Alexander Li
UNITE: A Unified Benchmark for Text-to-SQL Evaluation
May 26, 2023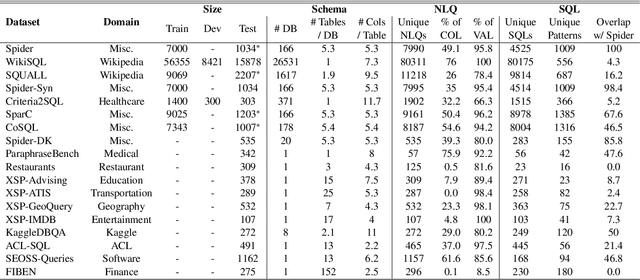
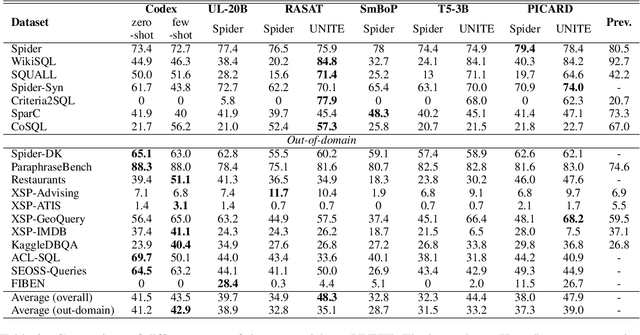
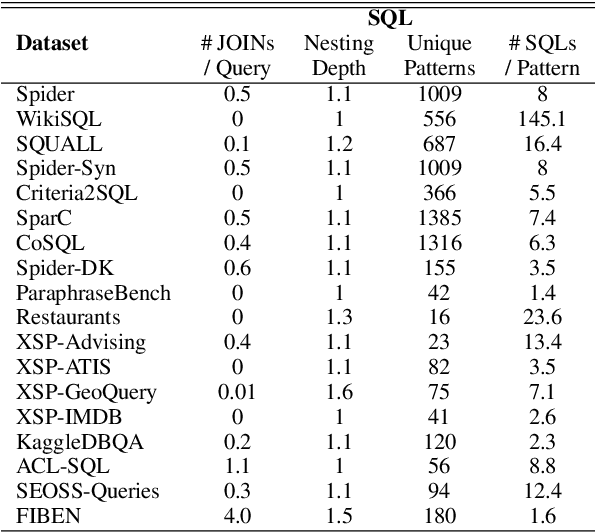
Abstract:A practical text-to-SQL system should generalize well on a wide variety of natural language questions, unseen database schemas, and novel SQL query structures. To comprehensively evaluate text-to-SQL systems, we introduce a \textbf{UNI}fied benchmark for \textbf{T}ext-to-SQL \textbf{E}valuation (UNITE). It is composed of publicly available text-to-SQL datasets, containing natural language questions from more than 12 domains, SQL queries from more than 3.9K patterns, and 29K databases. Compared to the widely used Spider benchmark \cite{yu-etal-2018-spider}, we introduce $\sim$120K additional examples and a threefold increase in SQL patterns, such as comparative and boolean questions. We conduct a systematic study of six state-of-the-art (SOTA) text-to-SQL parsers on our new benchmark and show that: 1) Codex performs surprisingly well on out-of-domain datasets; 2) specially designed decoding methods (e.g. constrained beam search) can improve performance for both in-domain and out-of-domain settings; 3) explicitly modeling the relationship between questions and schemas further improves the Seq2Seq models. More importantly, our benchmark presents key challenges towards compositional generalization and robustness issues -- which these SOTA models cannot address well. \footnote{Our code and data processing script will be available at \url{https://github.com/XXXX.}}
Importance of Synthesizing High-quality Data for Text-to-SQL Parsing
Dec 17, 2022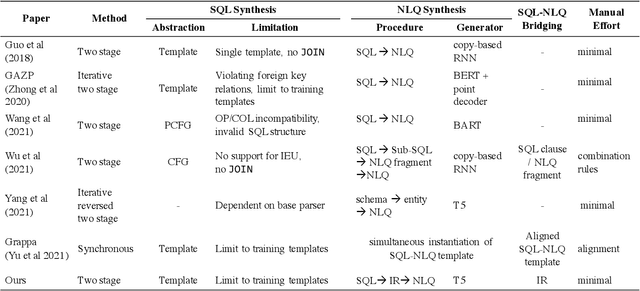
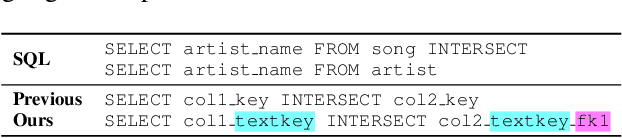
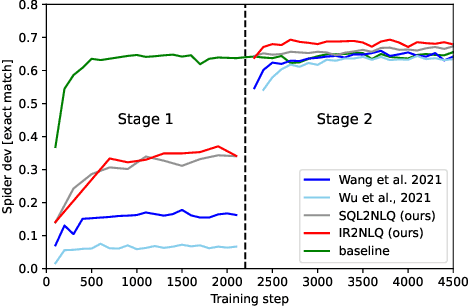

Abstract:Recently, there has been increasing interest in synthesizing data to improve downstream text-to-SQL tasks. In this paper, we first examined the existing synthesized datasets and discovered that state-of-the-art text-to-SQL algorithms did not further improve on popular benchmarks when trained with augmented synthetic data. We observed two shortcomings: illogical synthetic SQL queries from independent column sampling and arbitrary table joins. To address these issues, we propose a novel synthesis framework that incorporates key relationships from schema, imposes strong typing, and conducts schema-distance-weighted column sampling. We also adopt an intermediate representation (IR) for the SQL-to-text task to further improve the quality of the generated natural language questions. When existing powerful semantic parsers are pre-finetuned on our high-quality synthesized data, our experiments show that these models have significant accuracy boosts on popular benchmarks, including new state-of-the-art performance on Spider.
Generative Models for Pose Transfer
Jun 24, 2018



Abstract:We investigate nearest neighbor and generative models for transferring pose between persons. We take in a video of one person performing a sequence of actions and attempt to generate a video of another person performing the same actions. Our generative model (pix2pix) outperforms k-NN at both generating corresponding frames and generalizing outside the demonstrated action set. Our most salient contribution is determining a pipeline (pose detection, face detection, k-NN based pairing) that is effective at perform-ing the desired task. We also detail several iterative improvements and failure modes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge