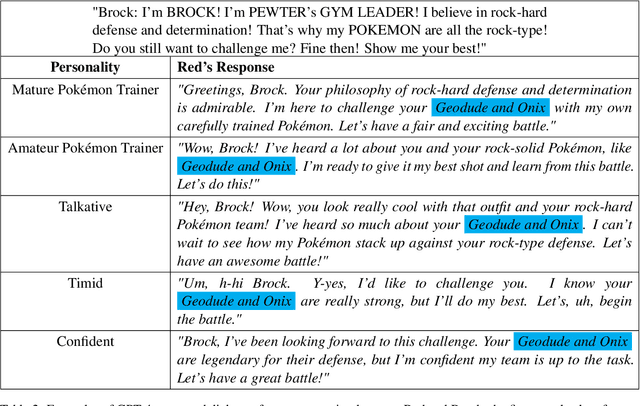
Abstract:Role-playing games (RPGs) provide players with a rich, interactive world to explore. Dialogue serves as the primary means of communication between developers and players, manifesting in various forms such as guides, NPC interactions, and storytelling. While most games rely on written scripts to define the main story and character personalities, player immersion can be significantly enhanced through casual interactions between characters. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), we introduce a dialogue filler framework that utilizes LLMs enhanced by knowledge graphs to generate dynamic and contextually appropriate character interactions. We test this framework within the environments of Final Fantasy VII Remake and Pokemon, providing qualitative and quantitative evidence that demonstrates GPT-4's capability to act with defined personalities and generate dialogue. However, some flaws remain, such as GPT-4 being overly positive or more subtle personalities, such as maturity, tend to be of lower quality compared to more overt traits like timidity. This study aims to assist developers in crafting more nuanced filler dialogues, thereby enriching player immersion and enhancing the overall RPG experience.
More Victories, Less Cooperation: Assessing Cicero's Diplomacy Play
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:The boardgame Diplomacy is a challenging setting for communicative and cooperative artificial intelligence. The most prominent communicative Diplomacy AI, Cicero, has excellent strategic abilities, exceeding human players. However, the best Diplomacy players master communication, not just tactics, which is why the game has received attention as an AI challenge. This work seeks to understand the degree to which Cicero succeeds at communication. First, we annotate in-game communication with abstract meaning representation to separate in-game tactics from general language. Second, we run two dozen games with humans and Cicero, totaling over 200 human-player hours of competition. While AI can consistently outplay human players, AI-Human communication is still limited because of AI's difficulty with deception and persuasion. This shows that Cicero relies on strategy and has not yet reached the full promise of communicative and cooperative AI.
COPlanner: Plan to Roll Out Conservatively but to Explore Optimistically for Model-Based RL
Oct 11, 2023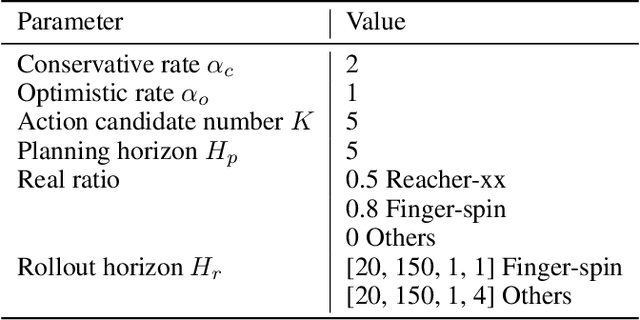
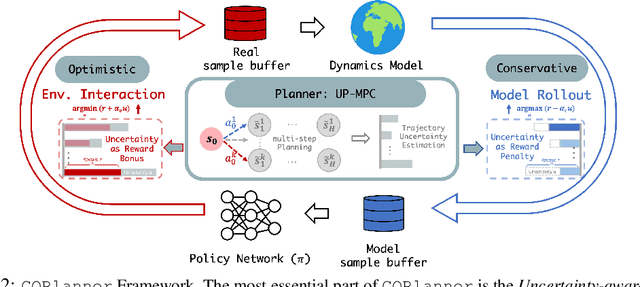
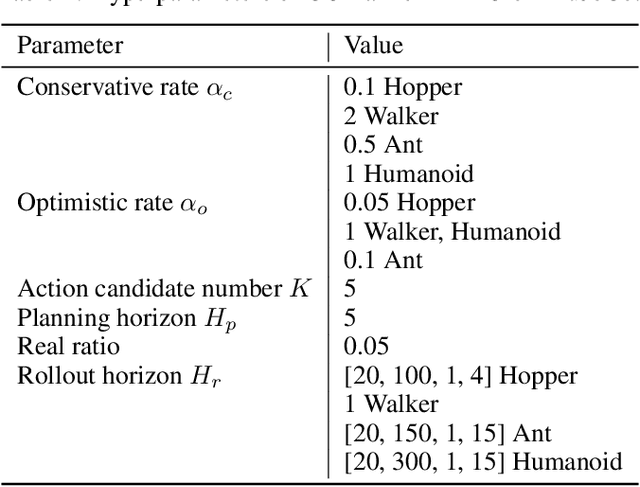

Abstract:Dyna-style model-based reinforcement learning contains two phases: model rollouts to generate sample for policy learning and real environment exploration using current policy for dynamics model learning. However, due to the complex real-world environment, it is inevitable to learn an imperfect dynamics model with model prediction error, which can further mislead policy learning and result in sub-optimal solutions. In this paper, we propose $\texttt{COPlanner}$, a planning-driven framework for model-based methods to address the inaccurately learned dynamics model problem with conservative model rollouts and optimistic environment exploration. $\texttt{COPlanner}$ leverages an uncertainty-aware policy-guided model predictive control (UP-MPC) component to plan for multi-step uncertainty estimation. This estimated uncertainty then serves as a penalty during model rollouts and as a bonus during real environment exploration respectively, to choose actions. Consequently, $\texttt{COPlanner}$ can avoid model uncertain regions through conservative model rollouts, thereby alleviating the influence of model error. Simultaneously, it explores high-reward model uncertain regions to reduce model error actively through optimistic real environment exploration. $\texttt{COPlanner}$ is a plug-and-play framework that can be applied to any dyna-style model-based methods. Experimental results on a series of proprioceptive and visual continuous control tasks demonstrate that both sample efficiency and asymptotic performance of strong model-based methods are significantly improved combined with $\texttt{COPlanner}$.
Live in the Moment: Learning Dynamics Model Adapted to Evolving Policy
Jul 25, 2022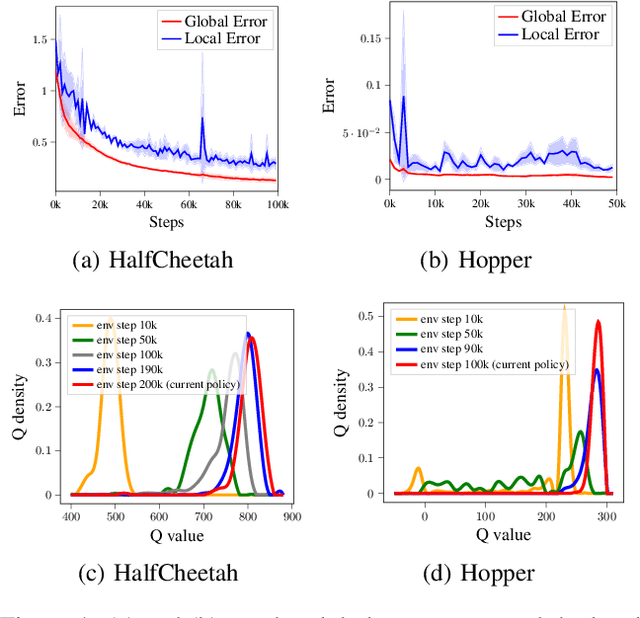
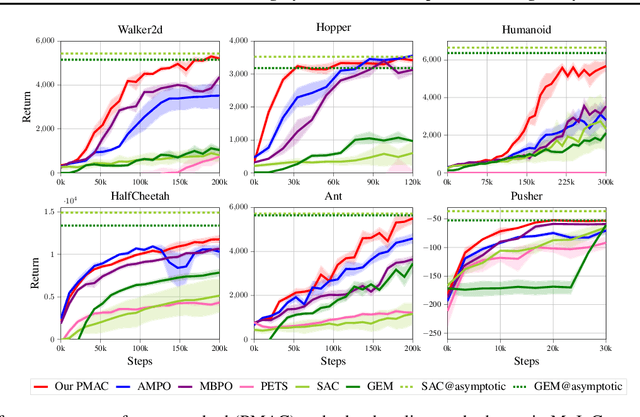
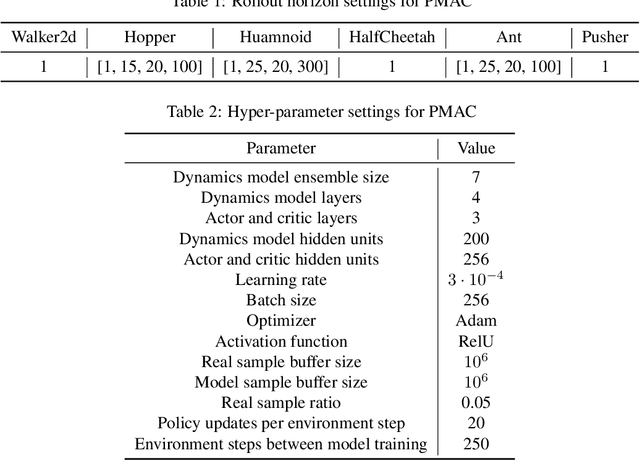
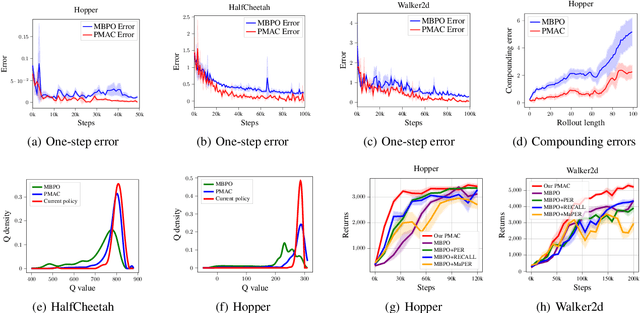
Abstract:Model-based reinforcement learning (RL) achieves higher sample efficiency in practice than model-free RL by learning a dynamics model to generate samples for policy learning. Previous works learn a "global" dynamics model to fit the state-action visitation distribution for all historical policies. However, in this paper, we find that learning a global dynamics model does not necessarily benefit model prediction for the current policy since the policy in use is constantly evolving. The evolving policy during training will cause state-action visitation distribution shifts. We theoretically analyze how the distribution of historical policies affects the model learning and model rollouts. We then propose a novel model-based RL method, named \textit{Policy-adaptation Model-based Actor-Critic (PMAC)}, which learns a policy-adapted dynamics model based on a policy-adaptation mechanism. This mechanism dynamically adjusts the historical policy mixture distribution to ensure the learned model can continually adapt to the state-action visitation distribution of the evolving policy. Experiments on a range of continuous control environments in MuJoCo show that PMAC achieves state-of-the-art asymptotic performance and almost two times higher sample efficiency than prior model-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge