Michael Saxon
VEAT Quantifies Implicit Associations in Text-to-Video Generator Sora and Reveals Challenges in Bias Mitigation
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Text-to-Video (T2V) generators such as Sora raise concerns about whether generated content reflects societal bias. We extend embedding-association tests from words and images to video by introducing the Video Embedding Association Test (VEAT) and Single-Category VEAT (SC-VEAT). We validate these methods by reproducing the direction and magnitude of associations from widely used baselines, including Implicit Association Test (IAT) scenarios and OASIS image categories. We then quantify race (African American vs. European American) and gender (women vs. men) associations with valence (pleasant vs. unpleasant) across 17 occupations and 7 awards. Sora videos associate European Americans and women more with pleasantness (both d>0.8). Effect sizes correlate with real-world demographic distributions: percent men and White in occupations (r=0.93, r=0.83) and percent male and non-Black among award recipients (r=0.88, r=0.99). Applying explicit debiasing prompts generally reduces effect-size magnitudes, but can backfire: two Black-associated occupations (janitor, postal service) become more Black-associated after debiasing. Together, these results reveal that easily accessible T2V generators can actually amplify representational harms if not rigorously evaluated and responsibly deployed.
CAIRe: Cultural Attribution of Images by Retrieval-Augmented Evaluation
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:As text-to-image models become increasingly prevalent, ensuring their equitable performance across diverse cultural contexts is critical. Efforts to mitigate cross-cultural biases have been hampered by trade-offs, including a loss in performance, factual inaccuracies, or offensive outputs. Despite widespread recognition of these challenges, an inability to reliably measure these biases has stalled progress. To address this gap, we introduce CAIRe, a novel evaluation metric that assesses the degree of cultural relevance of an image, given a user-defined set of labels. Our framework grounds entities and concepts in the image to a knowledge base and uses factual information to give independent graded judgments for each culture label. On a manually curated dataset of culturally salient but rare items built using language models, CAIRe surpasses all baselines by 28% F1 points. Additionally, we construct two datasets for culturally universal concept, one comprising of T2I-generated outputs and another retrieved from naturally occurring data. CAIRe achieves Pearson's correlations of 0.56 and 0.66 with human ratings on these sets, based on a 5-point Likert scale of cultural relevance. This demonstrates its strong alignment with human judgment across diverse image sources.
THOUGHTTERMINATOR: Benchmarking, Calibrating, and Mitigating Overthinking in Reasoning Models
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:Reasoning models have demonstrated impressive performance on difficult tasks that traditional language models struggle at. However, many are plagued with the problem of overthinking--generating large amounts of unnecessary tokens which don't improve accuracy on a question. We introduce approximate measures of problem-level difficulty and demonstrate that a clear relationship between problem difficulty and optimal token spend exists, and evaluate how well calibrated a variety of reasoning models are in terms of efficiently allocating the optimal token count. We find that in general, reasoning models are poorly calibrated, particularly on easy problems. To evaluate calibration on easy questions we introduce DUMB500, a dataset of extremely easy math, reasoning, code, and task problems, and jointly evaluate reasoning model on these simple examples and extremely difficult examples from existing frontier benchmarks on the same task domain. Finally, we introduce THOUGHTTERMINATOR, a training-free black box decoding technique that significantly improves reasoning model calibration.
Benchmarks as Microscopes: A Call for Model Metrology
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:Modern language models (LMs) pose a new challenge in capability assessment. Static benchmarks inevitably saturate without providing confidence in the deployment tolerances of LM-based systems, but developers nonetheless claim that their models have generalized traits such as reasoning or open-domain language understanding based on these flawed metrics. The science and practice of LMs requires a new approach to benchmarking which measures specific capabilities with dynamic assessments. To be confident in our metrics, we need a new discipline of model metrology -- one which focuses on how to generate benchmarks that predict performance under deployment. Motivated by our evaluation criteria, we outline how building a community of model metrology practitioners -- one focused on building tools and studying how to measure system capabilities -- is the best way to meet these needs to and add clarity to the AI discussion.
VSP: Assessing the dual challenges of perception and reasoning in spatial planning tasks for VLMs
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Vision language models (VLMs) are an exciting emerging class of language models (LMs) that have merged classic LM capabilities with those of image processing systems. However, the ways that these capabilities combine are not always intuitive and warrant direct investigation. One understudied capability in VLMs is visual spatial planning -- the ability to comprehend the spatial arrangements of objects and devise action plans to achieve desired outcomes in visual scenes. In our study, we introduce VSP, a benchmark that 1) evaluates the spatial planning capability in these models in general, and 2) breaks down the visual planning task into finer-grained sub-tasks, including perception and reasoning, and measure the LMs capabilities in these sub-tasks. Our evaluation shows that both open-source and private VLMs fail to generate effective plans for even simple spatial planning tasks. Evaluations on the fine-grained analytical tasks further reveal fundamental deficiencies in the models' visual perception and bottlenecks in reasoning abilities, explaining their worse performance in the general spatial planning tasks. Our work illuminates future directions for improving VLMs' abilities in spatial planning. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/UCSB-NLP-Chang/Visual-Spatial-Planning.
Losing Visual Needles in Image Haystacks: Vision Language Models are Easily Distracted in Short and Long Contexts
Jun 24, 2024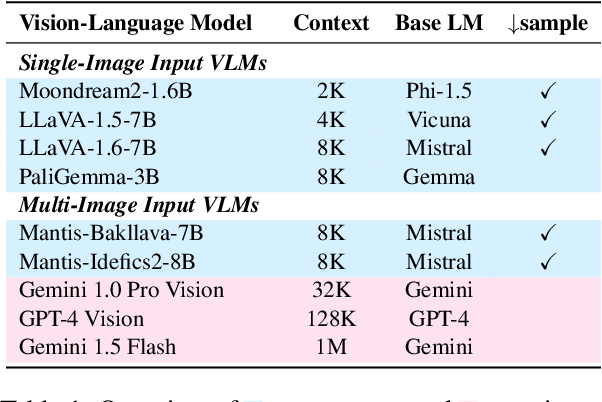

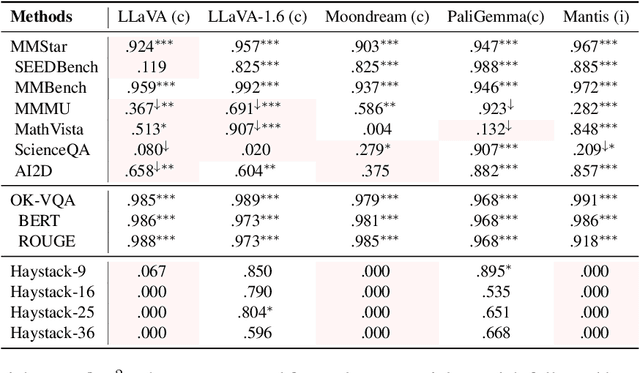
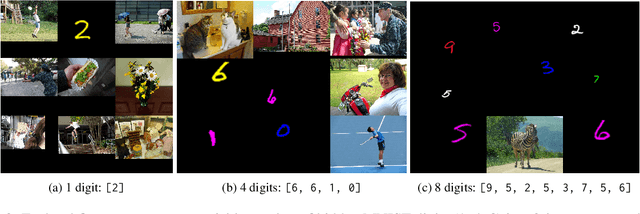
Abstract:We present LoCoVQA, a dynamic benchmark generator for evaluating long-context extractive reasoning in vision language models (VLMs). LoCoVQA augments test examples for mathematical reasoning, VQA, and character recognition tasks with increasingly long visual contexts composed of both in-distribution and out-of-distribution distractor images. Across these tasks, a diverse set of VLMs rapidly lose performance as the visual context length grows, often exhibiting a striking exponential decay trend. This test assesses how well VLMs can ignore irrelevant information when answering queries -- a task that is quite easy for language models (LMs) in the text domain -- demonstrating that current state-of-the-art VLMs lack this essential capability for many long-context applications.
TC-Bench: Benchmarking Temporal Compositionality in Text-to-Video and Image-to-Video Generation
Jun 12, 2024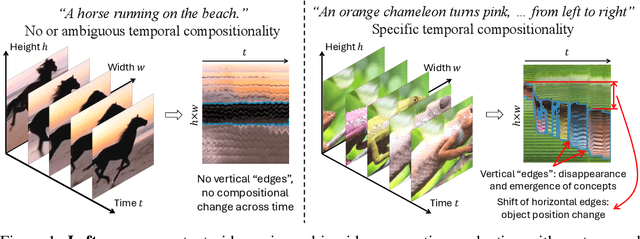



Abstract:Video generation has many unique challenges beyond those of image generation. The temporal dimension introduces extensive possible variations across frames, over which consistency and continuity may be violated. In this study, we move beyond evaluating simple actions and argue that generated videos should incorporate the emergence of new concepts and their relation transitions like in real-world videos as time progresses. To assess the Temporal Compositionality of video generation models, we propose TC-Bench, a benchmark of meticulously crafted text prompts, corresponding ground truth videos, and robust evaluation metrics. The prompts articulate the initial and final states of scenes, effectively reducing ambiguities for frame development and simplifying the assessment of transition completion. In addition, by collecting aligned real-world videos corresponding to the prompts, we expand TC-Bench's applicability from text-conditional models to image-conditional ones that can perform generative frame interpolation. We also develop new metrics to measure the completeness of component transitions in generated videos, which demonstrate significantly higher correlations with human judgments than existing metrics. Our comprehensive experimental results reveal that most video generators achieve less than 20% of the compositional changes, highlighting enormous space for future improvement. Our analysis indicates that current video generation models struggle to interpret descriptions of compositional changes and synthesize various components across different time steps.
Who Evaluates the Evaluations? Objectively Scoring Text-to-Image Prompt Coherence Metrics with T2IScoreScore (TS2)
Apr 05, 2024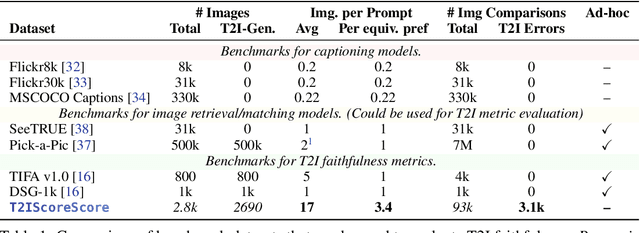
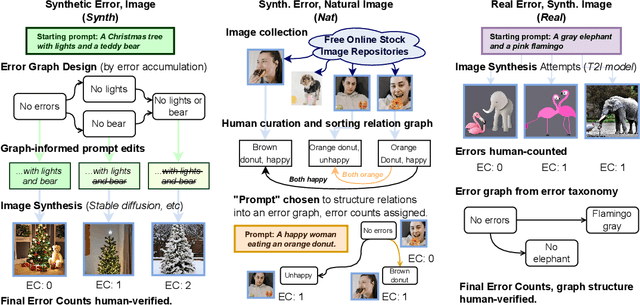
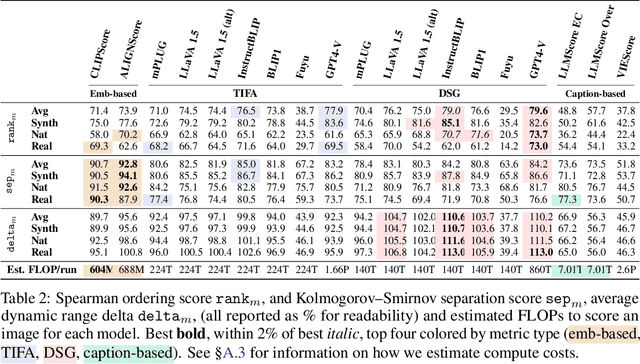
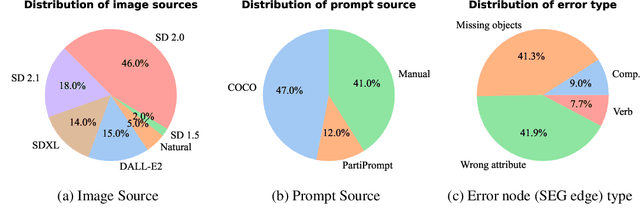
Abstract:With advances in the quality of text-to-image (T2I) models has come interest in benchmarking their prompt faithfulness-the semantic coherence of generated images to the prompts they were conditioned on. A variety of T2I faithfulness metrics have been proposed, leveraging advances in cross-modal embeddings and vision-language models (VLMs). However, these metrics are not rigorously compared and benchmarked, instead presented against few weak baselines by correlation to human Likert scores over a set of easy-to-discriminate images. We introduce T2IScoreScore (TS2), a curated set of semantic error graphs containing a prompt and a set increasingly erroneous images. These allow us to rigorously judge whether a given prompt faithfulness metric can correctly order images with respect to their objective error count and significantly discriminate between different error nodes, using meta-metric scores derived from established statistical tests. Surprisingly, we find that the state-of-the-art VLM-based metrics (e.g., TIFA, DSG, LLMScore, VIEScore) we tested fail to significantly outperform simple feature-based metrics like CLIPScore, particularly on a hard subset of naturally-occurring T2I model errors. TS2 will enable the development of better T2I prompt faithfulness metrics through more rigorous comparison of their conformity to expected orderings and separations under objective criteria.
Lost in Translation? Translation Errors and Challenges for Fair Assessment of Text-to-Image Models on Multilingual Concepts
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:Benchmarks of the multilingual capabilities of text-to-image (T2I) models compare generated images prompted in a test language to an expected image distribution over a concept set. One such benchmark, "Conceptual Coverage Across Languages" (CoCo-CroLa), assesses the tangible noun inventory of T2I models by prompting them to generate pictures from a concept list translated to seven languages and comparing the output image populations. Unfortunately, we find that this benchmark contains translation errors of varying severity in Spanish, Japanese, and Chinese. We provide corrections for these errors and analyze how impactful they are on the utility and validity of CoCo-CroLa as a benchmark. We reassess multiple baseline T2I models with the revisions, compare the outputs elicited under the new translations to those conditioned on the old, and show that a correction's impactfulness on the image-domain benchmark results can be predicted in the text domain with similarity scores. Our findings will guide the future development of T2I multilinguality metrics by providing analytical tools for practical translation decisions.
Automatically Correcting Large Language Models: Surveying the landscape of diverse self-correction strategies
Aug 06, 2023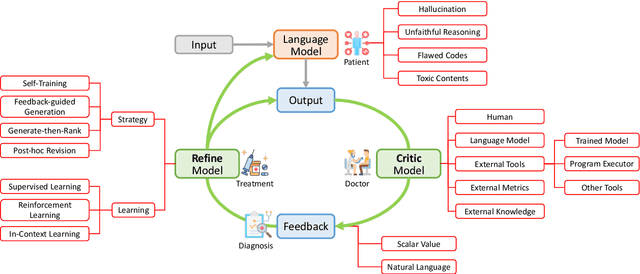
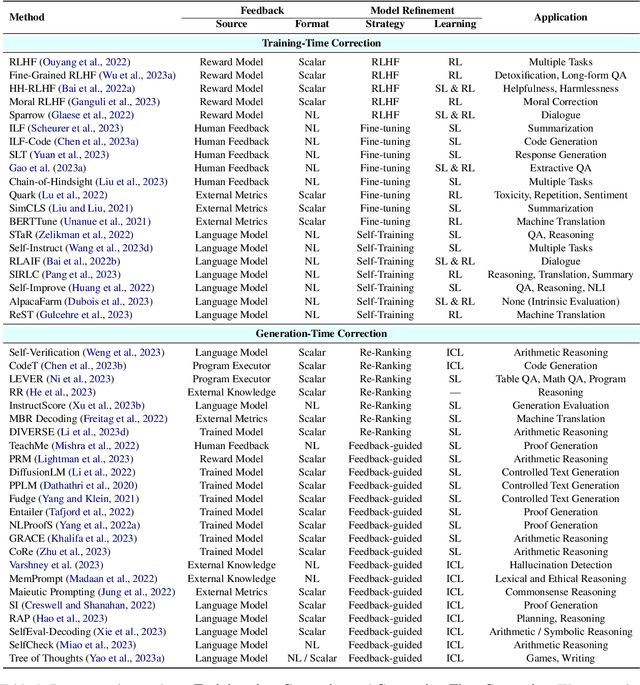
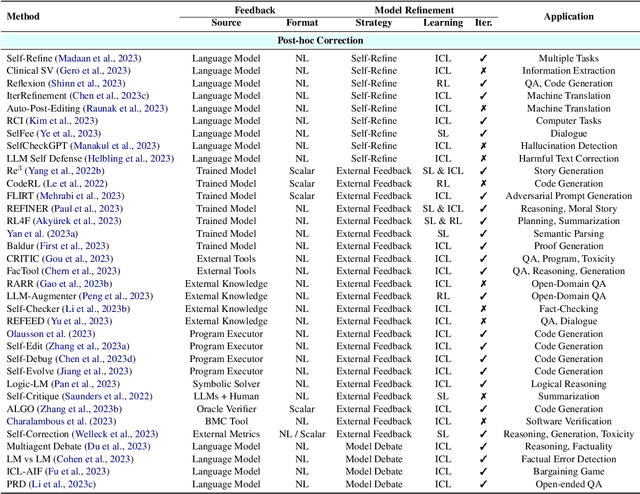
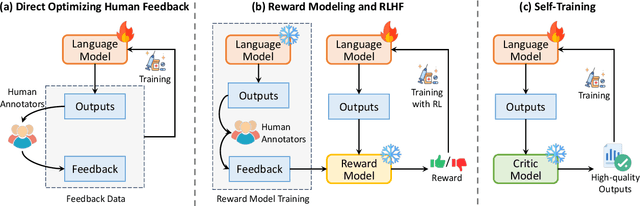
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across a wide array of NLP tasks. However, their efficacy is undermined by undesired and inconsistent behaviors, including hallucination, unfaithful reasoning, and toxic content. A promising approach to rectify these flaws is self-correction, where the LLM itself is prompted or guided to fix problems in its own output. Techniques leveraging automated feedback -- either produced by the LLM itself or some external system -- are of particular interest as they are a promising way to make LLM-based solutions more practical and deployable with minimal human feedback. This paper presents a comprehensive review of this emerging class of techniques. We analyze and taxonomize a wide array of recent work utilizing these strategies, including training-time, generation-time, and post-hoc correction. We also summarize the major applications of this strategy and conclude by discussing future directions and challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge