Henghui Zhu
Towards Better Understanding Table Instruction Tuning: Decoupling the Effects from Data versus Models
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in natural language processing have leveraged instruction tuning to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) for table-related tasks. However, previous works train different base models with different training data, lacking an apples-to-apples comparison across the result table LLMs. To address this, we fine-tune base models from the Mistral, OLMo, and Phi families on existing public training datasets. Our replication achieves performance on par with or surpassing existing table LLMs, establishing new state-of-the-art performance on Hitab, a table question-answering dataset. More importantly, through systematic out-of-domain evaluation, we decouple the contributions of training data and the base model, providing insight into their individual impacts. In addition, we assess the effects of table-specific instruction tuning on general-purpose benchmarks, revealing trade-offs between specialization and generalization.
PRACTIQ: A Practical Conversational Text-to-SQL dataset with Ambiguous and Unanswerable Queries
Oct 14, 2024
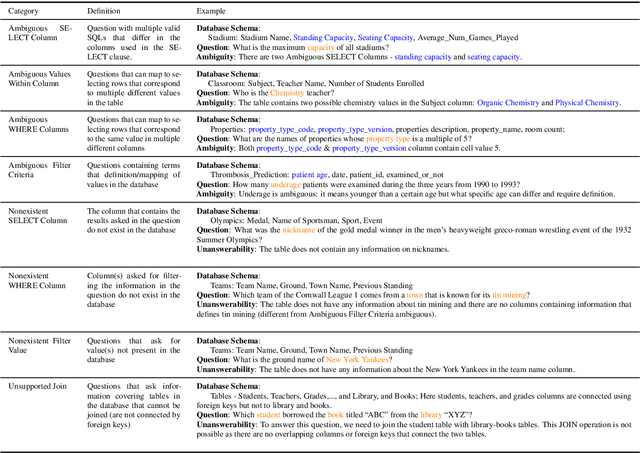
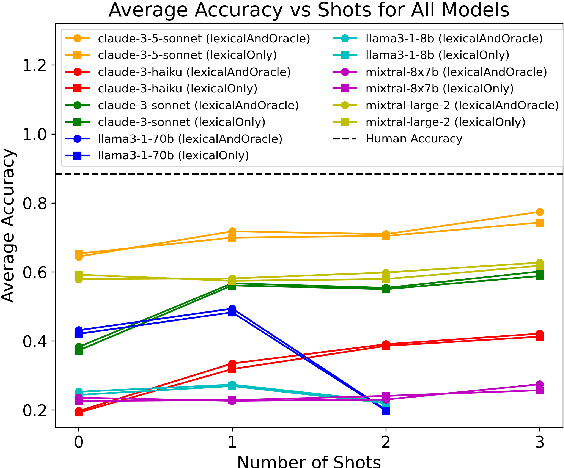
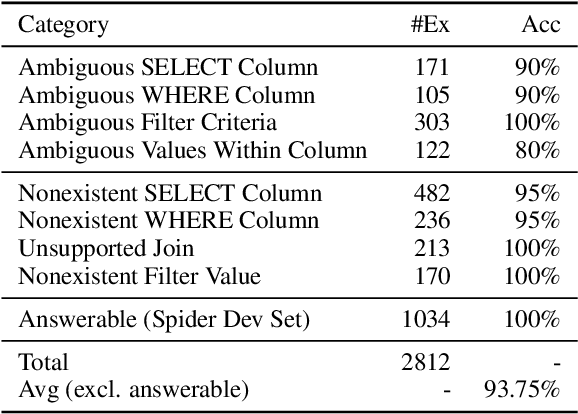
Abstract:Previous text-to-SQL datasets and systems have primarily focused on user questions with clear intentions that can be answered. However, real user questions can often be ambiguous with multiple interpretations or unanswerable due to a lack of relevant data. In this work, we construct a practical conversational text-to-SQL dataset called PRACTIQ, consisting of ambiguous and unanswerable questions inspired by real-world user questions. We first identified four categories of ambiguous questions and four categories of unanswerable questions by studying existing text-to-SQL datasets. Then, we generate conversations with four turns: the initial user question, an assistant response seeking clarification, the user's clarification, and the assistant's clarified SQL response with the natural language explanation of the execution results. For some ambiguous queries, we also directly generate helpful SQL responses, that consider multiple aspects of ambiguity, instead of requesting user clarification. To benchmark the performance on ambiguous, unanswerable, and answerable questions, we implemented large language model (LLM)-based baselines using various LLMs. Our approach involves two steps: question category classification and clarification SQL prediction. Our experiments reveal that state-of-the-art systems struggle to handle ambiguous and unanswerable questions effectively. We will release our code for data generation and experiments on GitHub.
You Only Read Once (YORO): Learning to Internalize Database Knowledge for Text-to-SQL
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:While significant progress has been made on the text-to-SQL task, recent solutions repeatedly encode the same database schema for every question, resulting in unnecessary high inference cost and often overlooking crucial database knowledge. To address these issues, we propose You Only Read Once (YORO), a novel paradigm that directly internalizes database knowledge into the parametric knowledge of a text-to-SQL model during training and eliminates the need for schema encoding during inference. YORO significantly reduces the input token length by 66%-98%. Despite its shorter inputs, our empirical results demonstrate YORO's competitive performances with traditional systems on three benchmarks as well as its significant outperformance on large databases. Furthermore, YORO excels in handling questions with challenging value retrievals such as abbreviation.
Propagation and Pitfalls: Reasoning-based Assessment of Knowledge Editing through Counterfactual Tasks
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Current approaches of knowledge editing struggle to effectively propagate updates to interconnected facts. In this work, we delve into the barriers that hinder the appropriate propagation of updated knowledge within these models for accurate reasoning. To support our analysis, we introduce a novel reasoning-based benchmark -- ReCoE (Reasoning-based Counterfactual Editing dataset) -- which covers six common reasoning schemes in real world. We conduct a thorough analysis of existing knowledge editing techniques, including input augmentation, finetuning, and locate-and-edit. We found that all model editing methods show notably low performance on this dataset, especially in certain reasoning schemes. Our analysis over the chain-of-thought generation of edited models further uncover key reasons behind the inadequacy of existing knowledge editing methods from a reasoning standpoint, involving aspects on fact-wise editing, fact recall ability, and coherence in generation. We will make our benchmark publicly available.
Generate then Select: Open-ended Visual Question Answering Guided by World Knowledge
May 30, 2023
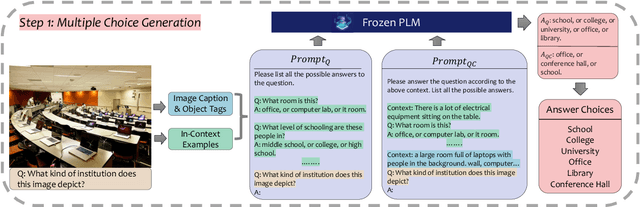
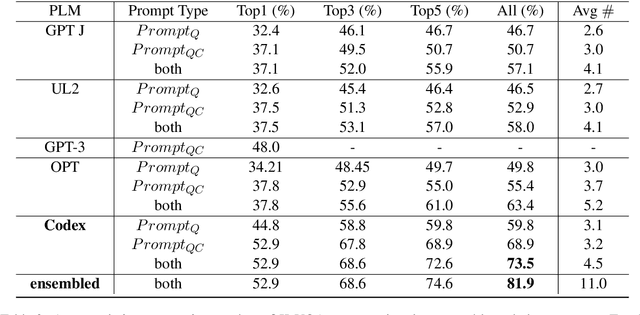
Abstract:The open-ended Visual Question Answering (VQA) task requires AI models to jointly reason over visual and natural language inputs using world knowledge. Recently, pre-trained Language Models (PLM) such as GPT-3 have been applied to the task and shown to be powerful world knowledge sources. However, these methods suffer from low knowledge coverage caused by PLM bias -- the tendency to generate certain tokens over other tokens regardless of prompt changes, and high dependency on the PLM quality -- only models using GPT-3 can achieve the best result. To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose RASO: a new VQA pipeline that deploys a generate-then-select strategy guided by world knowledge for the first time. Rather than following the de facto standard to train a multi-modal model that directly generates the VQA answer, RASO first adopts PLM to generate all the possible answers, and then trains a lightweight answer selection model for the correct answer. As proved in our analysis, RASO expands the knowledge coverage from in-domain training data by a large margin. We provide extensive experimentation and show the effectiveness of our pipeline by advancing the state-of-the-art by 4.1% on OK-VQA, without additional computation cost. Code and models are released at http://cogcomp.org/page/publication_view/1010
UNITE: A Unified Benchmark for Text-to-SQL Evaluation
May 26, 2023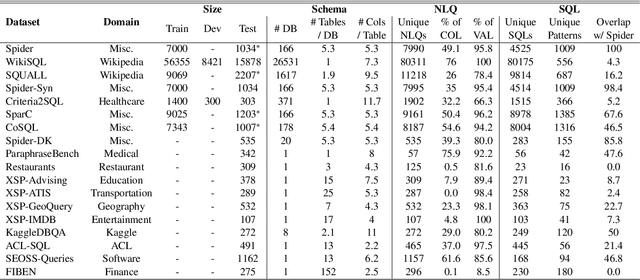
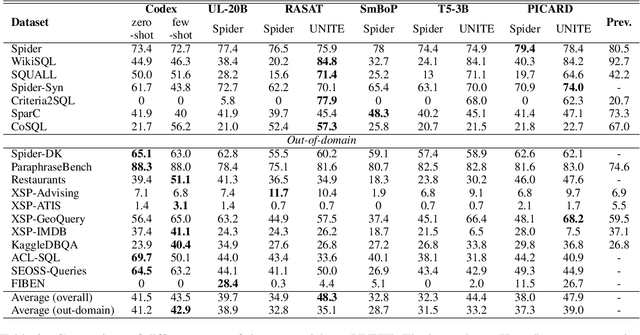
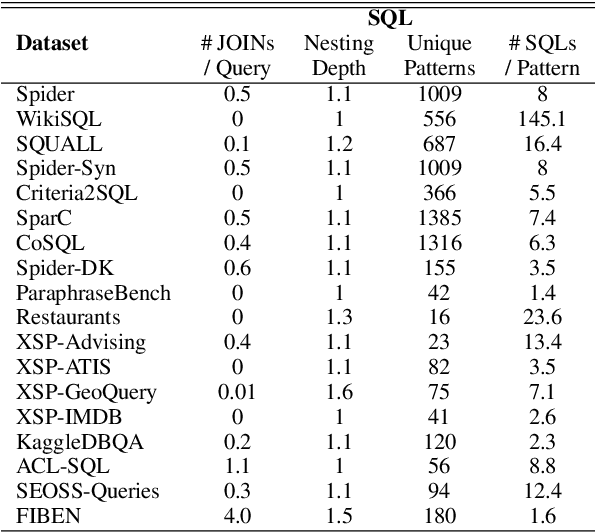
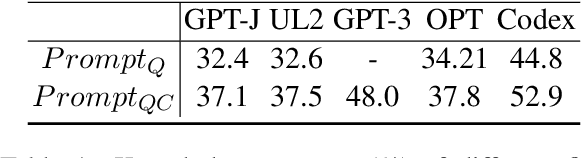
Abstract:A practical text-to-SQL system should generalize well on a wide variety of natural language questions, unseen database schemas, and novel SQL query structures. To comprehensively evaluate text-to-SQL systems, we introduce a \textbf{UNI}fied benchmark for \textbf{T}ext-to-SQL \textbf{E}valuation (UNITE). It is composed of publicly available text-to-SQL datasets, containing natural language questions from more than 12 domains, SQL queries from more than 3.9K patterns, and 29K databases. Compared to the widely used Spider benchmark \cite{yu-etal-2018-spider}, we introduce $\sim$120K additional examples and a threefold increase in SQL patterns, such as comparative and boolean questions. We conduct a systematic study of six state-of-the-art (SOTA) text-to-SQL parsers on our new benchmark and show that: 1) Codex performs surprisingly well on out-of-domain datasets; 2) specially designed decoding methods (e.g. constrained beam search) can improve performance for both in-domain and out-of-domain settings; 3) explicitly modeling the relationship between questions and schemas further improves the Seq2Seq models. More importantly, our benchmark presents key challenges towards compositional generalization and robustness issues -- which these SOTA models cannot address well. \footnote{Our code and data processing script will be available at \url{https://github.com/XXXX.}}
Dr.Spider: A Diagnostic Evaluation Benchmark towards Text-to-SQL Robustness
Jan 21, 2023



Abstract:Neural text-to-SQL models have achieved remarkable performance in translating natural language questions into SQL queries. However, recent studies reveal that text-to-SQL models are vulnerable to task-specific perturbations. Previous curated robustness test sets usually focus on individual phenomena. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive robustness benchmark based on Spider, a cross-domain text-to-SQL benchmark, to diagnose the model robustness. We design 17 perturbations on databases, natural language questions, and SQL queries to measure the robustness from different angles. In order to collect more diversified natural question perturbations, we utilize large pretrained language models (PLMs) to simulate human behaviors in creating natural questions. We conduct a diagnostic study of the state-of-the-art models on the robustness set. Experimental results reveal that even the most robust model suffers from a 14.0% performance drop overall and a 50.7% performance drop on the most challenging perturbation. We also present a breakdown analysis regarding text-to-SQL model designs and provide insights for improving model robustness.
DecAF: Joint Decoding of Answers and Logical Forms for Question Answering over Knowledge Bases
Sep 30, 2022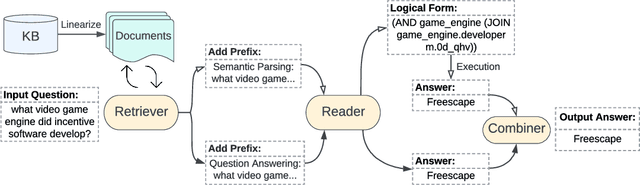



Abstract:Question answering over knowledge bases (KBs) aims to answer natural language questions with factual information such as entities and relations in KBs. Previous methods either generate logical forms that can be executed over KBs to obtain final answers or predict answers directly. Empirical results show that the former often produces more accurate answers, but it suffers from non-execution issues due to potential syntactic and semantic errors in the generated logical forms. In this work, we propose a novel framework DecAF that jointly generates both logical forms and direct answers, and then combines the merits of them to get the final answers. Moreover, different from most of the previous methods, DecAF is based on simple free-text retrieval without relying on any entity linking tools -- this simplification eases its adaptation to different datasets. DecAF achieves new state-of-the-art accuracy on WebQSP, FreebaseQA, and GrailQA benchmarks, while getting competitive results on the ComplexWebQuestions benchmark.
QaNER: Prompting Question Answering Models for Few-shot Named Entity Recognition
Mar 04, 2022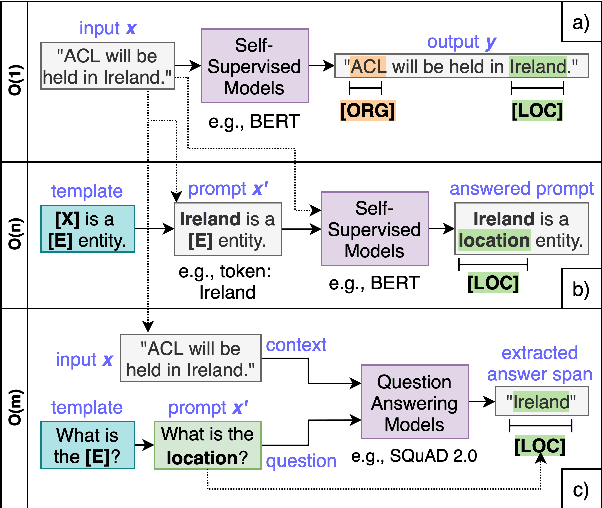
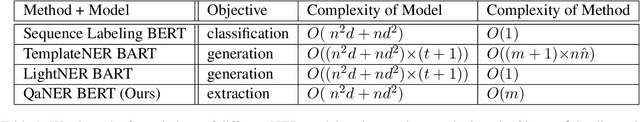
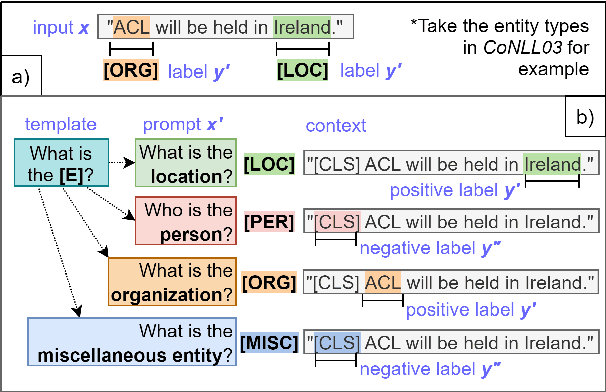
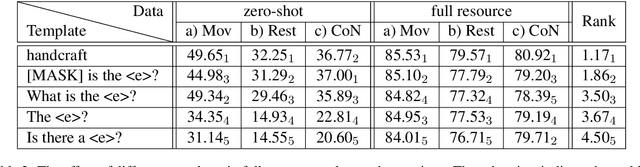
Abstract:Recently, prompt-based learning for pre-trained language models has succeeded in few-shot Named Entity Recognition (NER) by exploiting prompts as task guidance to increase label efficiency. However, previous prompt-based methods for few-shot NER have limitations such as a higher computational complexity, poor zero-shot ability, requiring manual prompt engineering, or lack of prompt robustness. In this work, we address these shortcomings by proposing a new prompt-based learning NER method with Question Answering (QA), called QaNER. Our approach includes 1) a refined strategy for converting NER problems into the QA formulation; 2) NER prompt generation for QA models; 3) prompt-based tuning with QA models on a few annotated NER examples; 4) zero-shot NER by prompting the QA model. Comparing the proposed approach with previous methods, QaNER is faster at inference, insensitive to the prompt quality, and robust to hyper-parameters, as well as demonstrating significantly better low-resource performance and zero-shot capability.
Virtual Augmentation Supported Contrastive Learning of Sentence Representations
Oct 16, 2021



Abstract:Despite profound successes, contrastive representation learning relies on carefully designed data augmentations using domain specific knowledge. This challenge is magnified in natural language processing where no general rules exist for data augmentation due to the discrete nature of natural language. We tackle this challenge by presenting a Virtual augmentation Supported Contrastive Learning of sentence representations (VaSCL). Originating from the interpretation that data augmentation essentially constructs the neighborhoods of each training instance, we in turn utilize the neighborhood to generate effective data augmentations. Leveraging the large training batch size of contrastive learning, we approximate the neighborhood of an instance via its K-nearest in-batch neighbors in the representation space. We then define an instance discrimination task within this neighborhood, and generate the virtual augmentation in an adversarial training manner. We access the performance of VaSCL on a wide range of downstream tasks, and set a new state-of-the-art for unsupervised sentence representation learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge