Weining Qian
NAT-NL2GQL: A Novel Multi-Agent Framework for Translating Natural Language to Graph Query Language
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized many fields, not only traditional natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Recently, research on applying LLMs to the database field has been booming, and as a typical non-relational database, the use of LLMs in graph database research has naturally gained significant attention. Recent efforts have increasingly focused on leveraging LLMs to translate natural language into graph query language (NL2GQL). Although some progress has been made, these methods have clear limitations, such as their reliance on streamlined processes that often overlook the potential of LLMs to autonomously plan and collaborate with other LLMs in tackling complex NL2GQL challenges. To address this gap, we propose NAT-NL2GQL, a novel multi-agent framework for translating natural language to graph query language. Specifically, our framework consists of three synergistic agents: the Preprocessor agent, the Generator agent, and the Refiner agent. The Preprocessor agent manages data processing as context, including tasks such as name entity recognition, query rewriting, path linking, and the extraction of query-related schemas. The Generator agent is a fine-tuned LLM trained on NL-GQL data, responsible for generating corresponding GQL statements based on queries and their related schemas. The Refiner agent is tasked with refining the GQL or context using error information obtained from the GQL execution results. Given the scarcity of high-quality open-source NL2GQL datasets based on nGQL syntax, we developed StockGQL, a dataset constructed from a financial market graph database. It is available at: https://github.com/leonyuancode/StockGQL. Experimental results on the StockGQL and SpCQL datasets reveal that our method significantly outperforms baseline approaches, highlighting its potential for advancing NL2GQL research.
RELIEF: Reinforcement Learning Empowered Graph Feature Prompt Tuning
Aug 06, 2024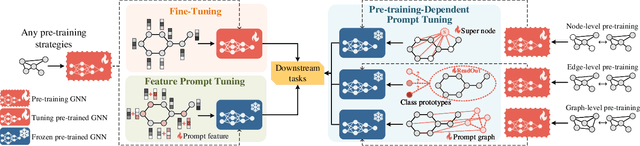
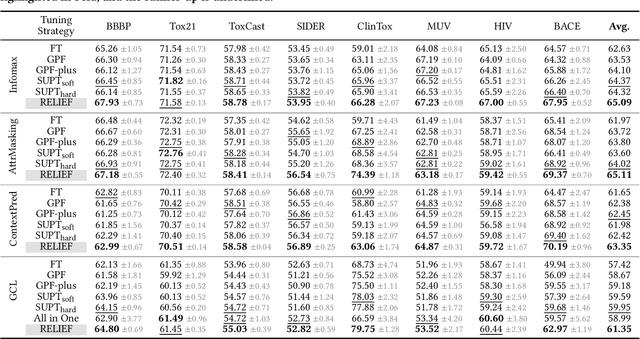
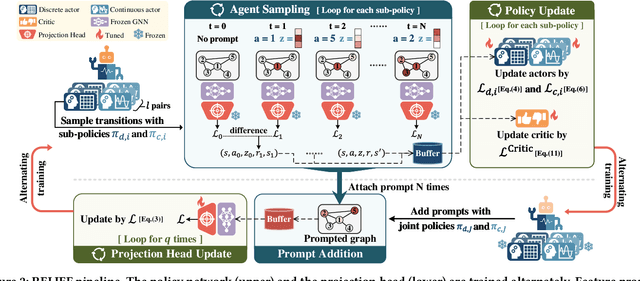
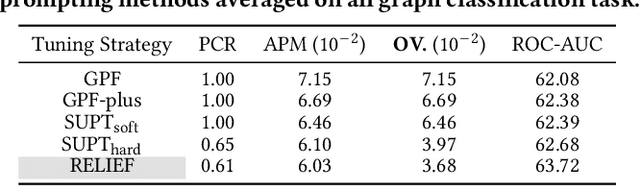
Abstract:The advent of the "pre-train, prompt" paradigm has recently extended its generalization ability and data efficiency to graph representation learning, following its achievements in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Initial graph prompt tuning approaches tailored specialized prompting functions for Graph Neural Network (GNN) models pre-trained with specific strategies, such as edge prediction, thus limiting their applicability. In contrast, another pioneering line of research has explored universal prompting via adding prompts to the input graph's feature space, thereby removing the reliance on specific pre-training strategies. However, the necessity to add feature prompts to all nodes remains an open question. Motivated by findings from prompt tuning research in the NLP domain, which suggest that highly capable pre-trained models need less conditioning signal to achieve desired behaviors, we advocate for strategically incorporating necessary and lightweight feature prompts to certain graph nodes to enhance downstream task performance. This introduces a combinatorial optimization problem, requiring a policy to decide 1) which nodes to prompt and 2) what specific feature prompts to attach. We then address the problem by framing the prompt incorporation process as a sequential decision-making problem and propose our method, RELIEF, which employs Reinforcement Learning (RL) to optimize it. At each step, the RL agent selects a node (discrete action) and determines the prompt content (continuous action), aiming to maximize cumulative performance gain. Extensive experiments on graph and node-level tasks with various pre-training strategies in few-shot scenarios demonstrate that our RELIEF outperforms fine-tuning and other prompt-based approaches in classification performance and data efficiency.
ExVideo: Extending Video Diffusion Models via Parameter-Efficient Post-Tuning
Jun 20, 2024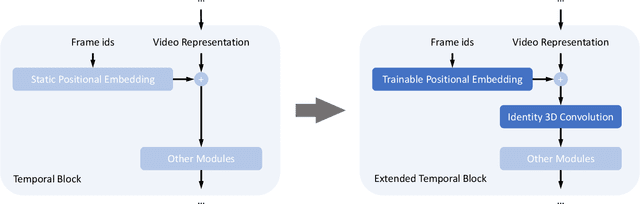



Abstract:Recently, advancements in video synthesis have attracted significant attention. Video synthesis models such as AnimateDiff and Stable Video Diffusion have demonstrated the practical applicability of diffusion models in creating dynamic visual content. The emergence of SORA has further spotlighted the potential of video generation technologies. Nonetheless, the extension of video lengths has been constrained by the limitations in computational resources. Most existing video synthesis models can only generate short video clips. In this paper, we propose a novel post-tuning methodology for video synthesis models, called ExVideo. This approach is designed to enhance the capability of current video synthesis models, allowing them to produce content over extended temporal durations while incurring lower training expenditures. In particular, we design extension strategies across common temporal model architectures respectively, including 3D convolution, temporal attention, and positional embedding. To evaluate the efficacy of our proposed post-tuning approach, we conduct extension training on the Stable Video Diffusion model. Our approach augments the model's capacity to generate up to $5\times$ its original number of frames, requiring only 1.5k GPU hours of training on a dataset comprising 40k videos. Importantly, the substantial increase in video length doesn't compromise the model's innate generalization capabilities, and the model showcases its advantages in generating videos of diverse styles and resolutions. We will release the source code and the enhanced model publicly.
Aligning Large Language Models to a Domain-specific Graph Database
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Graph Databases (Graph DB) are widely applied in various fields, including finance, social networks, and medicine. However, translating Natural Language (NL) into the Graph Query Language (GQL), commonly known as NL2GQL, proves to be challenging due to its inherent complexity and specialized nature. Some approaches have sought to utilize Large Language Models (LLMs) to address analogous tasks like text2SQL. Nevertheless, when it comes to NL2GQL taskson a particular domain, the absence of domain-specific NL-GQL data pairs makes it difficult to establish alignment between LLMs and the graph DB. To address this challenge, we propose a well-defined pipeline. Specifically, we utilize ChatGPT to create NL-GQL data pairs based on the given graph DB with self-instruct. Then, we use the created data to fine-tune LLMs, thereby achieving alignment between LLMs and the graph DB. Additionally, during inference, we propose a method that extracts relevant schema to the queried NL as the input context to guide LLMs for generating accurate GQLs.We evaluate our method on two constructed datasets deriving from graph DBs in finance domain and medicine domain, namely FinGQL and MediGQL. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms a set of baseline methods, with improvements of 5.90 and 6.36 absolute points on EM, and 6.00 and 7.09 absolute points on EX, respectively.
Unsupervised Text Style Transfer via LLMs and Attention Masking with Multi-way Interactions
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Unsupervised Text Style Transfer (UTST) has emerged as a critical task within the domain of Natural Language Processing (NLP), aiming to transfer one stylistic aspect of a sentence into another style without changing its semantics, syntax, or other attributes. This task is especially challenging given the intrinsic lack of parallel text pairings. Among existing methods for UTST tasks, attention masking approach and Large Language Models (LLMs) are deemed as two pioneering methods. However, they have shortcomings in generating unsmooth sentences and changing the original contents, respectively. In this paper, we investigate if we can combine these two methods effectively. We propose four ways of interactions, that are pipeline framework with tuned orders; knowledge distillation from LLMs to attention masking model; in-context learning with constructed parallel examples. We empirically show these multi-way interactions can improve the baselines in certain perspective of style strength, content preservation and text fluency. Experiments also demonstrate that simply conducting prompting followed by attention masking-based revision can consistently surpass the other systems, including supervised text style transfer systems. On Yelp-clean and Amazon-clean datasets, it improves the previously best mean metric by 0.5 and 3.0 absolute percentages respectively, and achieves new SOTA results.
Survey of Natural Language Processing for Education: Taxonomy, Systematic Review, and Future Trends
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) aims to analyze the text via techniques in the computer science field. It serves the applications in healthcare, commerce, and education domains. Particularly, NLP has been applied to the education domain to help teaching and learning. In this survey, we review recent advances in NLP with a focus on solving problems related to the education domain. In detail, we begin with introducing the relevant background. Then, we present the taxonomy of NLP in the education domain. Next, we illustrate the task definition, challenges, and corresponding techniques based on the above taxonomy. After that, we showcase some off-the-shelf demonstrations in this domain and conclude with future directions.
Diffutoon: High-Resolution Editable Toon Shading via Diffusion Models
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Toon shading is a type of non-photorealistic rendering task of animation. Its primary purpose is to render objects with a flat and stylized appearance. As diffusion models have ascended to the forefront of image synthesis methodologies, this paper delves into an innovative form of toon shading based on diffusion models, aiming to directly render photorealistic videos into anime styles. In video stylization, extant methods encounter persistent challenges, notably in maintaining consistency and achieving high visual quality. In this paper, we model the toon shading problem as four subproblems: stylization, consistency enhancement, structure guidance, and colorization. To address the challenges in video stylization, we propose an effective toon shading approach called \textit{Diffutoon}. Diffutoon is capable of rendering remarkably detailed, high-resolution, and extended-duration videos in anime style. It can also edit the content according to prompts via an additional branch. The efficacy of Diffutoon is evaluated through quantitive metrics and human evaluation. Notably, Diffutoon surpasses both open-source and closed-source baseline approaches in our experiments. Our work is accompanied by the release of both the source code and example videos on Github (Project page: https://ecnu-cilab.github.io/DiffutoonProjectPage/).
FastBlend: a Powerful Model-Free Toolkit Making Video Stylization Easier
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:With the emergence of diffusion models and rapid development in image processing, it has become effortless to generate fancy images in tasks such as style transfer and image editing. However, these impressive image processing approaches face consistency issues in video processing. In this paper, we propose a powerful model-free toolkit called FastBlend to address the consistency problem for video processing. Based on a patch matching algorithm, we design two inference modes, including blending and interpolation. In the blending mode, FastBlend eliminates video flicker by blending the frames within a sliding window. Moreover, we optimize both computational efficiency and video quality according to different application scenarios. In the interpolation mode, given one or more keyframes rendered by diffusion models, FastBlend can render the whole video. Since FastBlend does not modify the generation process of diffusion models, it exhibits excellent compatibility. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness of FastBlend. In the blending mode, FastBlend outperforms existing methods for video deflickering and video synthesis. In the interpolation mode, FastBlend surpasses video interpolation and model-based video processing approaches. The source codes have been released on GitHub.
Improving Zero-shot Visual Question Answering via Large Language Models with Reasoning Question Prompts
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Zero-shot Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a prominent vision-language task that examines both the visual and textual understanding capability of systems in the absence of training data. Recently, by converting the images into captions, information across multi-modalities is bridged and Large Language Models (LLMs) can apply their strong zero-shot generalization capability to unseen questions. To design ideal prompts for solving VQA via LLMs, several studies have explored different strategies to select or generate question-answer pairs as the exemplar prompts, which guide LLMs to answer the current questions effectively. However, they totally ignore the role of question prompts. The original questions in VQA tasks usually encounter ellipses and ambiguity which require intermediate reasoning. To this end, we present Reasoning Question Prompts for VQA tasks, which can further activate the potential of LLMs in zero-shot scenarios. Specifically, for each question, we first generate self-contained questions as reasoning question prompts via an unsupervised question edition module considering sentence fluency, semantic integrity and syntactic invariance. Each reasoning question prompt clearly indicates the intent of the original question. This results in a set of candidate answers. Then, the candidate answers associated with their confidence scores acting as answer heuristics are fed into LLMs and produce the final answer. We evaluate reasoning question prompts on three VQA challenges, experimental results demonstrate that they can significantly improve the results of LLMs on zero-shot setting and outperform existing state-of-the-art zero-shot methods on three out of four data sets. Our source code is publicly released at \url{https://github.com/ECNU-DASE-NLP/RQP}.
Learning Knowledge-Enhanced Contextual Language Representations for Domain Natural Language Understanding
Nov 12, 2023Abstract:Knowledge-Enhanced Pre-trained Language Models (KEPLMs) improve the performance of various downstream NLP tasks by injecting knowledge facts from large-scale Knowledge Graphs (KGs). However, existing methods for pre-training KEPLMs with relational triples are difficult to be adapted to close domains due to the lack of sufficient domain graph semantics. In this paper, we propose a Knowledge-enhanced lANGuAge Representation learning framework for various clOsed dOmains (KANGAROO) via capturing the implicit graph structure among the entities. Specifically, since the entity coverage rates of closed-domain KGs can be relatively low and may exhibit the global sparsity phenomenon for knowledge injection, we consider not only the shallow relational representations of triples but also the hyperbolic embeddings of deep hierarchical entity-class structures for effective knowledge fusion.Moreover, as two closed-domain entities under the same entity-class often have locally dense neighbor subgraphs counted by max point biconnected component, we further propose a data augmentation strategy based on contrastive learning over subgraphs to construct hard negative samples of higher quality. It makes the underlying KELPMs better distinguish the semantics of these neighboring entities to further complement the global semantic sparsity. In the experiments, we evaluate KANGAROO over various knowledge-aware and general NLP tasks in both full and few-shot learning settings, outperforming various KEPLM training paradigms performance in closed-domains significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge