Bing Xiang
Adaptation of Embedding Models to Financial Filings via LLM Distillation
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in generative large language models (LLMs), practical application of specialized conversational AI agents remains constrained by computation costs, latency requirements, and the need for precise domain-specific relevance measures. While existing embedding models address the first two constraints, they underperform on information retrieval in specialized domains like finance. This paper introduces a scalable pipeline that trains specialized models from an unlabeled corpus using a general purpose retrieval embedding model as foundation. Our method yields an average of 27.7% improvement in MRR$\texttt{@}$5, 44.6% improvement in mean DCG$\texttt{@}$5 across 14 financial filing types measured over 21,800 query-document pairs, and improved NDCG on 3 of 4 document classes in FinanceBench. We adapt retrieval embeddings (bi-encoder) for RAG, not LLM generators, using LLM-judged relevance to distill domain knowledge into a compact retriever. There are prior works which pair synthetically generated queries with real passages to directly fine-tune the retrieval model. Our pipeline differs from these by introducing interaction between student and teacher models that interleaves retrieval-based mining of hard positive/negative examples from the unlabeled corpus with iterative retraining of the student model's weights using these examples. Each retrieval iteration uses the refined student model to mine the corpus for progressively harder training examples for the subsequent training iteration. The methodology provides a cost-effective solution to bridging the gap between general-purpose models and specialized domains without requiring labor-intensive human annotation.
Token Alignment via Character Matching for Subword Completion
Mar 13, 2024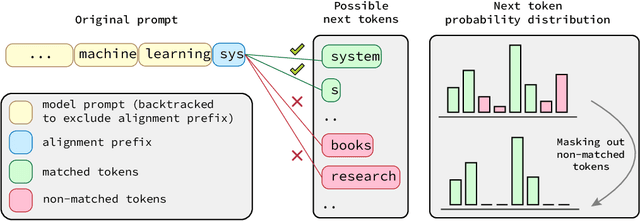



Abstract:Generative models, widely utilized in various applications, can often struggle with prompts corresponding to partial tokens. This struggle stems from tokenization, where partial tokens fall out of distribution during inference, leading to incorrect or nonsensical outputs. This paper examines a technique to alleviate the tokenization artifact on text completion in generative models, maintaining performance even in regular non-subword cases. The method, termed token alignment, involves backtracking to the last complete tokens and ensuring the model's generation aligns with the prompt. This approach showcases marked improvement across many partial token scenarios, including nuanced cases like space-prefix and partial indentation, with only a minor time increase. The technique and analysis detailed in this paper contribute to the continuous advancement of generative models in handling partial inputs, bearing relevance for applications like code completion and text autocompletion.
Bifurcated Attention for Single-Context Large-Batch Sampling
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:In our study, we present bifurcated attention, a method developed for language model inference in single-context batch sampling contexts. This approach aims to reduce redundant memory IO costs, a significant factor in latency for high batch sizes and long context lengths. Bifurcated attention achieves this by dividing the attention mechanism during incremental decoding into two distinct GEMM operations, focusing on the KV cache from prefill and the decoding process. This method ensures precise computation and maintains the usual computational load (FLOPs) of standard attention mechanisms, but with reduced memory IO. Bifurcated attention is also compatible with multi-query attention mechanism known for reduced memory IO for KV cache, further enabling higher batch size and context length. The resulting efficiency leads to lower latency, improving suitability for real-time applications, e.g., enabling massively-parallel answer generation without substantially increasing latency, enhancing performance when integrated with postprocessing techniques such as reranking.
Code Representation Learning At Scale
Feb 02, 2024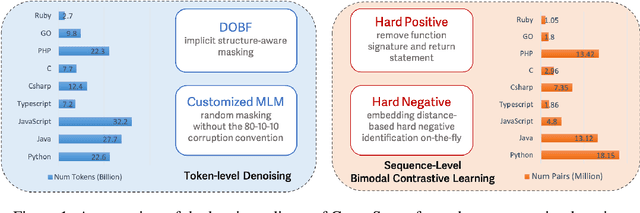
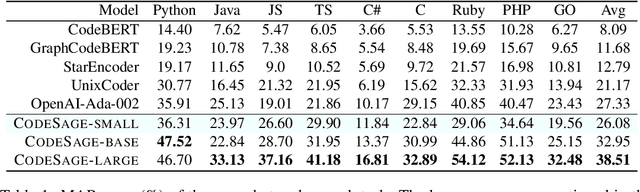
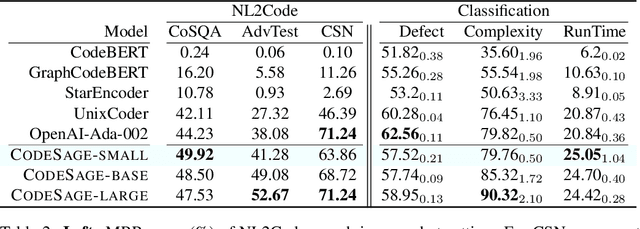
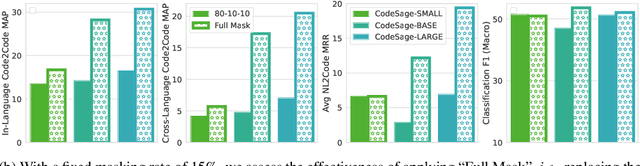
Abstract:Recent studies have shown that code language models at scale demonstrate significant performance gains on downstream tasks, i.e., code generation. However, most of the existing works on code representation learning train models at a hundred million parameter scale using very limited pretraining corpora. In this work, we fuel code representation learning with a vast amount of code data via a two-stage pretraining scheme. We first train the encoders via a mix that leverages both randomness in masking language modeling and the structure aspect of programming language. We then enhance the representations via contrastive learning with hard negative and hard positive constructed in an unsupervised manner. We establish an off-the-shelf encoder model that persistently outperforms the existing models on a wide variety of downstream tasks by large margins. To comprehend the factors contributing to successful code representation learning, we conduct detailed ablations and share our findings on (i) a customized and effective token-level denoising scheme for source code; (ii) the importance of hard negatives and hard positives; (iii) how the proposed bimodal contrastive learning boost the cross-lingual semantic search performance; and (iv) how the pretraining schemes decide the downstream task performance scales with the model size.
* 10 pages
CrossCodeEval: A Diverse and Multilingual Benchmark for Cross-File Code Completion
Oct 17, 2023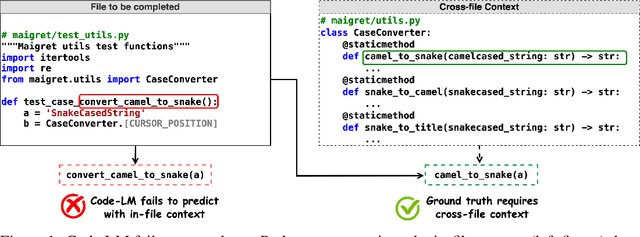
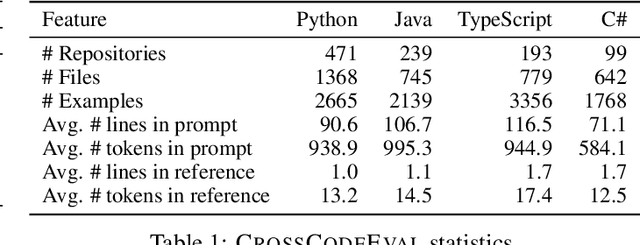
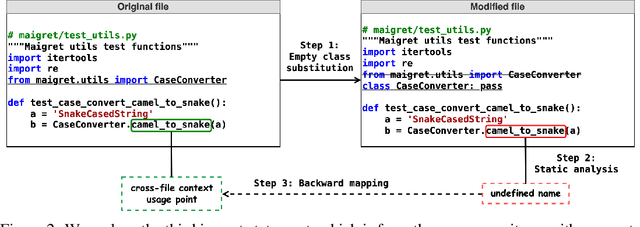
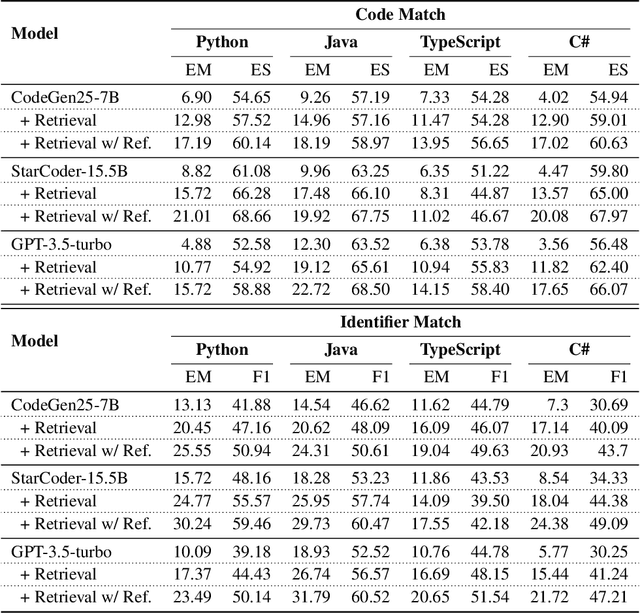
Abstract:Code completion models have made significant progress in recent years, yet current popular evaluation datasets, such as HumanEval and MBPP, predominantly focus on code completion tasks within a single file. This over-simplified setting falls short of representing the real-world software development scenario where repositories span multiple files with numerous cross-file dependencies, and accessing and understanding cross-file context is often required to complete the code correctly. To fill in this gap, we propose CrossCodeEval, a diverse and multilingual code completion benchmark that necessitates an in-depth cross-file contextual understanding to complete the code accurately. CrossCodeEval is built on a diverse set of real-world, open-sourced, permissively-licensed repositories in four popular programming languages: Python, Java, TypeScript, and C#. To create examples that strictly require cross-file context for accurate completion, we propose a straightforward yet efficient static-analysis-based approach to pinpoint the use of cross-file context within the current file. Extensive experiments on state-of-the-art code language models like CodeGen and StarCoder demonstrate that CrossCodeEval is extremely challenging when the relevant cross-file context is absent, and we see clear improvements when adding these context into the prompt. However, despite such improvements, the pinnacle of performance remains notably unattained even with the highest-performing model, indicating that CrossCodeEval is also capable of assessing model's capability in leveraging extensive context to make better code completion. Finally, we benchmarked various methods in retrieving cross-file context, and show that CrossCodeEval can also be used to measure the capability of code retrievers.
Few-Shot Data-to-Text Generation via Unified Representation and Multi-Source Learning
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:We present a novel approach for structured data-to-text generation that addresses the limitations of existing methods that primarily focus on specific types of structured data. Our proposed method aims to improve performance in multi-task training, zero-shot and few-shot scenarios by providing a unified representation that can handle various forms of structured data such as tables, knowledge graph triples, and meaning representations. We demonstrate that our proposed approach can effectively adapt to new structured forms, and can improve performance in comparison to current methods. For example, our method resulted in a 66% improvement in zero-shot BLEU scores when transferring models trained on table inputs to a knowledge graph dataset. Our proposed method is an important step towards a more general data-to-text generation framework.
Self-consistency for open-ended generations
Jul 11, 2023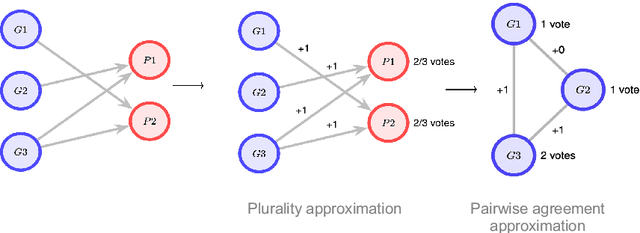
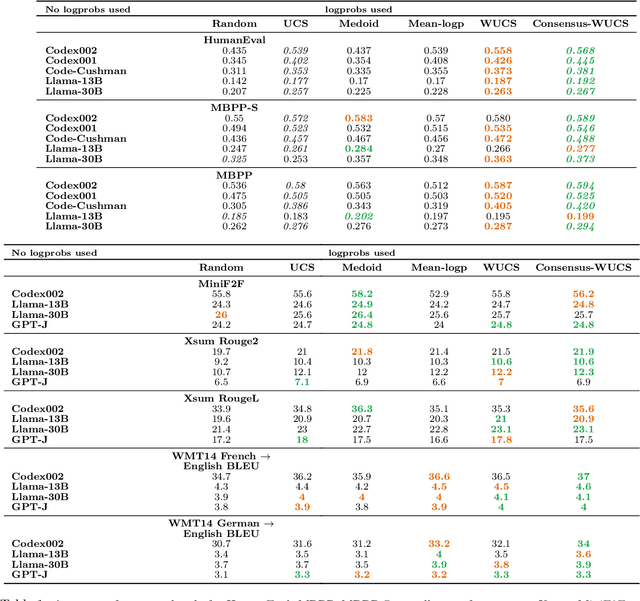
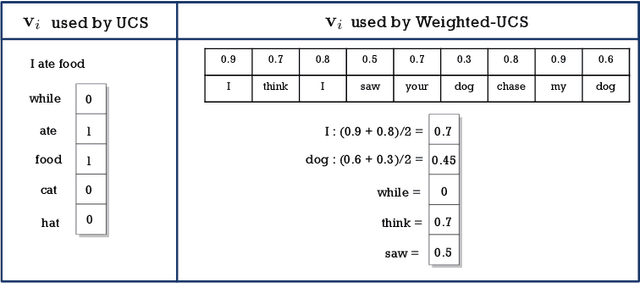
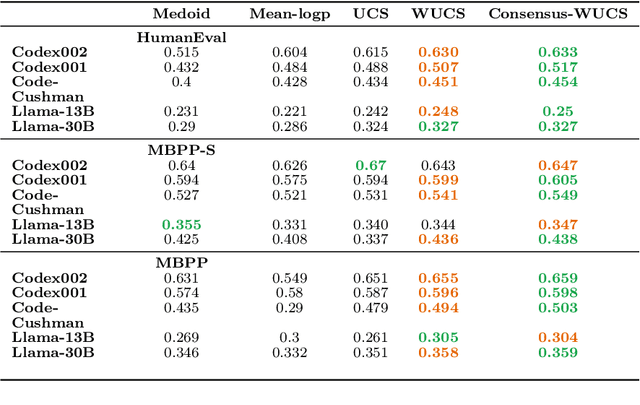
Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel approach for improving the quality and consistency of generated outputs from large-scale pre-trained language models (LLMs). Self-consistency has emerged as an effective approach for prompts with fixed answers, selecting the answer with the highest number of votes. In this paper, we introduce a generalized framework for self-consistency that extends its applicability beyond problems that have fixed-answer answers. Through extensive simulations, we demonstrate that our approach consistently recovers the optimal or near-optimal generation from a set of candidates. We also propose lightweight parameter-free similarity functions that show significant and consistent improvements across code generation, autoformalization, and summarization tasks, even without access to token log probabilities. Our method incurs minimal computational overhead, requiring no auxiliary reranker models or modifications to the existing model.
Exploring Continual Learning for Code Generation Models
Jul 05, 2023



Abstract:Large-scale code generation models such as Codex and CodeT5 have achieved impressive performance. However, libraries are upgraded or deprecated very frequently and re-training large-scale language models is computationally expensive. Therefore, Continual Learning (CL) is an important aspect that remains underexplored in the code domain. In this paper, we introduce a benchmark called CodeTask-CL that covers a wide range of tasks, including code generation, translation, summarization, and refinement, with different input and output programming languages. Next, on our CodeTask-CL benchmark, we compare popular CL techniques from NLP and Vision domains. We find that effective methods like Prompt Pooling (PP) suffer from catastrophic forgetting due to the unstable training of the prompt selection mechanism caused by stark distribution shifts in coding tasks. We address this issue with our proposed method, Prompt Pooling with Teacher Forcing (PP-TF), that stabilizes training by enforcing constraints on the prompt selection mechanism and leads to a 21.54% improvement over Prompt Pooling. Along with the benchmark, we establish a training pipeline that can be used for CL on code models, which we believe can motivate further development of CL methods for code models. Our code is available at https://github.com/amazon-science/codetaskcl-pptf
A Static Evaluation of Code Completion by Large Language Models
Jun 05, 2023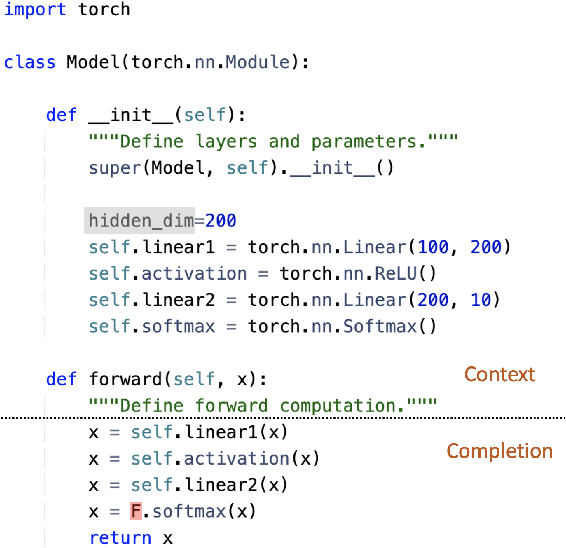
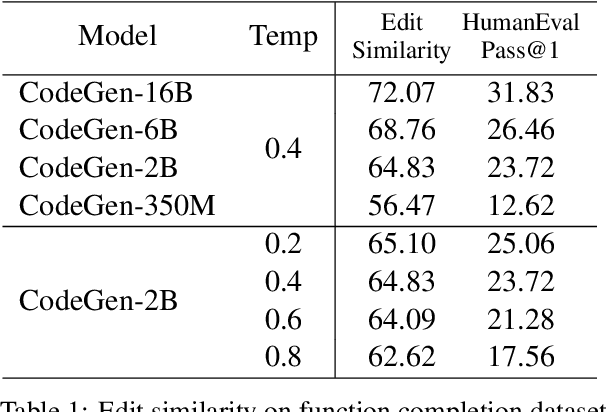
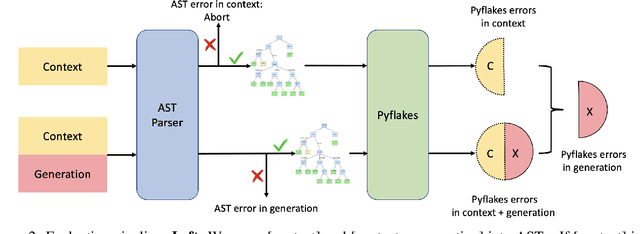
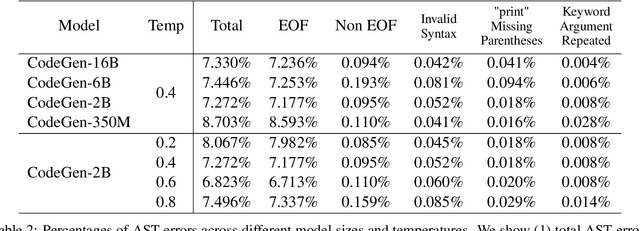
Abstract:Large language models trained on code have shown great potential to increase productivity of software developers. Several execution-based benchmarks have been proposed to evaluate functional correctness of model-generated code on simple programming problems. Nevertheless, it is expensive to perform the same evaluation on complex real-world projects considering the execution cost. On the contrary, static analysis tools such as linters, which can detect errors without running the program, haven't been well explored for evaluating code generation models. In this work, we propose a static evaluation framework to quantify static errors in Python code completions, by leveraging Abstract Syntax Trees. Compared with execution-based evaluation, our method is not only more efficient, but also applicable to code in the wild. For experiments, we collect code context from open source repos to generate one million function bodies using public models. Our static analysis reveals that Undefined Name and Unused Variable are the most common errors among others made by language models. Through extensive studies, we also show the impact of sampling temperature, model size, and context on static errors in code completions.
Efficient Shapley Values Estimation by Amortization for Text Classification
May 31, 2023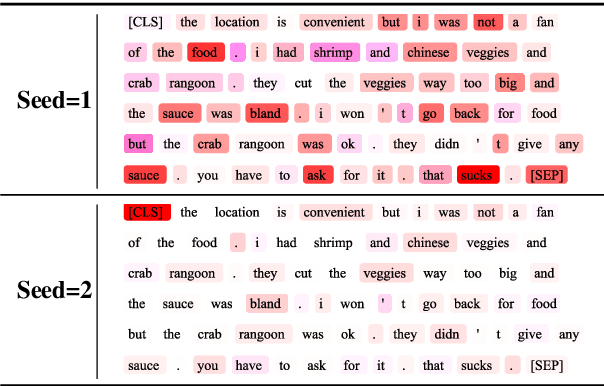
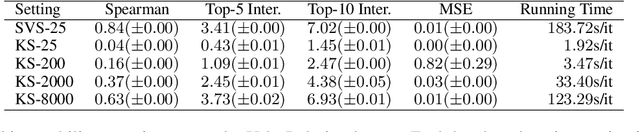
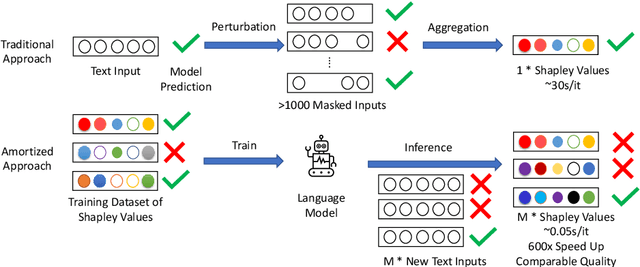
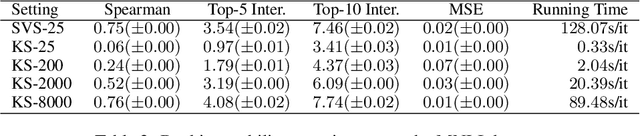
Abstract:Despite the popularity of Shapley Values in explaining neural text classification models, computing them is prohibitive for large pretrained models due to a large number of model evaluations. In practice, Shapley Values are often estimated with a small number of stochastic model evaluations. However, we show that the estimated Shapley Values are sensitive to random seed choices -- the top-ranked features often have little overlap across different seeds, especially on examples with longer input texts. This can only be mitigated by aggregating thousands of model evaluations, which on the other hand, induces substantial computational overheads. To mitigate the trade-off between stability and efficiency, we develop an amortized model that directly predicts each input feature's Shapley Value without additional model evaluations. It is trained on a set of examples whose Shapley Values are estimated from a large number of model evaluations to ensure stability. Experimental results on two text classification datasets demonstrate that our amortized model estimates Shapley Values accurately with up to 60 times speedup compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, the estimated values are stable as the inference is deterministic. We release our code at https://github.com/yangalan123/Amortized-Interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge