Debadutta Dash
Towards Fine-Grained Video Question Answering
Mar 10, 2025

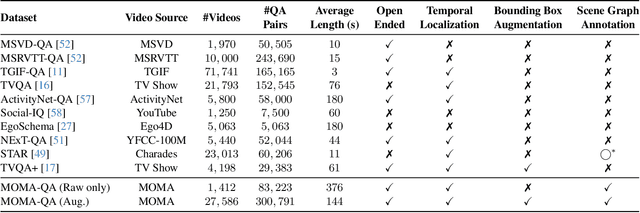
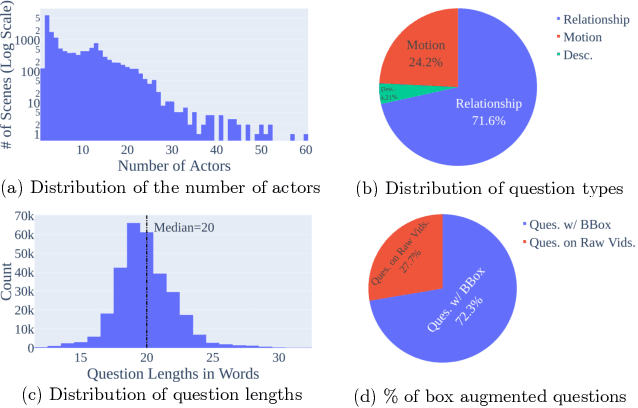
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving domain of video understanding, Video Question Answering (VideoQA) remains a focal point. However, existing datasets exhibit gaps in temporal and spatial granularity, which consequently limits the capabilities of existing VideoQA methods. This paper introduces the Multi-Object Multi-Actor Question Answering (MOMA-QA) dataset, which is designed to address these shortcomings by emphasizing temporal localization, spatial relationship reasoning, and entity-centric queries. With ground truth scene graphs and temporal interval annotations, MOMA-QA is ideal for developing models for fine-grained video understanding. Furthermore, we present a novel video-language model, SGVLM, which incorporates a scene graph predictor, an efficient frame retriever, and a pre-trained large language model for temporal localization and fine-grained relationship understanding. Evaluations on MOMA-QA and other public datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our model, setting new benchmarks for VideoQA.
Standing on FURM ground -- A framework for evaluating Fair, Useful, and Reliable AI Models in healthcare systems
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:The impact of using artificial intelligence (AI) to guide patient care or operational processes is an interplay of the AI model's output, the decision-making protocol based on that output, and the capacity of the stakeholders involved to take the necessary subsequent action. Estimating the effects of this interplay before deployment, and studying it in real time afterwards, are essential to bridge the chasm between AI model development and achievable benefit. To accomplish this, the Data Science team at Stanford Health Care has developed a Testing and Evaluation (T&E) mechanism to identify fair, useful and reliable AI models (FURM) by conducting an ethical review to identify potential value mismatches, simulations to estimate usefulness, financial projections to assess sustainability, as well as analyses to determine IT feasibility, design a deployment strategy, and recommend a prospective monitoring and evaluation plan. We report on FURM assessments done to evaluate six AI guided solutions for potential adoption, spanning clinical and operational settings, each with the potential to impact from several dozen to tens of thousands of patients each year. We describe the assessment process, summarize the six assessments, and share our framework to enable others to conduct similar assessments. Of the six solutions we assessed, two have moved into a planning and implementation phase. Our novel contributions - usefulness estimates by simulation, financial projections to quantify sustainability, and a process to do ethical assessments - as well as their underlying methods and open source tools, are available for other healthcare systems to conduct actionable evaluations of candidate AI solutions.
Evaluation of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 for supporting real-world information needs in healthcare delivery
May 01, 2023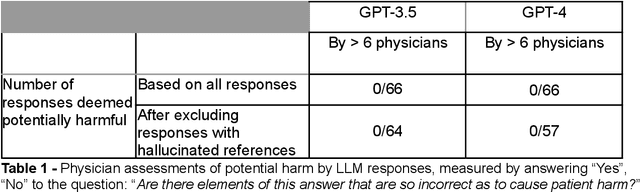
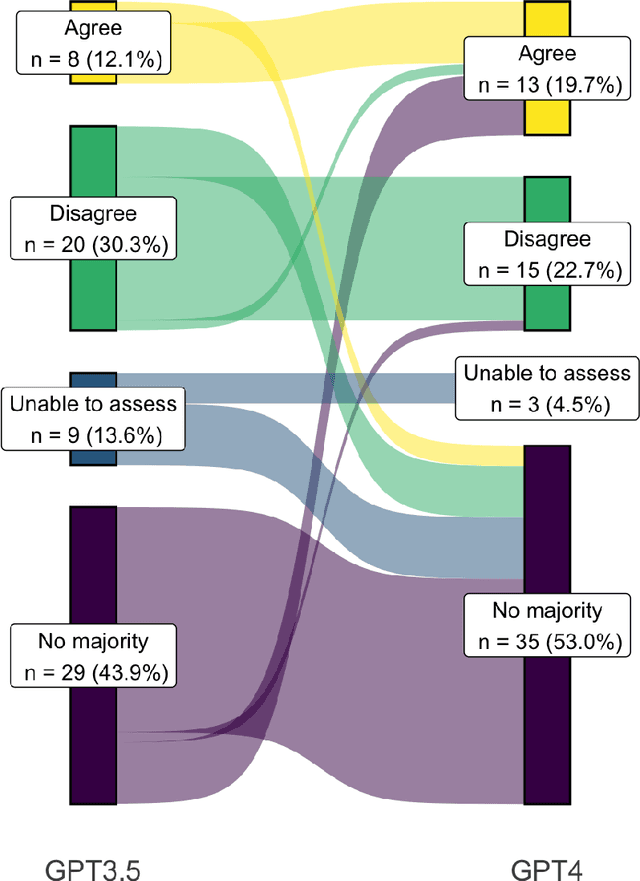
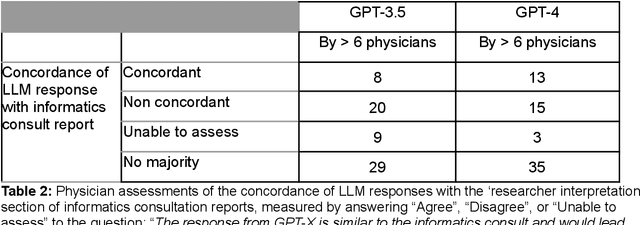
Abstract:Despite growing interest in using large language models (LLMs) in healthcare, current explorations do not assess the real-world utility and safety of LLMs in clinical settings. Our objective was to determine whether two LLMs can serve information needs submitted by physicians as questions to an informatics consultation service in a safe and concordant manner. Sixty six questions from an informatics consult service were submitted to GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 via simple prompts. 12 physicians assessed the LLM responses' possibility of patient harm and concordance with existing reports from an informatics consultation service. Physician assessments were summarized based on majority vote. For no questions did a majority of physicians deem either LLM response as harmful. For GPT-3.5, responses to 8 questions were concordant with the informatics consult report, 20 discordant, and 9 were unable to be assessed. There were 29 responses with no majority on "Agree", "Disagree", and "Unable to assess". For GPT-4, responses to 13 questions were concordant, 15 discordant, and 3 were unable to be assessed. There were 35 responses with no majority. Responses from both LLMs were largely devoid of overt harm, but less than 20% of the responses agreed with an answer from an informatics consultation service, responses contained hallucinated references, and physicians were divided on what constitutes harm. These results suggest that while general purpose LLMs are able to provide safe and credible responses, they often do not meet the specific information need of a given question. A definitive evaluation of the usefulness of LLMs in healthcare settings will likely require additional research on prompt engineering, calibration, and custom-tailoring of general purpose models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge