Neeraj Agrawal
Building a Few-Shot Cross-Domain Multilingual NLU Model for Customer Care
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Customer care is an essential pillar of the e-commerce shopping experience with companies spending millions of dollars each year, employing automation and human agents, across geographies (like US, Canada, Mexico, Chile), channels (like Chat, Interactive Voice Response (IVR)), and languages (like English, Spanish). SOTA pre-trained models like multilingual-BERT, fine-tuned on annotated data have shown good performance in downstream tasks relevant to Customer Care. However, model performance is largely subject to the availability of sufficient annotated domain-specific data. Cross-domain availability of data remains a bottleneck, thus building an intent classifier that generalizes across domains (defined by channel, geography, and language) with only a few annotations, is of great practical value. In this paper, we propose an embedder-cum-classifier model architecture which extends state-of-the-art domain-specific models to other domains with only a few labeled samples. We adopt a supervised fine-tuning approach with isotropic regularizers to train a domain-specific sentence embedder and a multilingual knowledge distillation strategy to generalize this embedder across multiple domains. The trained embedder, further augmented with a simple linear classifier can be deployed for new domains. Experiments on Canada and Mexico e-commerce Customer Care dataset with few-shot intent detection show an increase in accuracy by 20-23% against the existing state-of-the-art pre-trained models.
Hierarchical Text Classification Using Contrastive Learning Informed Path Guided Hierarchy
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Hierarchical Text Classification (HTC) has recently gained traction given the ability to handle complex label hierarchy. This has found applications in domains like E- commerce, customer care and medicine industry among other real-world applications. Existing HTC models either encode label hierarchy separately and mix it with text encoding or guide the label hierarchy structure in the text encoder. Both approaches capture different characteristics of label hierarchy and are complementary to each other. In this paper, we propose a Hierarchical Text Classification using Contrastive Learning Informed Path guided hierarchy (HTC-CLIP), which learns hierarchy-aware text representation and text informed path guided hierarchy representation using contrastive learning. During the training of HTC-CLIP, we learn two different sets of class probabilities distributions and during inference, we use the pooled output of both probabilities for each class to get the best of both representations. Our results show that the two previous approaches can be effectively combined into one architecture to achieve improved performance. Tests on two public benchmark datasets showed an improvement of 0.99 - 2.37% in Macro F1 score using HTC-CLIP over the existing state-of-the-art models.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2203.03825 by other authors
Spoken Language Understanding on Unseen Tasks With In-Context Learning
May 12, 2025Abstract:Spoken language understanding (SLU) tasks involve diverse skills that probe the information extraction, classification and/or generation capabilities of models. In this setting, task-specific training data may not always be available. While traditional task-specific SLU models are unable to cater to such requirements, the speech-text large language models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative with emergent abilities. However, out of-the-box, our evaluations indicate that the zero/few-shot performance of prominent open-source speech-text LLMs on SLU tasks are not up to the mark. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to robust task-agnostic fine-tuning using randomized class labels. With this proposed fine-tuning, we illustrate that the performance of the speech-text LLMs on an unseen task is significantly improved over standard approaches. Critically, the proposed approach avoids the requirement of task-specific data annotations for enabling new tasks in speech-text LLMs.
Improving Few-Shot Cross-Domain Named Entity Recognition by Instruction Tuning a Word-Embedding based Retrieval Augmented Large Language Model
Nov 01, 2024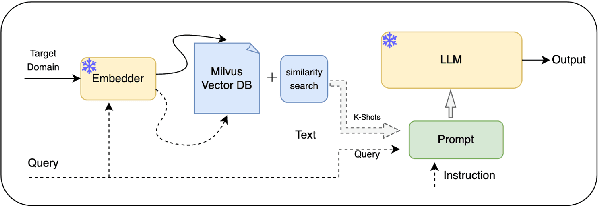
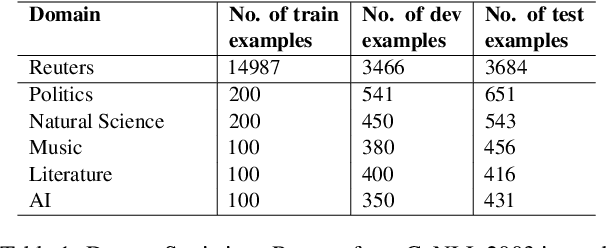
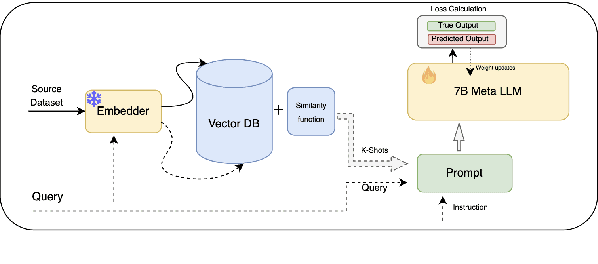
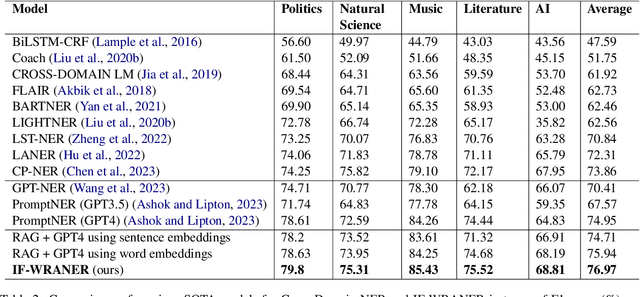
Abstract:Few-Shot Cross-Domain NER is the process of leveraging knowledge from data-rich source domains to perform entity recognition on data scarce target domains. Most previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches use pre-trained language models (PLMs) for cross-domain NER. However, these models are often domain specific. To successfully use these models for new target domains, we need to modify either the model architecture or perform model finetuning using data from the new domains. Both of these result in the creation of entirely new NER models for each target domain which is infeasible for practical scenarios. Recently,several works have attempted to use LLMs to solve Few-Shot Cross-Domain NER. However, most of these are either too expensive for practical purposes or struggle to follow LLM prompt instructions. In this paper, we propose IF-WRANER (Instruction Finetuned Word-embedding based Retrieval Augmented large language model for Named Entity Recognition), a retrieval augmented LLM, finetuned for the NER task. By virtue of the regularization techniques used during LLM finetuning and the adoption of word-level embedding over sentence-level embedding during the retrieval of in-prompt examples, IF-WRANER is able to outperform previous SOTA Few-Shot Cross-Domain NER approaches. We have demonstrated the effectiveness of our model by benchmarking its performance on the open source CrossNER dataset, on which it shows more than 2% F1 score improvement over the previous SOTA model. We have deployed the model for multiple customer care domains of an enterprise. Accurate entity prediction through IF-WRANER helps direct customers to automated workflows for the domains, thereby reducing escalations to human agents by almost 15% and leading to millions of dollars in yearly savings for the company.
Impact of data-splits on generalization: Identifying COVID-19 from cough and context
Jun 05, 2021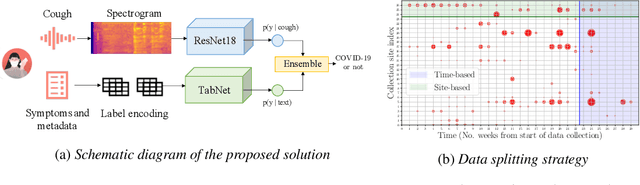
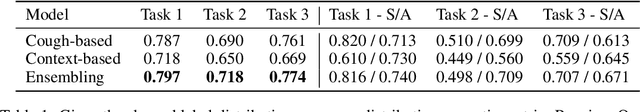
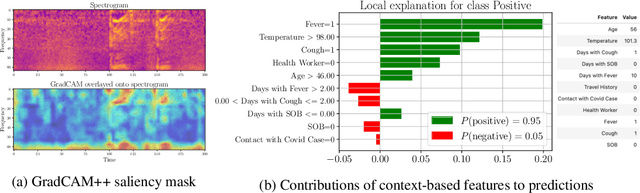
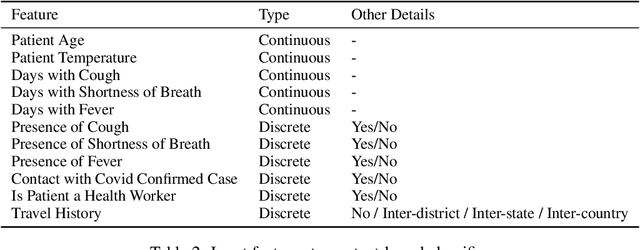
Abstract:Rapidly scaling screening, testing and quarantine has shown to be an effective strategy to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. We consider the application of deep learning techniques to distinguish individuals with COVID from non-COVID by using data acquirable from a phone. Using cough and context (symptoms and meta-data) represent such a promising approach. Several independent works in this direction have shown promising results. However, none of them report performance across clinically relevant data splits. Specifically, the performance where the development and test sets are split in time (retrospective validation) and across sites (broad validation). Although there is meaningful generalization across these splits the performance significantly varies (up to 0.1 AUC score). In addition, we study the performance of symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals across these three splits. Finally, we show that our model focuses on meaningful features of the input, cough bouts for cough and relevant symptoms for context. The code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/WadhwaniAI/cough-against-covid
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge