Aditya Sharma
MedHELM: Holistic Evaluation of Large Language Models for Medical Tasks
May 26, 2025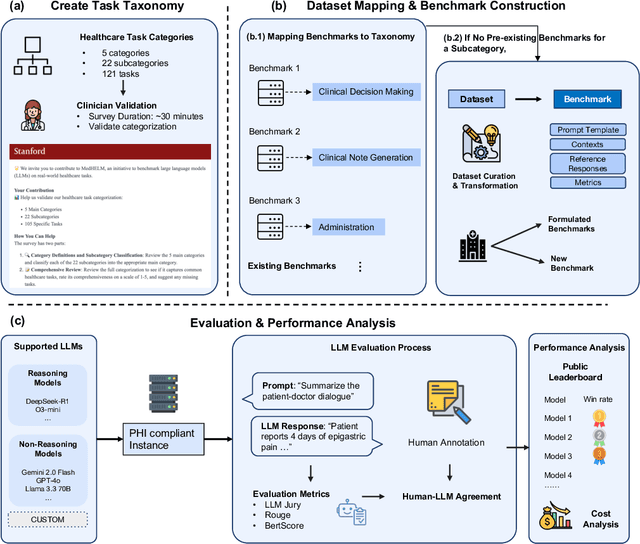
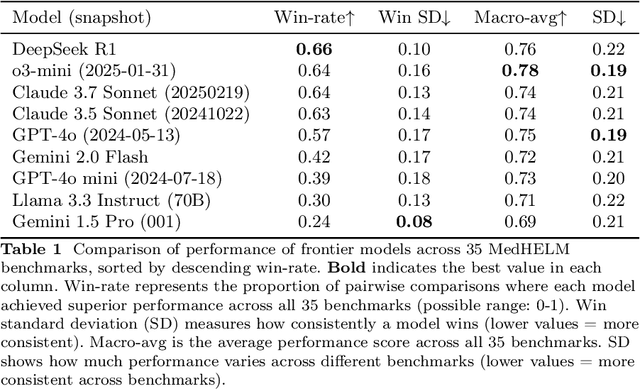
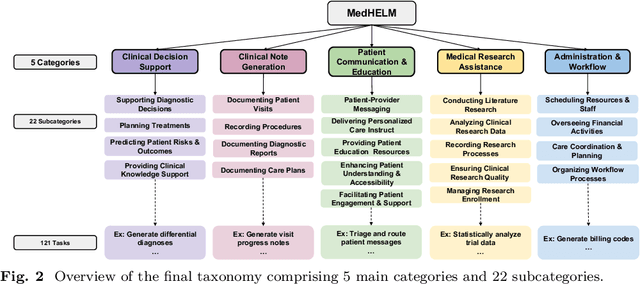
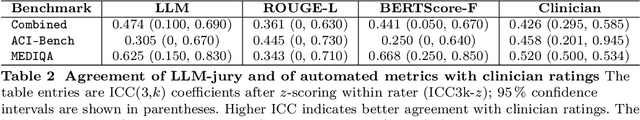
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) achieve near-perfect scores on medical licensing exams, these evaluations inadequately reflect the complexity and diversity of real-world clinical practice. We introduce MedHELM, an extensible evaluation framework for assessing LLM performance for medical tasks with three key contributions. First, a clinician-validated taxonomy spanning 5 categories, 22 subcategories, and 121 tasks developed with 29 clinicians. Second, a comprehensive benchmark suite comprising 35 benchmarks (17 existing, 18 newly formulated) providing complete coverage of all categories and subcategories in the taxonomy. Third, a systematic comparison of LLMs with improved evaluation methods (using an LLM-jury) and a cost-performance analysis. Evaluation of 9 frontier LLMs, using the 35 benchmarks, revealed significant performance variation. Advanced reasoning models (DeepSeek R1: 66% win-rate; o3-mini: 64% win-rate) demonstrated superior performance, though Claude 3.5 Sonnet achieved comparable results at 40% lower estimated computational cost. On a normalized accuracy scale (0-1), most models performed strongly in Clinical Note Generation (0.73-0.85) and Patient Communication & Education (0.78-0.83), moderately in Medical Research Assistance (0.65-0.75), and generally lower in Clinical Decision Support (0.56-0.72) and Administration & Workflow (0.53-0.63). Our LLM-jury evaluation method achieved good agreement with clinician ratings (ICC = 0.47), surpassing both average clinician-clinician agreement (ICC = 0.43) and automated baselines including ROUGE-L (0.36) and BERTScore-F1 (0.44). Claude 3.5 Sonnet achieved comparable performance to top models at lower estimated cost. These findings highlight the importance of real-world, task-specific evaluation for medical use of LLMs and provides an open source framework to enable this.
Reducing Hallucinations in Language Model-based SPARQL Query Generation Using Post-Generation Memory Retrieval
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:The ability to generate SPARQL queries from natural language questions is crucial for ensuring efficient and accurate retrieval of structured data from knowledge graphs (KG). While large language models (LLMs) have been widely adopted for SPARQL query generation, they are often susceptible to hallucinations and out-of-distribution errors when producing KG elements like Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) based on internal parametric knowledge. This often results in content that appears plausible but is factually incorrect, posing significant challenges for their use in real-world information retrieval (IR) applications. This has led to increased research aimed at detecting and mitigating such errors. In this paper, we introduce PGMR (Post-Generation Memory Retrieval), a modular framework that incorporates a non-parametric memory module to retrieve KG elements and enhance LLM-based SPARQL query generation. Our experimental results indicate that PGMR consistently delivers strong performance across diverse datasets, data distributions, and LLMs. Notably, PGMR significantly mitigates URI hallucinations, nearly eliminating the problem in several scenarios.
GeoCoder: Solving Geometry Problems by Generating Modular Code through Vision-Language Models
Oct 17, 2024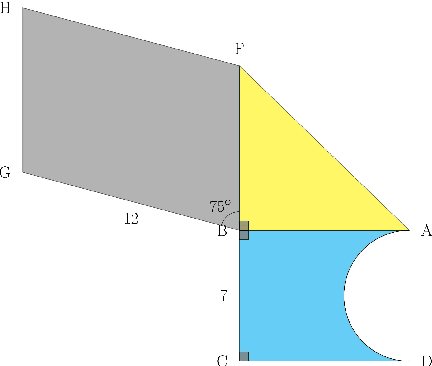

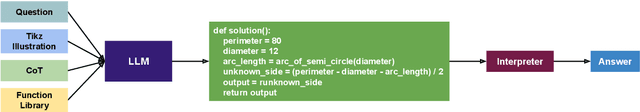

Abstract:Geometry problem-solving demands advanced reasoning abilities to process multimodal inputs and employ mathematical knowledge effectively. Vision-language models (VLMs) have made significant progress in various multimodal tasks. Yet, they still struggle with geometry problems and are significantly limited by their inability to perform mathematical operations not seen during pre-training, such as calculating the cosine of an arbitrary angle, and by difficulties in correctly applying relevant geometry formulas. To overcome these challenges, we present GeoCoder, which leverages modular code-finetuning to generate and execute code using a predefined geometry function library. By executing the code, we achieve accurate and deterministic calculations, contrasting the stochastic nature of autoregressive token prediction, while the function library minimizes errors in formula usage. We also propose a multimodal retrieval-augmented variant of GeoCoder, named RAG-GeoCoder, which incorporates a non-parametric memory module for retrieving functions from the geometry library, thereby reducing reliance on parametric memory. Our modular code-finetuning approach enhances the geometric reasoning capabilities of VLMs, yielding an average improvement of over 16% across various question complexities on the GeomVerse dataset compared to other finetuning methods.
Losing Visual Needles in Image Haystacks: Vision Language Models are Easily Distracted in Short and Long Contexts
Jun 24, 2024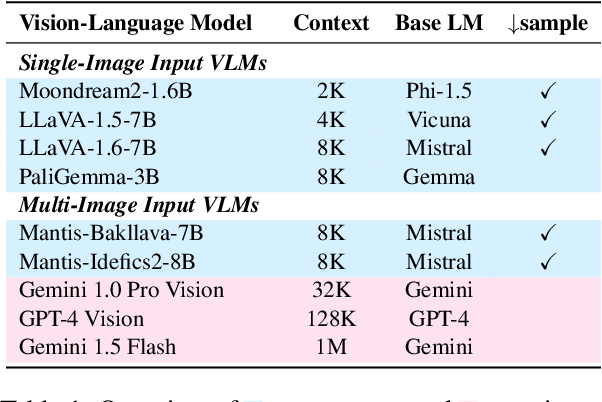

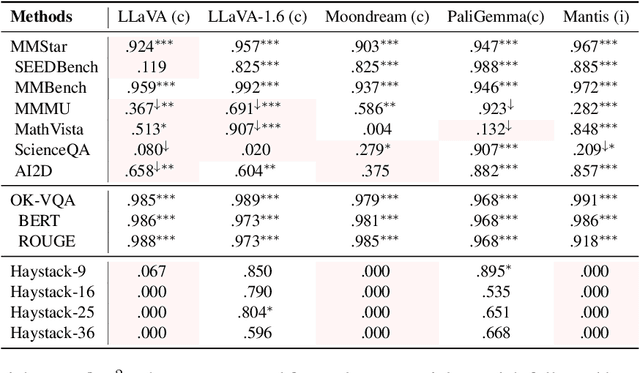
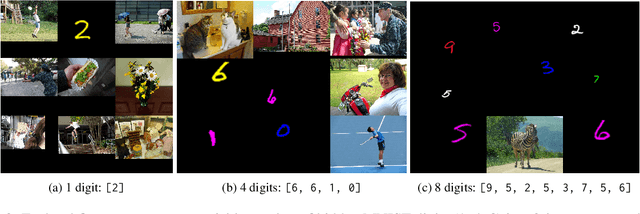
Abstract:We present LoCoVQA, a dynamic benchmark generator for evaluating long-context extractive reasoning in vision language models (VLMs). LoCoVQA augments test examples for mathematical reasoning, VQA, and character recognition tasks with increasingly long visual contexts composed of both in-distribution and out-of-distribution distractor images. Across these tasks, a diverse set of VLMs rapidly lose performance as the visual context length grows, often exhibiting a striking exponential decay trend. This test assesses how well VLMs can ignore irrelevant information when answering queries -- a task that is quite easy for language models (LMs) in the text domain -- demonstrating that current state-of-the-art VLMs lack this essential capability for many long-context applications.
Bi-level Trajectory Optimization on Uneven Terrains with Differentiable Wheel-Terrain Interaction Model
Apr 11, 2024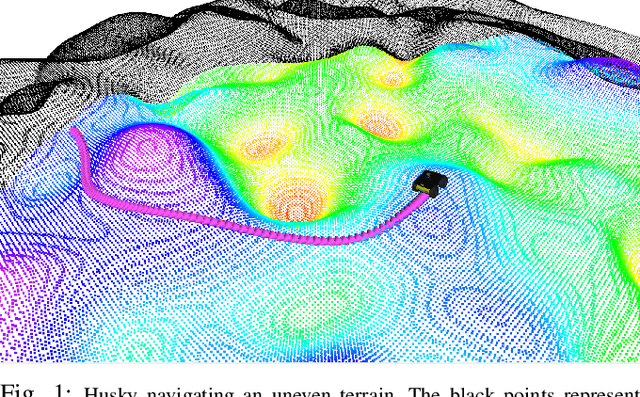
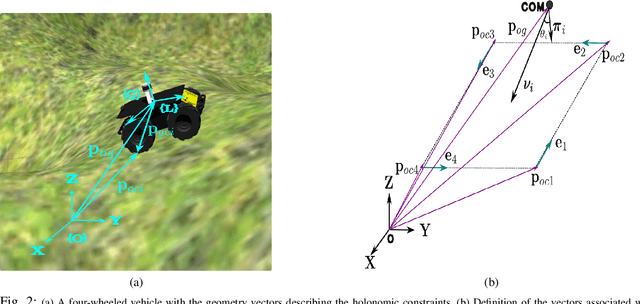
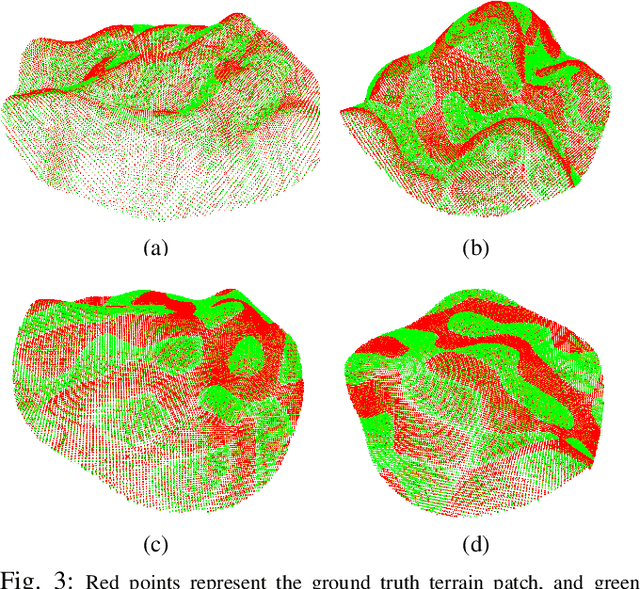
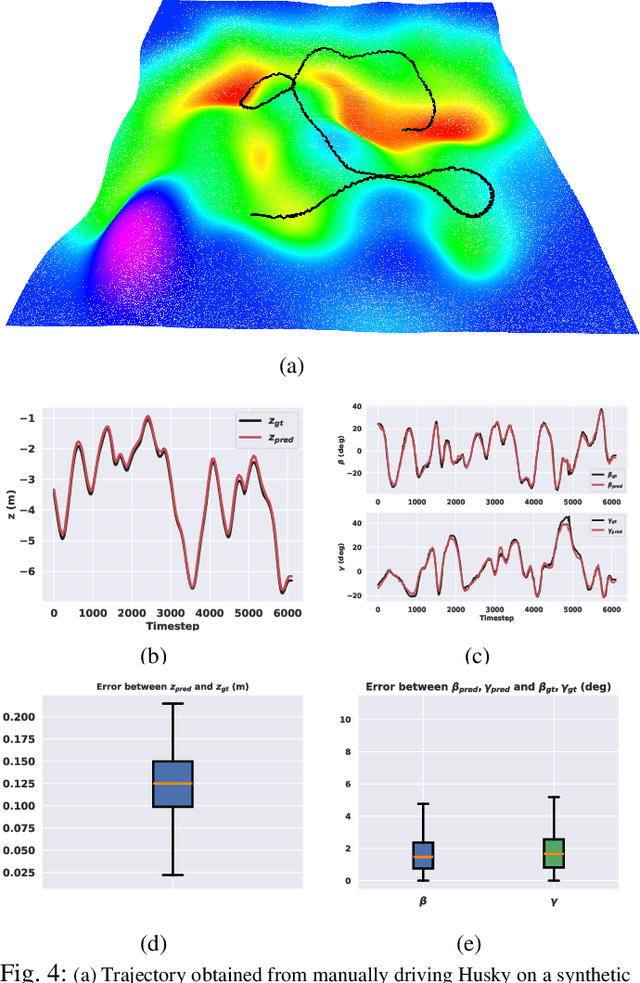
Abstract:Navigation of wheeled vehicles on uneven terrain necessitates going beyond the 2D approaches for trajectory planning. Specifically, it is essential to incorporate the full 6dof variation of vehicle pose and its associated stability cost in the planning process. To this end, most recent works aim to learn a neural network model to predict the vehicle evolution. However, such approaches are data-intensive and fraught with generalization issues. In this paper, we present a purely model-based approach that just requires the digital elevation information of the terrain. Specifically, we express the wheel-terrain interaction and 6dof pose prediction as a non-linear least squares (NLS) problem. As a result, trajectory planning can be viewed as a bi-level optimization. The inner optimization layer predicts the pose on the terrain along a given trajectory, while the outer layer deforms the trajectory itself to reduce the stability and kinematic costs of the pose. We improve the state-of-the-art in the following respects. First, we show that our NLS based pose prediction closely matches the output from a high-fidelity physics engine. This result coupled with the fact that we can query gradients of the NLS solver, makes our pose predictor, a differentiable wheel-terrain interaction model. We further leverage this differentiability to efficiently solve the proposed bi-level trajectory optimization problem. Finally, we perform extensive experiments, and comparison with a baseline to showcase the effectiveness of our approach in obtaining smooth, stable trajectories.
Who Evaluates the Evaluations? Objectively Scoring Text-to-Image Prompt Coherence Metrics with T2IScoreScore (TS2)
Apr 05, 2024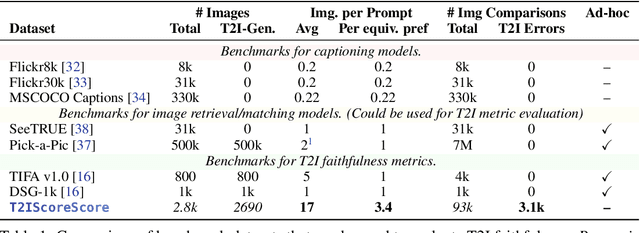
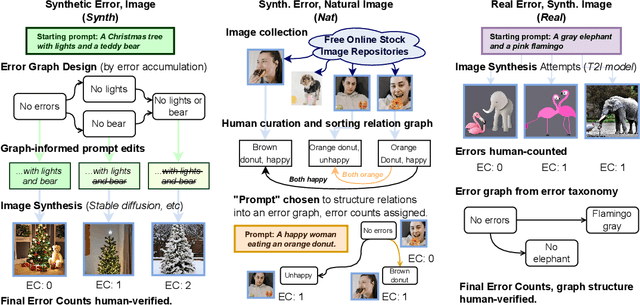
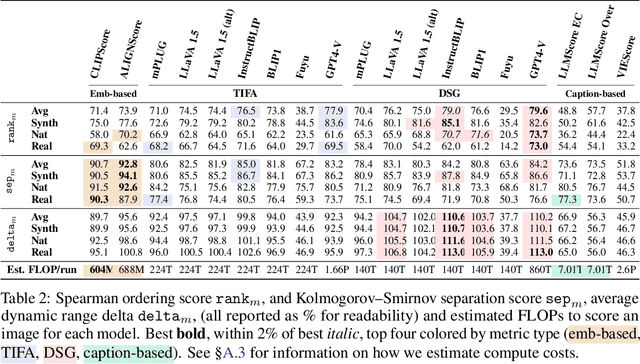
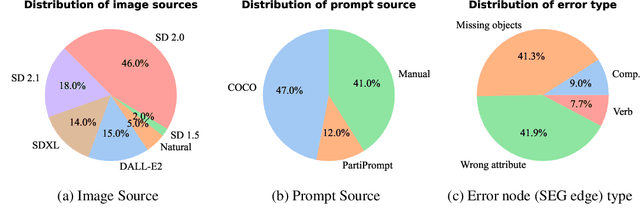
Abstract:With advances in the quality of text-to-image (T2I) models has come interest in benchmarking their prompt faithfulness-the semantic coherence of generated images to the prompts they were conditioned on. A variety of T2I faithfulness metrics have been proposed, leveraging advances in cross-modal embeddings and vision-language models (VLMs). However, these metrics are not rigorously compared and benchmarked, instead presented against few weak baselines by correlation to human Likert scores over a set of easy-to-discriminate images. We introduce T2IScoreScore (TS2), a curated set of semantic error graphs containing a prompt and a set increasingly erroneous images. These allow us to rigorously judge whether a given prompt faithfulness metric can correctly order images with respect to their objective error count and significantly discriminate between different error nodes, using meta-metric scores derived from established statistical tests. Surprisingly, we find that the state-of-the-art VLM-based metrics (e.g., TIFA, DSG, LLMScore, VIEScore) we tested fail to significantly outperform simple feature-based metrics like CLIPScore, particularly on a hard subset of naturally-occurring T2I model errors. TS2 will enable the development of better T2I prompt faithfulness metrics through more rigorous comparison of their conformity to expected orderings and separations under objective criteria.
Standing on FURM ground -- A framework for evaluating Fair, Useful, and Reliable AI Models in healthcare systems
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:The impact of using artificial intelligence (AI) to guide patient care or operational processes is an interplay of the AI model's output, the decision-making protocol based on that output, and the capacity of the stakeholders involved to take the necessary subsequent action. Estimating the effects of this interplay before deployment, and studying it in real time afterwards, are essential to bridge the chasm between AI model development and achievable benefit. To accomplish this, the Data Science team at Stanford Health Care has developed a Testing and Evaluation (T&E) mechanism to identify fair, useful and reliable AI models (FURM) by conducting an ethical review to identify potential value mismatches, simulations to estimate usefulness, financial projections to assess sustainability, as well as analyses to determine IT feasibility, design a deployment strategy, and recommend a prospective monitoring and evaluation plan. We report on FURM assessments done to evaluate six AI guided solutions for potential adoption, spanning clinical and operational settings, each with the potential to impact from several dozen to tens of thousands of patients each year. We describe the assessment process, summarize the six assessments, and share our framework to enable others to conduct similar assessments. Of the six solutions we assessed, two have moved into a planning and implementation phase. Our novel contributions - usefulness estimates by simulation, financial projections to quantify sustainability, and a process to do ethical assessments - as well as their underlying methods and open source tools, are available for other healthcare systems to conduct actionable evaluations of candidate AI solutions.
ATPPNet: Attention based Temporal Point cloud Prediction Network
Jan 30, 2024Abstract:Point cloud prediction is an important yet challenging task in the field of autonomous driving. The goal is to predict future point cloud sequences that maintain object structures while accurately representing their temporal motion. These predicted point clouds help in other subsequent tasks like object trajectory estimation for collision avoidance or estimating locations with the least odometry drift. In this work, we present ATPPNet, a novel architecture that predicts future point cloud sequences given a sequence of previous time step point clouds obtained with LiDAR sensor. ATPPNet leverages Conv-LSTM along with channel-wise and spatial attention dually complemented by a 3D-CNN branch for extracting an enhanced spatio-temporal context to recover high quality fidel predictions of future point clouds. We conduct extensive experiments on publicly available datasets and report impressive performance outperforming the existing methods. We also conduct a thorough ablative study of the proposed architecture and provide an application study that highlights the potential of our model for tasks like odometry estimation.
OCTO+: A Suite for Automatic Open-Vocabulary Object Placement in Mixed Reality
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:One key challenge in Augmented Reality is the placement of virtual content in natural locations. Most existing automated techniques can only work with a closed-vocabulary, fixed set of objects. In this paper, we introduce and evaluate several methods for automatic object placement using recent advances in open-vocabulary vision-language models. Through a multifaceted evaluation, we identify a new state-of-the-art method, OCTO+. We also introduce a benchmark for automatically evaluating the placement of virtual objects in augmented reality, alleviating the need for costly user studies. Through this, in addition to human evaluations, we find that OCTO+ places objects in a valid region over 70% of the time, outperforming other methods on a range of metrics.
OCTOPUS: Open-vocabulary Content Tracking and Object Placement Using Semantic Understanding in Mixed Reality
Dec 20, 2023

Abstract:One key challenge in augmented reality is the placement of virtual content in natural locations. Existing automated techniques are only able to work with a closed-vocabulary, fixed set of objects. In this paper, we introduce a new open-vocabulary method for object placement. Our eight-stage pipeline leverages recent advances in segmentation models, vision-language models, and LLMs to place any virtual object in any AR camera frame or scene. In a preliminary user study, we show that our method performs at least as well as human experts 57% of the time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge