Xin Ma
A Unified Complementarity-based Approach for Rigid-Body Manipulation and Motion Prediction
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Robotic manipulation in unstructured environments requires planners to reason jointly about free-space motion and sustained, frictional contact with the environment. Existing (local) planning and simulation frameworks typically separate these regimes or rely on simplified contact representations, particularly when modeling non-convex or distributed contact patches. Such approximations limit the fidelity of contact-mode transitions and hinder the robust execution of contact-rich behaviors in real time. This paper presents a unified discrete-time modeling framework for robotic manipulation that consistently captures both free motion and frictional contact within a single mathematical formalism (Unicomp). Building on complementarity-based rigid-body dynamics, we formulate free-space motion and contact interactions as coupled linear and nonlinear complementarity problems, enabling principled transitions between contact modes without enforcing fixed-contact assumptions. For planar patch contact, we derive a frictional contact model from the maximum power dissipation principle in which the set of admissible contact wrenches is represented by an ellipsoidal limit surface. This representation captures coupled force-moment effects, including torsional friction, while remaining agnostic to the underlying pressure distribution across the contact patch. The resulting formulation yields a discrete-time predictive model that relates generalized velocities and contact wrenches through quadratic constraints and is suitable for real-time optimization-based planning. Experimental results show that the proposed approach enables stable, physically consistent behavior at interactive speeds across tasks, from planar pushing to contact-rich whole-body maneuvers.
Dynamic Facial Expressions Analysis Based Parkinson's Disease Auxiliary Diagnosis
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD), a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, significantly affects patients' daily functioning and social interactions. To facilitate a more efficient and accessible diagnostic approach for PD, we propose a dynamic facial expression analysis-based PD auxiliary diagnosis method. This method targets hypomimia, a characteristic clinical symptom of PD, by analyzing two manifestations: reduced facial expressivity and facial rigidity, thereby facilitating the diagnosis process. We develop a multimodal facial expression analysis network to extract expression intensity features during patients' performance of various facial expressions. This network leverages the CLIP architecture to integrate visual and textual features while preserving the temporal dynamics of facial expressions. Subsequently, the expression intensity features are processed and input into an LSTM-based classification network for PD diagnosis. Our method achieves an accuracy of 93.1%, outperforming other in-vitro PD diagnostic approaches. This technique offers a more convenient detection method for potential PD patients, improving their diagnostic experience.
Everything-Grasping (EG) Gripper: A Universal Gripper with Synergistic Suction-Grasping Capabilities for Cross-Scale and Cross-State Manipulation
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Grasping objects across vastly different sizes and physical states-including both solids and liquids-with a single robotic gripper remains a fundamental challenge in soft robotics. We present the Everything-Grasping (EG) Gripper, a soft end-effector that synergistically integrates distributed surface suction with internal granular jamming, enabling cross-scale and cross-state manipulation without requiring airtight sealing at the contact interface with target objects. The EG Gripper can handle objects with surface areas ranging from sub-millimeter scale 0.2 mm2 (glass bead) to over 62,000 mm2 (A4 sized paper and woven bag), enabling manipulation of objects nearly 3,500X smaller and 88X larger than its own contact area (approximated at 707 mm2 for a 30 mm-diameter base). We further introduce a tactile sensing framework that combines liquid detection and pressure-based suction feedback, enabling real-time differentiation between solid and liquid targets. Guided by the actile-Inferred Grasping Mode Selection (TIGMS) algorithm, the gripper autonomously selects grasping modes based on distributed pressure and voltage signals. Experiments across diverse tasks-including underwater grasping, fragile object handling, and liquid capture-demonstrate robust and repeatable performance. To our knowledge, this is the first soft gripper to reliably grasp both solid and liquid objects across scales using a unified compliant architecture.
Consistent and Controllable Image Animation with Motion Linear Diffusion Transformers
Aug 10, 2025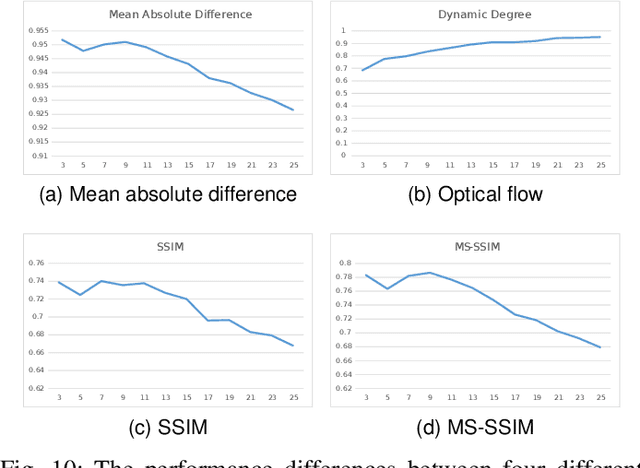
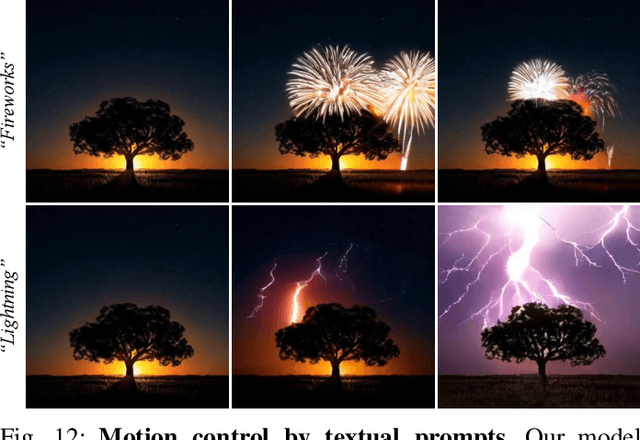
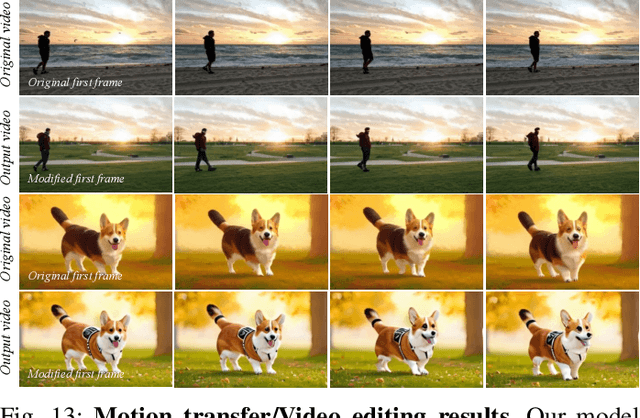



Abstract:Image animation has seen significant progress, driven by the powerful generative capabilities of diffusion models. However, maintaining appearance consistency with static input images and mitigating abrupt motion transitions in generated animations remain persistent challenges. While text-to-video (T2V) generation has demonstrated impressive performance with diffusion transformer models, the image animation field still largely relies on U-Net-based diffusion models, which lag behind the latest T2V approaches. Moreover, the quadratic complexity of vanilla self-attention mechanisms in Transformers imposes heavy computational demands, making image animation particularly resource-intensive. To address these issues, we propose MiraMo, a framework designed to enhance efficiency, appearance consistency, and motion smoothness in image animation. Specifically, MiraMo introduces three key elements: (1) A foundational text-to-video architecture replacing vanilla self-attention with efficient linear attention to reduce computational overhead while preserving generation quality; (2) A novel motion residual learning paradigm that focuses on modeling motion dynamics rather than directly predicting frames, improving temporal consistency; and (3) A DCT-based noise refinement strategy during inference to suppress sudden motion artifacts, complemented by a dynamics control module to balance motion smoothness and expressiveness. Extensive experiments against state-of-the-art methods validate the superiority of MiraMo in generating consistent, smooth, and controllable animations with accelerated inference speed. Additionally, we demonstrate the versatility of MiraMo through applications in motion transfer and video editing tasks.
Training-free Stylized Text-to-Image Generation with Fast Inference
May 25, 2025Abstract:Although diffusion models exhibit impressive generative capabilities, existing methods for stylized image generation based on these models often require textual inversion or fine-tuning with style images, which is time-consuming and limits the practical applicability of large-scale diffusion models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel stylized image generation method leveraging a pre-trained large-scale diffusion model without requiring fine-tuning or any additional optimization, termed as OmniPainter. Specifically, we exploit the self-consistency property of latent consistency models to extract the representative style statistics from reference style images to guide the stylization process. Additionally, we then introduce the norm mixture of self-attention, which enables the model to query the most relevant style patterns from these statistics for the intermediate output content features. This mechanism also ensures that the stylized results align closely with the distribution of the reference style images. Our qualitative and quantitative experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
Fish Mouth Inspired Origami Gripper for Robust Multi-Type Underwater Grasping
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:Robotic grasping and manipulation in underwater environments present unique challenges for robotic hands traditionally used on land. These challenges stem from dynamic water conditions, a wide range of object properties from soft to stiff, irregular object shapes, and varying surface frictions. One common approach involves developing finger-based hands with embedded compliance using underactuation and soft actuators. This study introduces an effective alternative solution that does not rely on finger-based hand designs. We present a fish mouth inspired origami gripper that utilizes a single degree of freedom to perform a variety of robust grasping tasks underwater. The innovative structure transforms a simple uniaxial pulling motion into a grasping action based on the Yoshimura crease pattern folding. The origami gripper offers distinct advantages, including scalable and optimizable design, grasping compliance, and robustness, with four grasping types: pinch, power grasp, simultaneous grasping of multiple objects, and scooping from the seabed. In this work, we detail the design, modeling, fabrication, and validation of a specialized underwater gripper capable of handling various marine creatures, including jellyfish, crabs, and abalone. By leveraging an origami and bio-inspired approach, the presented gripper demonstrates promising potential for robotic grasping and manipulation in underwater environments.
Prismatic-Bending Transformable (PBT) Joint for a Modular, Foldable Manipulator with Enhanced Reachability and Dexterity
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Robotic manipulators, traditionally designed with classical joint-link articulated structures, excel in industrial applications but face challenges in human-centered and general-purpose tasks requiring greater dexterity and adaptability. Addressing these limitations, we introduce the Prismatic-Bending Transformable (PBT) Joint, a novel design inspired by the scissors mechanism, enabling transformable kinematic chains. Each PBT joint module provides three degrees of freedom-bending, rotation, and elongation/contraction-allowing scalable and reconfigurable assemblies to form diverse kinematic configurations tailored to specific tasks. This innovative design surpasses conventional systems, delivering superior flexibility and performance across various applications. We present the design, modeling, and experimental validation of the PBT joint, demonstrating its integration into modular and foldable robotic arms. The PBT joint functions as a single SKU, enabling manipulators to be constructed entirely from standardized PBT joints without additional customized components. It also serves as a modular extension for existing systems, such as wrist modules, streamlining design, deployment, transportation, and maintenance. Three sizes-large, medium, and small-have been developed and integrated into robotic manipulators, highlighting their enhanced dexterity, reachability, and adaptability for manipulation tasks. This work represents a significant advancement in robotic design, offering scalable and efficient solutions for dynamic and unstructured environments.
Few-shot Sim2Real Based on High Fidelity Rendering with Force Feedback Teleoperation
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Teleoperation offers a promising approach to robotic data collection and human-robot interaction. However, existing teleoperation methods for data collection are still limited by efficiency constraints in time and space, and the pipeline for simulation-based data collection remains unclear. The problem is how to enhance task performance while minimizing reliance on real-world data. To address this challenge, we propose a teleoperation pipeline for collecting robotic manipulation data in simulation and training a few-shot sim-to-real visual-motor policy. Force feedback devices are integrated into the teleoperation system to provide precise end-effector gripping force feedback. Experiments across various manipulation tasks demonstrate that force feedback significantly improves both success rates and execution efficiency, particularly in simulation. Furthermore, experiments with different levels of visual rendering quality reveal that enhanced visual realism in simulation substantially boosts task performance while reducing the need for real-world data.
A Predefined-Time Convergent and Noise-Tolerant Zeroing Neural Network Model for Time Variant Quadratic Programming With Application to Robot Motion Planning
Dec 29, 2024Abstract:This paper develops a predefined-time convergent and noise-tolerant fractional-order zeroing neural network (PTC-NT-FOZNN) model, innovatively engineered to tackle time-variant quadratic programming (TVQP) challenges. The PTC-NT-FOZNN, stemming from a novel iteration within the variable-gain ZNN spectrum, known as FOZNNs, features diminishing gains over time and marries noise resistance with predefined-time convergence, making it ideal for energy-efficient robotic motion planning tasks. The PTC-NT-FOZNN enhances traditional ZNN models by incorporating a newly developed activation function that promotes optimal convergence irrespective of the model's order. When evaluated against six established ZNNs, the PTC-NT-FOZNN, with parameters $0 < \alpha \leq 1$, demonstrates enhanced positional precision and resilience to additive noises, making it exceptionally suitable for TVQP tasks. Thorough practical assessments, including simulations and experiments using a Flexiv Rizon robotic arm, confirm the PTC-NT-FOZNN's capabilities in achieving precise tracking and high computational efficiency, thereby proving its effectiveness for robust kinematic control applications.
COMO: Cross-Mamba Interaction and Offset-Guided Fusion for Multimodal Object Detection
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Single-modal object detection tasks often experience performance degradation when encountering diverse scenarios. In contrast, multimodal object detection tasks can offer more comprehensive information about object features by integrating data from various modalities. Current multimodal object detection methods generally use various fusion techniques, including conventional neural networks and transformer-based models, to implement feature fusion strategies and achieve complementary information. However, since multimodal images are captured by different sensors, there are often misalignments between them, making direct matching challenging. This misalignment hinders the ability to establish strong correlations for the same object across different modalities. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called the CrOss-Mamba interaction and Offset-guided fusion (COMO) framework for multimodal object detection tasks. The COMO framework employs the cross-mamba technique to formulate feature interaction equations, enabling multimodal serialized state computation. This results in interactive fusion outputs while reducing computational overhead and improving efficiency. Additionally, COMO leverages high-level features, which are less affected by misalignment, to facilitate interaction and transfer complementary information between modalities, addressing the positional offset challenges caused by variations in camera angles and capture times. Furthermore, COMO incorporates a global and local scanning mechanism in the cross-mamba module to capture features with local correlation, particularly in remote sensing images. To preserve low-level features, the offset-guided fusion mechanism ensures effective multiscale feature utilization, allowing the construction of a multiscale fusion data cube that enhances detection performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge