Aman Dalmia
Script Gap: Evaluating LLM Triage on Indian Languages in Native vs Roman Scripts in a Real World Setting
Dec 11, 2025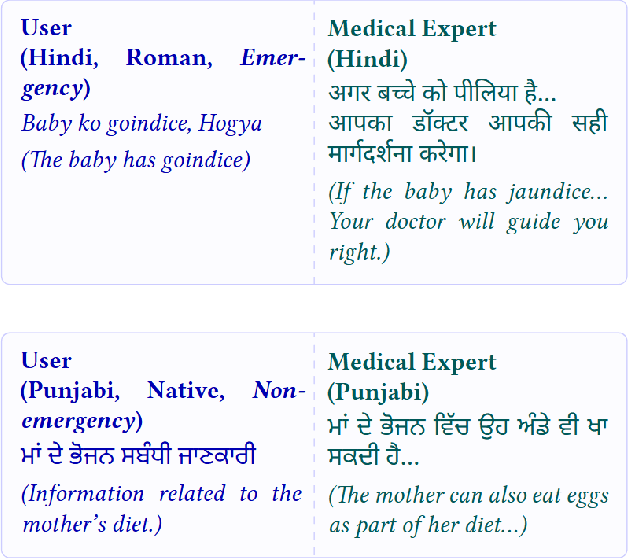
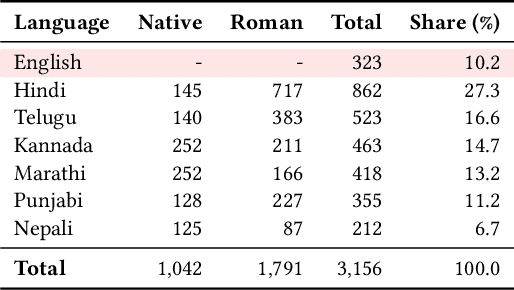


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in high-stakes clinical applications in India. In many such settings, speakers of Indian languages frequently communicate using romanized text rather than native scripts, yet existing research rarely evaluates this orthographic variation using real-world data. We investigate how romanization impacts the reliability of LLMs in a critical domain: maternal and newborn healthcare triage. We benchmark leading LLMs on a real-world dataset of user-generated queries spanning five Indian languages and Nepali. Our results reveal consistent degradation in performance for romanized messages, with F1 scores trailing those of native scripts by 5-12 points. At our partner maternal health organization in India, this gap could cause nearly 2 million excess errors in triage. Crucially, this performance gap by scripts is not due to a failure in clinical reasoning. We demonstrate that LLMs often correctly infer the semantic intent of romanized queries. Nevertheless, their final classification outputs remain brittle in the presence of orthographic noise in romanized inputs. Our findings highlight a critical safety blind spot in LLM-based health systems: models that appear to understand romanized input may still fail to act on it reliably.
GeoCoder: Solving Geometry Problems by Generating Modular Code through Vision-Language Models
Oct 17, 2024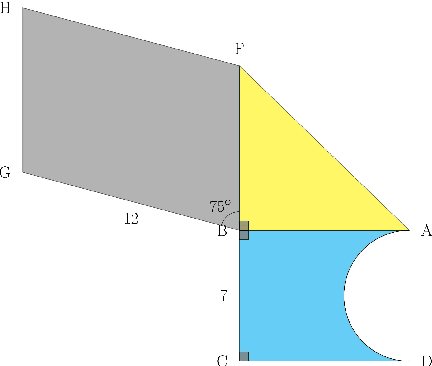

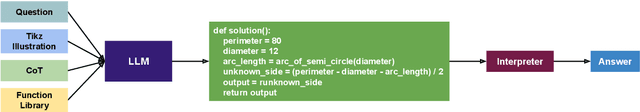

Abstract:Geometry problem-solving demands advanced reasoning abilities to process multimodal inputs and employ mathematical knowledge effectively. Vision-language models (VLMs) have made significant progress in various multimodal tasks. Yet, they still struggle with geometry problems and are significantly limited by their inability to perform mathematical operations not seen during pre-training, such as calculating the cosine of an arbitrary angle, and by difficulties in correctly applying relevant geometry formulas. To overcome these challenges, we present GeoCoder, which leverages modular code-finetuning to generate and execute code using a predefined geometry function library. By executing the code, we achieve accurate and deterministic calculations, contrasting the stochastic nature of autoregressive token prediction, while the function library minimizes errors in formula usage. We also propose a multimodal retrieval-augmented variant of GeoCoder, named RAG-GeoCoder, which incorporates a non-parametric memory module for retrieving functions from the geometry library, thereby reducing reliance on parametric memory. Our modular code-finetuning approach enhances the geometric reasoning capabilities of VLMs, yielding an average improvement of over 16% across various question complexities on the GeomVerse dataset compared to other finetuning methods.
NurtureNet: A Multi-task Video-based Approach for Newborn Anthropometry
May 09, 2024Abstract:Malnutrition among newborns is a top public health concern in developing countries. Identification and subsequent growth monitoring are key to successful interventions. However, this is challenging in rural communities where health systems tend to be inaccessible and under-equipped, with poor adherence to protocol. Our goal is to equip health workers and public health systems with a solution for contactless newborn anthropometry in the community. We propose NurtureNet, a multi-task model that fuses visual information (a video taken with a low-cost smartphone) with tabular inputs to regress multiple anthropometry estimates including weight, length, head circumference, and chest circumference. We show that visual proxy tasks of segmentation and keypoint prediction further improve performance. We establish the efficacy of the model through several experiments and achieve a relative error of 3.9% and mean absolute error of 114.3 g for weight estimation. Model compression to 15 MB also allows offline deployment to low-cost smartphones.
Impact of data-splits on generalization: Identifying COVID-19 from cough and context
Jun 05, 2021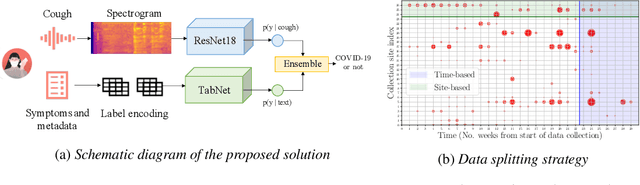
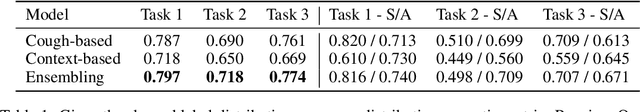
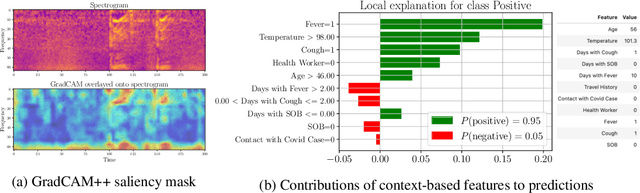
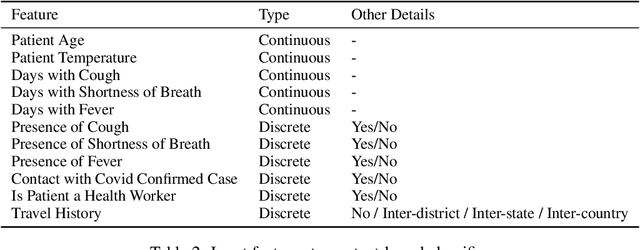
Abstract:Rapidly scaling screening, testing and quarantine has shown to be an effective strategy to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. We consider the application of deep learning techniques to distinguish individuals with COVID from non-COVID by using data acquirable from a phone. Using cough and context (symptoms and meta-data) represent such a promising approach. Several independent works in this direction have shown promising results. However, none of them report performance across clinically relevant data splits. Specifically, the performance where the development and test sets are split in time (retrospective validation) and across sites (broad validation). Although there is meaningful generalization across these splits the performance significantly varies (up to 0.1 AUC score). In addition, we study the performance of symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals across these three splits. Finally, we show that our model focuses on meaningful features of the input, cough bouts for cough and relevant symptoms for context. The code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/WadhwaniAI/cough-against-covid
Cough Against COVID: Evidence of COVID-19 Signature in Cough Sounds
Sep 23, 2020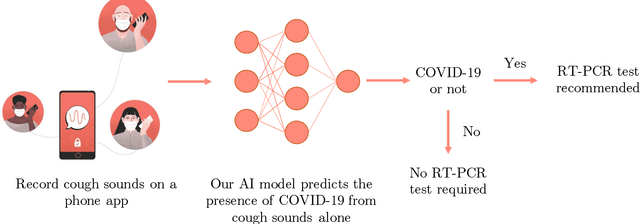
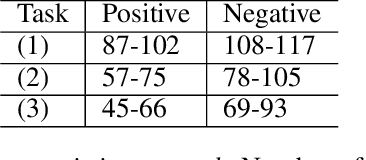
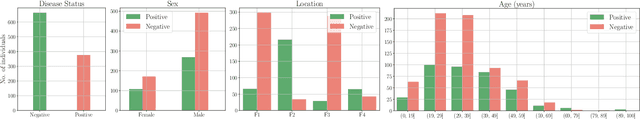
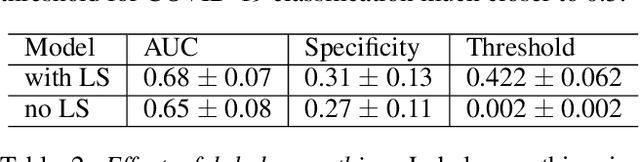
Abstract:Testing capacity for COVID-19 remains a challenge globally due to the lack of adequate supplies, trained personnel, and sample-processing equipment. These problems are even more acute in rural and underdeveloped regions. We demonstrate that solicited-cough sounds collected over a phone, when analysed by our AI model, have statistically significant signal indicative of COVID-19 status (AUC 0.72, t-test,p <0.01,95% CI 0.61-0.83). This holds true for asymptomatic patients as well. Towards this, we collect the largest known(to date) dataset of microbiologically confirmed COVID-19 cough sounds from 3,621 individuals. When used in a triaging step within an overall testing protocol, by enabling risk-stratification of individuals before confirmatory tests, our tool can increase the testing capacity of a healthcare system by 43% at disease prevalence of 5%, without additional supplies, trained personnel, or physical infrastructure
Siamese Neural Networks with Random Forest for detecting duplicate question pairs
Jan 28, 2018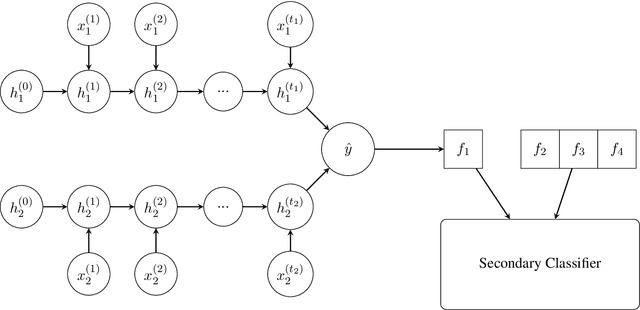



Abstract:Determining whether two given questions are semantically similar is a fairly challenging task given the different structures and forms that the questions can take. In this paper, we use Gated Recurrent Units(GRU) in combination with other highly used machine learning algorithms like Random Forest, Adaboost and SVM for the similarity prediction task on a dataset released by Quora, consisting of about 400k labeled question pairs. We got the best result by using the Siamese adaptation of a Bidirectional GRU with a Random Forest classifier, which landed us among the top 24% in the competition Quora Question Pairs hosted on Kaggle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge