Yuan Chen
for the ALFA study
IPCV: Information-Preserving Compression for MLLM Visual Encoders
Dec 21, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) deliver strong vision-language performance but at high computational cost, driven by numerous visual tokens processed by the Vision Transformer (ViT) encoder. Existing token pruning strategies are inadequate: LLM-stage token pruning overlooks the ViT's overhead, while conventional ViT token pruning, without language guidance, risks discarding textually critical visual cues and introduces feature distortions amplified by the ViT's bidirectional attention. To meet these challenges, we propose IPCV, a training-free, information-preserving compression framework for MLLM visual encoders. IPCV enables aggressive token pruning inside the ViT via Neighbor-Guided Reconstruction (NGR) that temporarily reconstructs pruned tokens to participate in attention with minimal overhead, then fully restores them before passing to the LLM. Besides, we introduce Attention Stabilization (AS) to further alleviate the negative influence from token pruning by approximating the K/V of pruned tokens. It can be directly applied to previous LLM-side token pruning methods to enhance their performance. Extensive experiments show that IPCV substantially reduces end-to-end computation and outperforms state-of-the-art training-free token compression methods across diverse image and video benchmarks. Our code is available at https://github.com/Perkzi/IPCV.
Quantum Recurrent Neural Networks with Encoder-Decoder for Time-Dependent Partial Differential Equations
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Nonlinear time-dependent partial differential equations are essential in modeling complex phenomena across diverse fields, yet they pose significant challenges due to their computational complexity, especially in higher dimensions. This study explores Quantum Recurrent Neural Networks within an encoder-decoder framework, integrating Variational Quantum Circuits into Gated Recurrent Units and Long Short-Term Memory networks. Using this architecture, the model efficiently compresses high-dimensional spatiotemporal data into a compact latent space, facilitating more efficient temporal evolution. We evaluate the algorithms on the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation, Burgers' equation, the Gray-Scott reaction-diffusion system, and the three dimensional Michaelis-Menten reaction-diffusion equation. The results demonstrate the superior performance of the quantum-based algorithms in capturing nonlinear dynamics, handling high-dimensional spaces, and providing stable solutions, highlighting their potential as an innovative tool in solving challenging and complex systems.
FedRTS: Federated Robust Pruning via Combinatorial Thompson Sampling
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across distributed clients without data sharing, but its high computational and communication demands strain resource-constrained devices. While existing methods use dynamic pruning to improve efficiency by periodically adjusting sparse model topologies while maintaining sparsity, these approaches suffer from issues such as greedy adjustments, unstable topologies, and communication inefficiency, resulting in less robust models and suboptimal performance under data heterogeneity and partial client availability. To address these challenges, we propose Federated Robust pruning via combinatorial Thompson Sampling (FedRTS), a novel framework designed to develop robust sparse models. FedRTS enhances robustness and performance through its Thompson Sampling-based Adjustment (TSAdj) mechanism, which uses probabilistic decisions informed by stable, farsighted information instead of deterministic decisions reliant on unstable and myopic information in previous methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FedRTS achieves state-of-the-art performance in computer vision and natural language processing tasks while reducing communication costs, particularly excelling in scenarios with heterogeneous data distributions and partial client participation. Our codes are available at: https://github.com/Little0o0/FedRTS
Lightweight Multiplane Images Network for Real-Time Stereoscopic Conversion from Planar Video
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid development of stereoscopic display technologies, especially glasses-free 3D screens, and virtual reality devices, stereoscopic conversion has become an important task to address the lack of high-quality stereoscopic image and video resources. Current stereoscopic conversion algorithms typically struggle to balance reconstruction performance and inference efficiency. This paper proposes a planar video real-time stereoscopic conversion network based on multi-plane images (MPI), which consists of a detail branch for generating MPI and a depth-semantic branch for perceiving depth information. Unlike models that depend on explicit depth map inputs, the proposed method employs a lightweight depth-semantic branch to extract depth-aware features implicitly. To optimize the lightweight branch, a heavy training but light inference strategy is adopted, which involves designing a coarse-to-fine auxiliary branch that is only used during the training stage. In addition, the proposed method simplifies the MPI rendering process for stereoscopic conversion scenarios to further accelerate the inference. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve comparable performance to some state-of-the-art (SOTA) models and support real-time inference at 2K resolution. Compared to the SOTA TMPI algorithm, the proposed method obtains similar subjective quality while achieving over $40\times$ inference acceleration.
Controlling the Latent Diffusion Model for Generative Image Shadow Removal via Residual Generation
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:Large-scale generative models have achieved remarkable advancements in various visual tasks, yet their application to shadow removal in images remains challenging. These models often generate diverse, realistic details without adequate focus on fidelity, failing to meet the crucial requirements of shadow removal, which necessitates precise preservation of image content. In contrast to prior approaches that aimed to regenerate shadow-free images from scratch, this paper utilizes diffusion models to generate and refine image residuals. This strategy fully uses the inherent detailed information within shadowed images, resulting in a more efficient and faithful reconstruction of shadow-free content. Additionally, to revent the accumulation of errors during the generation process, a crosstimestep self-enhancement training strategy is proposed. This strategy leverages the network itself to augment the training data, not only increasing the volume of data but also enabling the network to dynamically correct its generation trajectory, ensuring a more accurate and robust output. In addition, to address the loss of original details in the process of image encoding and decoding of large generative models, a content-preserved encoder-decoder structure is designed with a control mechanism and multi-scale skip connections to achieve high-fidelity shadow-free image reconstruction. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can reproduce high-quality results based on a large latent diffusion prior and faithfully preserve the original contents in shadow regions.
Predicting Liquidity Coverage Ratio with Gated Recurrent Units: A Deep Learning Model for Risk Management
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:With the global economic integration and the high interconnection of financial markets, financial institutions are facing unprecedented challenges, especially liquidity risk. This paper proposes a liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) prediction model based on the gated recurrent unit (GRU) network to help financial institutions manage their liquidity risk more effectively. By utilizing the GRU network in deep learning technology, the model can automatically learn complex patterns from historical data and accurately predict LCR for a period of time in the future. The experimental results show that compared with traditional methods, the GRU model proposed in this study shows significant advantages in mean absolute error (MAE), proving its higher accuracy and robustness. This not only provides financial institutions with a more reliable liquidity risk management tool but also provides support for regulators to formulate more scientific and reasonable policies, which helps to improve the stability of the entire financial system.
A Training-Free Conditional Diffusion Model for Learning Stochastic Dynamical Systems
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:This study introduces a training-free conditional diffusion model for learning unknown stochastic differential equations (SDEs) using data. The proposed approach addresses key challenges in computational efficiency and accuracy for modeling SDEs by utilizing a score-based diffusion model to approximate their stochastic flow map. Unlike the existing methods, this technique is based on an analytically derived closed-form exact score function, which can be efficiently estimated by Monte Carlo method using the trajectory data, and eliminates the need for neural network training to learn the score function. By generating labeled data through solving the corresponding reverse ordinary differential equation, the approach enables supervised learning of the flow map. Extensive numerical experiments across various SDE types, including linear, nonlinear, and multi-dimensional systems, demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the method. The learned models exhibit significant improvements in predicting both short-term and long-term behaviors of unknown stochastic systems, often surpassing baseline methods like GANs in estimating drift and diffusion coefficients.
Chebyshev Feature Neural Network for Accurate Function Approximation
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:We present a new Deep Neural Network (DNN) architecture capable of approximating functions up to machine accuracy. Termed Chebyshev Feature Neural Network (CFNN), the new structure employs Chebyshev functions with learnable frequencies as the first hidden layer, followed by the standard fully connected hidden layers. The learnable frequencies of the Chebyshev layer are initialized with exponential distributions to cover a wide range of frequencies. Combined with a multi-stage training strategy, we demonstrate that this CFNN structure can achieve machine accuracy during training. A comprehensive set of numerical examples for dimensions up to $20$ are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of the method.
Data-driven Effective Modeling of Multiscale Stochastic Dynamical Systems
Aug 27, 2024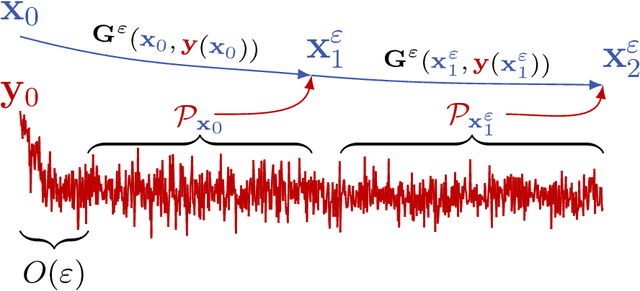
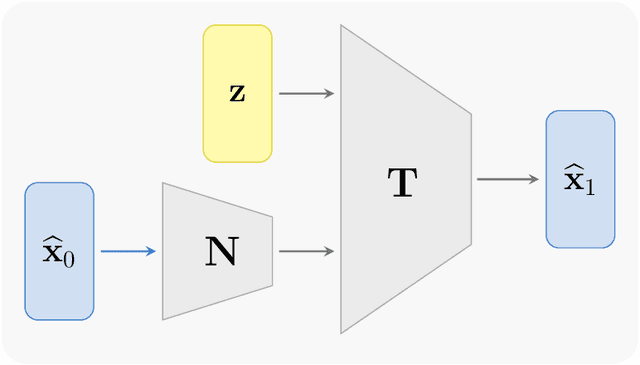
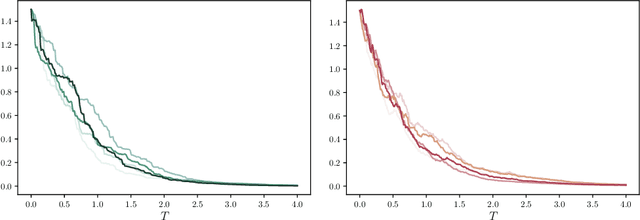
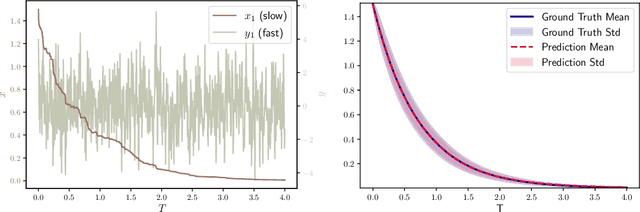
Abstract:We present a numerical method for learning the dynamics of slow components of unknown multiscale stochastic dynamical systems. While the governing equations of the systems are unknown, bursts of observation data of the slow variables are available. By utilizing the observation data, our proposed method is capable of constructing a generative stochastic model that can accurately capture the effective dynamics of the slow variables in distribution. We present a comprehensive set of numerical examples to demonstrate the performance of the proposed method.
Asynchronous Large Language Model Enhanced Planner for Autonomous Driving
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Despite real-time planners exhibiting remarkable performance in autonomous driving, the growing exploration of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened avenues for enhancing the interpretability and controllability of motion planning. Nevertheless, LLM-based planners continue to encounter significant challenges, including elevated resource consumption and extended inference times, which pose substantial obstacles to practical deployment. In light of these challenges, we introduce AsyncDriver, a new asynchronous LLM-enhanced closed-loop framework designed to leverage scene-associated instruction features produced by LLM to guide real-time planners in making precise and controllable trajectory predictions. On one hand, our method highlights the prowess of LLMs in comprehending and reasoning with vectorized scene data and a series of routing instructions, demonstrating its effective assistance to real-time planners. On the other hand, the proposed framework decouples the inference processes of the LLM and real-time planners. By capitalizing on the asynchronous nature of their inference frequencies, our approach have successfully reduced the computational cost introduced by LLM, while maintaining comparable performance. Experiments show that our approach achieves superior closed-loop evaluation performance on nuPlan's challenging scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge