Azalia Mirhoseini
Intelligence per Watt: Measuring Intelligence Efficiency of Local AI
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Large language model (LLM) queries are predominantly processed by frontier models in centralized cloud infrastructure. Rapidly growing demand strains this paradigm, and cloud providers struggle to scale infrastructure at pace. Two advances enable us to rethink this paradigm: small LMs (<=20B active parameters) now achieve competitive performance to frontier models on many tasks, and local accelerators (e.g., Apple M4 Max) run these models at interactive latencies. This raises the question: can local inference viably redistribute demand from centralized infrastructure? Answering this requires measuring whether local LMs can accurately answer real-world queries and whether they can do so efficiently enough to be practical on power-constrained devices (i.e., laptops). We propose intelligence per watt (IPW), task accuracy divided by unit of power, as a metric for assessing capability and efficiency of local inference across model-accelerator pairs. We conduct a large-scale empirical study across 20+ state-of-the-art local LMs, 8 accelerators, and a representative subset of LLM traffic: 1M real-world single-turn chat and reasoning queries. For each query, we measure accuracy, energy, latency, and power. Our analysis reveals $3$ findings. First, local LMs can accurately answer 88.7% of single-turn chat and reasoning queries with accuracy varying by domain. Second, from 2023-2025, IPW improved 5.3x and local query coverage rose from 23.2% to 71.3%. Third, local accelerators achieve at least 1.4x lower IPW than cloud accelerators running identical models, revealing significant headroom for optimization. These findings demonstrate that local inference can meaningfully redistribute demand from centralized infrastructure, with IPW serving as the critical metric for tracking this transition. We release our IPW profiling harness for systematic intelligence-per-watt benchmarking.
Astra: A Multi-Agent System for GPU Kernel Performance Optimization
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:GPU kernel optimization has long been a central challenge at the intersection of high-performance computing and machine learning. Efficient kernels are crucial for accelerating large language model (LLM) training and serving, yet attaining high performance typically requires extensive manual tuning. Compiler-based systems reduce some of this burden, but still demand substantial manual design and engineering effort. Recently, researchers have explored using LLMs for GPU kernel generation, though prior work has largely focused on translating high-level PyTorch modules into CUDA code. In this work, we introduce Astra, the first LLM-based multi-agent system for GPU kernel optimization. Unlike previous approaches, Astra starts from existing CUDA implementations extracted from SGLang, a widely deployed framework for serving LLMs, rather than treating PyTorch modules as the specification. Within Astra, specialized LLM agents collaborate through iterative code generation, testing, profiling, and planning to produce kernels that are both correct and high-performance. On kernels from SGLang, Astra achieves an average speedup of 1.32x using zero-shot prompting with OpenAI o4-mini. A detailed case study further demonstrates that LLMs can autonomously apply loop transformations, optimize memory access patterns, exploit CUDA intrinsics, and leverage fast math operations to yield substantial performance gains. Our work highlights multi-agent LLM systems as a promising new paradigm for GPU kernel optimization.
Cartridges: Lightweight and general-purpose long context representations via self-study
Jun 06, 2025



Abstract:Large language models are often used to answer queries grounded in large text corpora (e.g. codebases, legal documents, or chat histories) by placing the entire corpus in the context window and leveraging in-context learning (ICL). Although current models support contexts of 100K-1M tokens, this setup is costly to serve because the memory consumption of the KV cache scales with input length. We explore an alternative: training a smaller KV cache offline on each corpus. At inference time, we load this trained KV cache, which we call a Cartridge, and decode a response. Critically, the cost of training a Cartridge can be amortized across all the queries referencing the same corpus. However, we find that the naive approach of training the Cartridge with next-token prediction on the corpus is not competitive with ICL. Instead, we propose self-study, a training recipe in which we generate synthetic conversations about the corpus and train the Cartridge with a context-distillation objective. We find that Cartridges trained with self-study replicate the functionality of ICL, while being significantly cheaper to serve. On challenging long-context benchmarks, Cartridges trained with self-study match ICL performance while using 38.6x less memory and enabling 26.4x higher throughput. Self-study also extends the model's effective context length (e.g. from 128k to 484k tokens on MTOB) and surprisingly, leads to Cartridges that can be composed at inference time without retraining.
Exploring Diffusion Transformer Designs via Grafting
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Designing model architectures requires decisions such as selecting operators (e.g., attention, convolution) and configurations (e.g., depth, width). However, evaluating the impact of these decisions on model quality requires costly pretraining, limiting architectural investigation. Inspired by how new software is built on existing code, we ask: can new architecture designs be studied using pretrained models? To this end, we present grafting, a simple approach for editing pretrained diffusion transformers (DiTs) to materialize new architectures under small compute budgets. Informed by our analysis of activation behavior and attention locality, we construct a testbed based on the DiT-XL/2 design to study the impact of grafting on model quality. Using this testbed, we develop a family of hybrid designs via grafting: replacing softmax attention with gated convolution, local attention, and linear attention, and replacing MLPs with variable expansion ratio and convolutional variants. Notably, many hybrid designs achieve good quality (FID: 2.38-2.64 vs. 2.27 for DiT-XL/2) using <2% pretraining compute. We then graft a text-to-image model (PixArt-Sigma), achieving a 1.43x speedup with less than a 2% drop in GenEval score. Finally, we present a case study that restructures DiT-XL/2 by converting every pair of sequential transformer blocks into parallel blocks via grafting. This reduces model depth by 2x and yields better quality (FID: 2.77) than other models of comparable depth. Together, we show that new diffusion model designs can be explored by grafting pretrained DiTs, with edits ranging from operator replacement to architecture restructuring. Code and grafted models: https://grafting.stanford.edu
SPRINT: Enabling Interleaved Planning and Parallelized Execution in Reasoning Models
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) excel at complex reasoning tasks but typically generate lengthy sequential chains-of-thought, resulting in long inference times before arriving at the final answer. To address this challenge, we introduce SPRINT, a novel post-training and inference-time framework designed to enable LRMs to dynamically identify and exploit opportunities for parallelization during their reasoning process. SPRINT incorporates an innovative data curation pipeline that reorganizes natural language reasoning trajectories into structured rounds of long-horizon planning and parallel execution. By fine-tuning LRMs on a small amount of such curated data, the models learn to dynamically identify independent subtasks within extended reasoning processes and effectively execute them in parallel. Through extensive evaluations, we show that the models fine-tuned with the SPRINT framework match the performance of reasoning models on complex domains such as mathematics while generating up to ~39% fewer sequential tokens on problems requiring more than 8000 output tokens. Finally, we observe consistent results transferred to two out-of-distribution tasks of GPQA and Countdown with up to 45% and 65% reduction in average sequential tokens for longer reasoning trajectories, while achieving the performance of the fine-tuned reasoning model.
Think, Prune, Train, Improve: Scaling Reasoning without Scaling Models
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in programming and mathematical reasoning tasks, but are constrained by limited high-quality training data. Synthetic data can be leveraged to enhance fine-tuning outcomes, but several factors influence this process, including model size, synthetic data volume, pruning strategy, and number of fine-tuning rounds. We explore these axes and investigate which conditions enable model self-improvement. We introduce the Think, Prune, Train process, a scalable framework that iteratively fine-tunes models on their own reasoning traces, using ground-truth pruning to ensure high-quality training data. This approach yields improved performance: on GSM8K, Gemma2-2B achieves a Pass@1 of 57.6% (from 41.9%), Gemma2-9B reaches 82%, matching LLaMA-3.1-70B, and LLaMA-3.1-70B attains 91%, even surpassing GPT-4o, demonstrating the effectiveness of self-generated reasoning and systematic data selection for improving LLM capabilities.
Synthetic Data Generation & Multi-Step RL for Reasoning & Tool Use
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning has been shown to improve the performance of large language models. However, traditional approaches like RLHF or RLAIF treat the problem as single-step. As focus shifts toward more complex reasoning and agentic tasks, language models must take multiple steps of text generation, reasoning and environment interaction before generating a solution. We propose a synthetic data generation and RL methodology targeting multi-step optimization scenarios. This approach, called Step-Wise Reinforcement Learning (SWiRL), iteratively generates multi-step reasoning and tool use data, and then learns from that data. It employs a simple step-wise decomposition that breaks each multi-step trajectory into multiple sub-trajectories corresponding to each action by the original model. It then applies synthetic data filtering and RL optimization on these sub-trajectories. We evaluated SWiRL on a number of multi-step tool use, question answering, and mathematical reasoning tasks. Our experiments show that SWiRL outperforms baseline approaches by 21.5%, 12.3%, 14.8%, 11.1%, and 15.3% in relative accuracy on GSM8K, HotPotQA, CofCA, MuSiQue, and BeerQA, respectively. Excitingly, the approach exhibits generalization across tasks: for example, training only on HotPotQA (text question-answering) improves zero-shot performance on GSM8K (a math dataset) by a relative 16.9%.
Reasoning-SQL: Reinforcement Learning with SQL Tailored Partial Rewards for Reasoning-Enhanced Text-to-SQL
Apr 01, 2025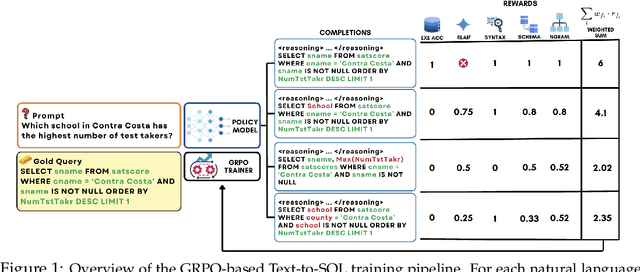
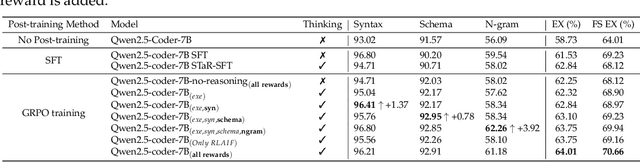
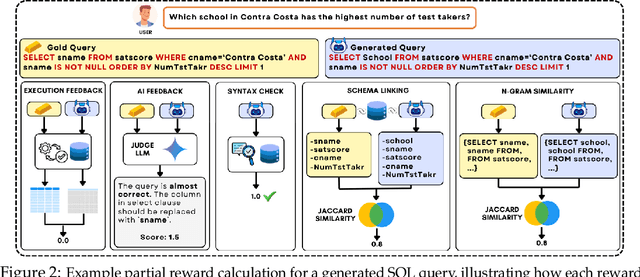
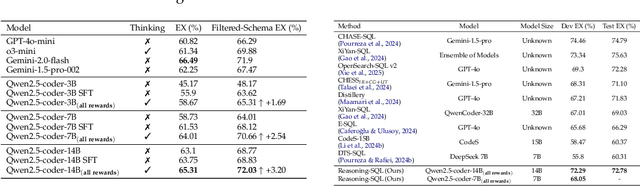
Abstract:Text-to-SQL is a challenging task involving multiple reasoning-intensive subtasks, including natural language understanding, database schema comprehension, and precise SQL query formulation. Existing approaches often rely on handcrafted reasoning paths with inductive biases that can limit their overall effectiveness. Motivated by the recent success of reasoning-enhanced models such as DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI o1, which effectively leverage reward-driven self-exploration to enhance reasoning capabilities and generalization, we propose a novel set of partial rewards tailored specifically for the Text-to-SQL task. Our reward set includes schema-linking, AI feedback, n-gram similarity, and syntax check, explicitly designed to address the reward sparsity issue prevalent in reinforcement learning (RL). Leveraging group relative policy optimization (GRPO), our approach explicitly encourages large language models (LLMs) to develop intrinsic reasoning skills necessary for accurate SQL query generation. With models of different sizes, we demonstrate that RL-only training with our proposed rewards consistently achieves higher accuracy and superior generalization compared to supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Remarkably, our RL-trained 14B-parameter model significantly outperforms larger proprietary models, e.g. o3-mini by 4% and Gemini-1.5-Pro-002 by 3% on the BIRD benchmark. These highlight the efficacy of our proposed RL-training framework with partial rewards for enhancing both accuracy and reasoning capabilities in Text-to-SQL tasks.
How Do Large Language Monkeys Get Their Power (Laws)?
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Recent research across mathematical problem solving, proof assistant programming and multimodal jailbreaking documents a striking finding: when (multimodal) language model tackle a suite of tasks with multiple attempts per task -- succeeding if any attempt is correct -- then the negative log of the average success rate scales a power law in the number of attempts. In this work, we identify an apparent puzzle: a simple mathematical calculation predicts that on each problem, the failure rate should fall exponentially with the number of attempts. We confirm this prediction empirically, raising a question: from where does aggregate polynomial scaling emerge? We then answer this question by demonstrating per-problem exponential scaling can be made consistent with aggregate polynomial scaling if the distribution of single-attempt success probabilities is heavy tailed such that a small fraction of tasks with extremely low success probabilities collectively warp the aggregate success trend into a power law - even as each problem scales exponentially on its own. We further demonstrate that this distributional perspective explains previously observed deviations from power law scaling, and provides a simple method for forecasting the power law exponent with an order of magnitude lower relative error, or equivalently, ${\sim}2-4$ orders of magnitude less inference compute. Overall, our work contributes to a better understanding of how neural language model performance improves with scaling inference compute and the development of scaling-predictable evaluations of (multimodal) language models.
CodeMonkeys: Scaling Test-Time Compute for Software Engineering
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Scaling test-time compute is a promising axis for improving LLM capabilities. However, test-time compute can be scaled in a variety of ways, and effectively combining different approaches remains an active area of research. Here, we explore this problem in the context of solving real-world GitHub issues from the SWE-bench dataset. Our system, named CodeMonkeys, allows models to iteratively edit a codebase by jointly generating and running a testing script alongside their draft edit. We sample many of these multi-turn trajectories for every issue to generate a collection of candidate edits. This approach lets us scale "serial" test-time compute by increasing the number of iterations per trajectory and "parallel" test-time compute by increasing the number of trajectories per problem. With parallel scaling, we can amortize up-front costs across multiple downstream samples, allowing us to identify relevant codebase context using the simple method of letting an LLM read every file. In order to select between candidate edits, we combine voting using model-generated tests with a final multi-turn trajectory dedicated to selection. Overall, CodeMonkeys resolves 57.4% of issues from SWE-bench Verified using a budget of approximately 2300 USD. Our selection method can also be used to combine candidates from different sources. Selecting over an ensemble of edits from existing top SWE-bench Verified submissions obtains a score of 66.2% and outperforms the best member of the ensemble on its own. We fully release our code and data at https://scalingintelligence.stanford.edu/pubs/codemonkeys.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge