Bradley Brown
CodeMonkeys: Scaling Test-Time Compute for Software Engineering
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Scaling test-time compute is a promising axis for improving LLM capabilities. However, test-time compute can be scaled in a variety of ways, and effectively combining different approaches remains an active area of research. Here, we explore this problem in the context of solving real-world GitHub issues from the SWE-bench dataset. Our system, named CodeMonkeys, allows models to iteratively edit a codebase by jointly generating and running a testing script alongside their draft edit. We sample many of these multi-turn trajectories for every issue to generate a collection of candidate edits. This approach lets us scale "serial" test-time compute by increasing the number of iterations per trajectory and "parallel" test-time compute by increasing the number of trajectories per problem. With parallel scaling, we can amortize up-front costs across multiple downstream samples, allowing us to identify relevant codebase context using the simple method of letting an LLM read every file. In order to select between candidate edits, we combine voting using model-generated tests with a final multi-turn trajectory dedicated to selection. Overall, CodeMonkeys resolves 57.4% of issues from SWE-bench Verified using a budget of approximately 2300 USD. Our selection method can also be used to combine candidates from different sources. Selecting over an ensemble of edits from existing top SWE-bench Verified submissions obtains a score of 66.2% and outperforms the best member of the ensemble on its own. We fully release our code and data at https://scalingintelligence.stanford.edu/pubs/codemonkeys.
Large Language Monkeys: Scaling Inference Compute with Repeated Sampling
Jul 31, 2024



Abstract:Scaling the amount of compute used to train language models has dramatically improved their capabilities. However, when it comes to inference, we often limit the amount of compute to only one attempt per problem. Here, we explore inference compute as another axis for scaling by increasing the number of generated samples. Across multiple tasks and models, we observe that coverage - the fraction of problems solved by any attempt - scales with the number of samples over four orders of magnitude. In domains like coding and formal proofs, where all answers can be automatically verified, these increases in coverage directly translate into improved performance. When we apply repeated sampling to SWE-bench Lite, the fraction of issues solved with DeepSeek-V2-Coder-Instruct increases from 15.9% with one sample to 56% with 250 samples, outperforming the single-attempt state-of-the-art of 43% which uses more capable frontier models. Moreover, using current API pricing, amplifying the cheaper DeepSeek model with five samples is more cost-effective and solves more issues than paying a premium for one sample from GPT-4o or Claude 3.5 Sonnet. Interestingly, the relationship between coverage and the number of samples is often log-linear and can be modelled with an exponentiated power law, suggesting the existence of inference-time scaling laws. Finally, we find that identifying correct samples out of many generations remains an important direction for future research in domains without automatic verifiers. When solving math word problems from GSM8K and MATH, coverage with Llama-3 models grows to over 95% with 10,000 samples. However, common methods to pick correct solutions from a sample collection, such as majority voting or reward models, plateau beyond several hundred samples and fail to fully scale with the sample budget.
Hydragen: High-Throughput LLM Inference with Shared Prefixes
Feb 07, 2024
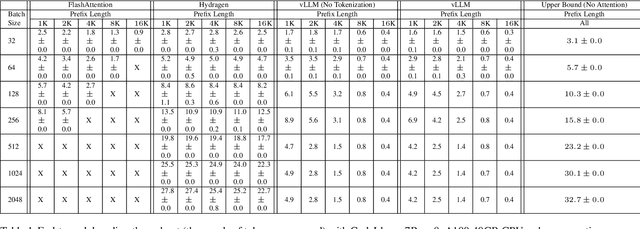
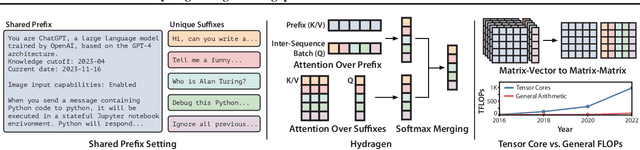

Abstract:Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) are now deployed to hundreds of millions of users. LLM inference is commonly performed on batches of sequences that share a prefix, such as few-shot examples or a chatbot system prompt. Decoding in this large-batch setting can be bottlenecked by the attention operation, which reads large key-value (KV) caches from memory and computes inefficient matrix-vector products for every sequence in the batch. In this work, we introduce Hydragen, a hardware-aware exact implementation of attention with shared prefixes. Hydragen computes attention over the shared prefix and unique suffixes separately. This decomposition enables efficient prefix attention by batching queries together across sequences, reducing redundant memory reads and enabling the use of hardware-friendly matrix multiplications. Our method can improve end-to-end LLM throughput by up to 32x against competitive baselines, with speedup growing with the batch size and shared prefix length. Hydragen also enables the use of very long shared contexts: with a high batch size, increasing the prefix length from 1K to 16K tokens decreases Hydragen throughput by less than 15%, while the throughput of baselines drops by over 90%. Hydragen generalizes beyond simple prefix-suffix decomposition and can be applied to tree-based prompt sharing patterns, allowing us to further reduce inference time on competitive programming problems by 55%.
NeuralField-LDM: Scene Generation with Hierarchical Latent Diffusion Models
Apr 19, 2023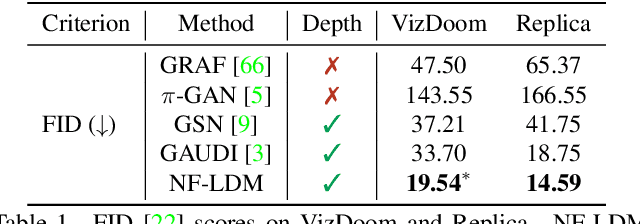
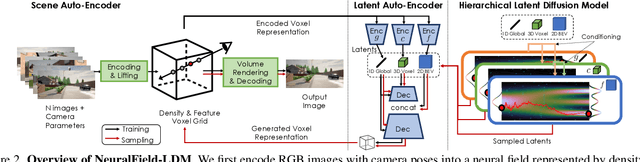
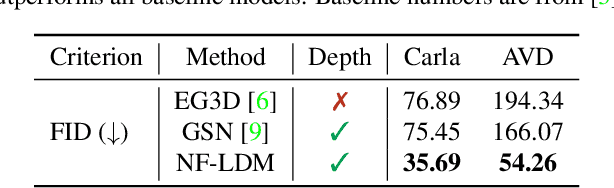
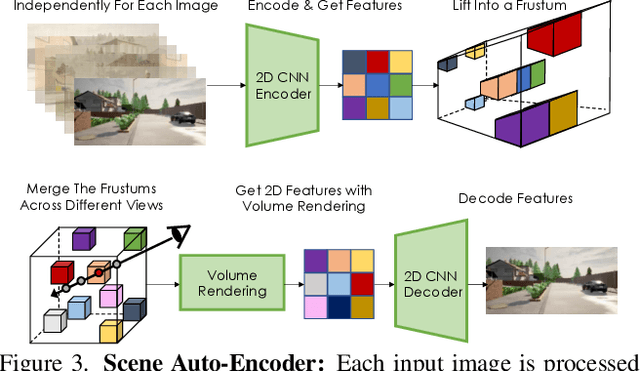
Abstract:Automatically generating high-quality real world 3D scenes is of enormous interest for applications such as virtual reality and robotics simulation. Towards this goal, we introduce NeuralField-LDM, a generative model capable of synthesizing complex 3D environments. We leverage Latent Diffusion Models that have been successfully utilized for efficient high-quality 2D content creation. We first train a scene auto-encoder to express a set of image and pose pairs as a neural field, represented as density and feature voxel grids that can be projected to produce novel views of the scene. To further compress this representation, we train a latent-autoencoder that maps the voxel grids to a set of latent representations. A hierarchical diffusion model is then fit to the latents to complete the scene generation pipeline. We achieve a substantial improvement over existing state-of-the-art scene generation models. Additionally, we show how NeuralField-LDM can be used for a variety of 3D content creation applications, including conditional scene generation, scene inpainting and scene style manipulation.
Towards Rotation Invariance in Object Detection
Oct 01, 2021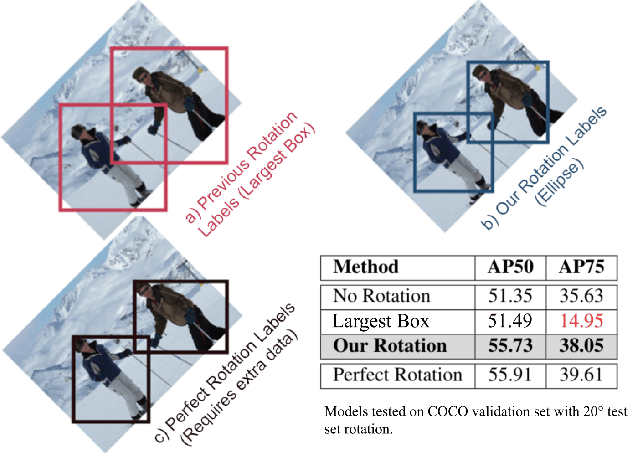
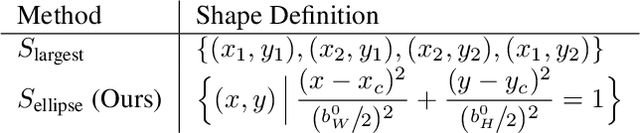
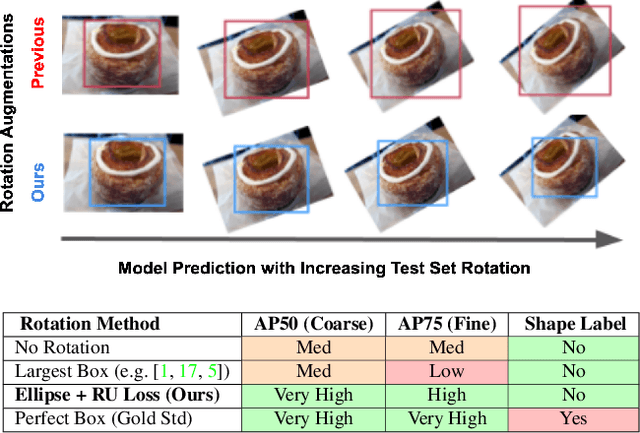
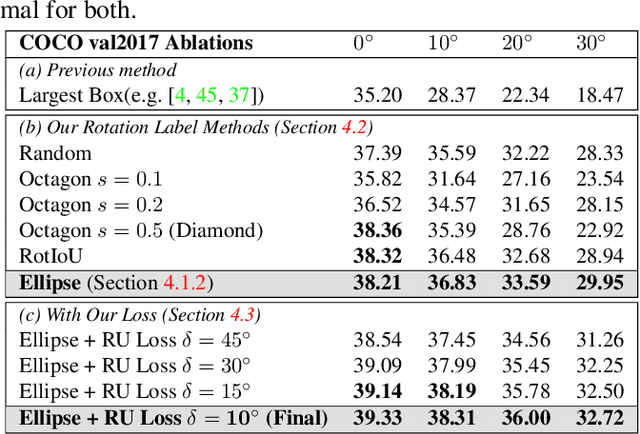
Abstract:Rotation augmentations generally improve a model's invariance/equivariance to rotation - except in object detection. In object detection the shape is not known, therefore rotation creates a label ambiguity. We show that the de-facto method for bounding box label rotation, the Largest Box Method, creates very large labels, leading to poor performance and in many cases worse performance than using no rotation at all. We propose a new method of rotation augmentation that can be implemented in a few lines of code. First, we create a differentiable approximation of label accuracy and show that axis-aligning the bounding box around an ellipse is optimal. We then introduce Rotation Uncertainty (RU) Loss, allowing the model to adapt to the uncertainty of the labels. On five different datasets (including COCO, PascalVOC, and Transparent Object Bin Picking), this approach improves the rotational invariance of both one-stage and two-stage architectures when measured with AP, AP50, and AP75. The code is available at https://github.com/akasha-imaging/ICCV2021.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge