Veronika Laippala
Hopes and Fears -- Emotion Distribution in the Topic Landscape of Finnish Parliamentary Speech 2000-2020
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Existing research often treats parliamentary discourse as a homogeneous whole, overlooking topic-specific patterns. Parliamentary speeches address a wide range of topics, some of which evoke stronger emotions than others. While everyone has intuitive assumptions about what the most emotive topics in a parliament may be, there has been little research into the emotions typically linked to different topics. This paper strives to fill this gap by examining emotion expression among the topics of parliamentary speeches delivered in Eduskunta, the Finnish Parliament, between 2000 and 2020. An emotion analysis model is used to investigate emotion expression in topics, from both synchronic and diachronic perspectives. The results strengthen evidence of increasing positivity in parliamentary speech and provide further insights into topic-specific emotion expression within parliamentary debate.
Register Always Matters: Analysis of LLM Pretraining Data Through the Lens of Language Variation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Pretraining data curation is a cornerstone in Large Language Model (LLM) development, leading to growing research on quality filtering of large web corpora. From statistical quality flags to LLM-based labeling systems, datasets are divided into categories, frequently reducing to a binary: those passing the filters deemed as valuable examples, others discarded as useless or detrimental. However, a more detailed understanding of the contribution of different kinds of texts to model performance is still largely lacking. In this article, we present the first study utilizing registers (also known as genres) - a widely used standard in corpus linguistics to model linguistic variation - to curate pretraining datasets and investigate the effect of register on the performance of LLMs. We perform comparative studies by training models with register classified data and evaluating them using standard benchmarks, and show that the register of pretraining data substantially affects model performance. We uncover surprising relationships between the pretraining material and the resulting models: using the News register results in subpar performance, and on the contrary, including the Opinion class, covering texts such as reviews and opinion blogs, is highly beneficial. While a model trained on the entire unfiltered dataset outperforms those trained on datasets limited to a single register, combining well-performing registers like How-to-Instructions, Informational Description, and Opinion leads to major improvements. Furthermore, analysis of individual benchmark results reveals key differences in the strengths and drawbacks of specific register classes as pretraining data. These findings show that register is an important explainer of model variation and can facilitate more deliberate future data selection practices.
An Expanded Massive Multilingual Dataset for High-Performance Language Technologies
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Training state-of-the-art large language models requires vast amounts of clean and diverse textual data. However, building suitable multilingual datasets remains a challenge. In this work, we present HPLT v2, a collection of high-quality multilingual monolingual and parallel corpora. The monolingual portion of the data contains 8T tokens covering 193 languages, while the parallel data contains 380M sentence pairs covering 51 languages. We document the entire data pipeline and release the code to reproduce it. We provide extensive analysis of the quality and characteristics of our data. Finally, we evaluate the performance of language models and machine translation systems trained on HPLT v2, demonstrating its value.
Untangling the Unrestricted Web: Automatic Identification of Multilingual Registers
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:This article explores deep learning models for the automatic identification of registers - text varieties such as news reports and discussion forums - in web-based datasets across 16 languages. Web register (or genre) identification would provide a robust solution for understanding the content of web-scale datasets, which have become crucial in computational linguistics. Despite recent advances, the potential of register classifiers on the noisy web remains largely unexplored, particularly in multilingual settings and when targeting the entire unrestricted web. We experiment with a range of deep learning models using the new Multilingual CORE corpora, which includes 16 languages annotated using a detailed, hierarchical taxonomy of 25 registers designed to cover the entire unrestricted web. Our models achieve state-of-the-art results, showing that a detailed taxonomy in a hierarchical multi-label setting can yield competitive classification performance. However, all models hit a glass ceiling at approximately 80% F1 score, which we attribute to the non-discrete nature of web registers and the inherent uncertainty in labeling some documents. By pruning ambiguous examples, we improve model performance to over 90%. Finally, multilingual models outperform monolingual ones, particularly benefiting languages with fewer training examples and smaller registers. Although a zero-shot setting decreases performance by an average of 7%, these drops are not linked to specific registers or languages. Instead, registers show surprising similarity across languages.
Aurora-M: The First Open Source Multilingual Language Model Red-teamed according to the U.S. Executive Order
Mar 30, 2024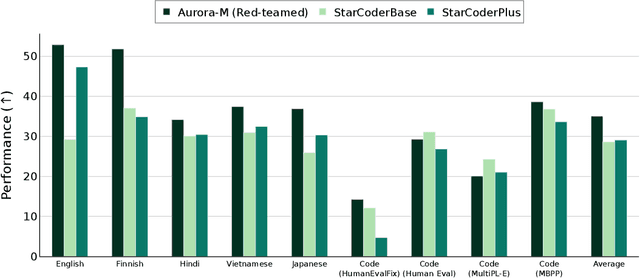
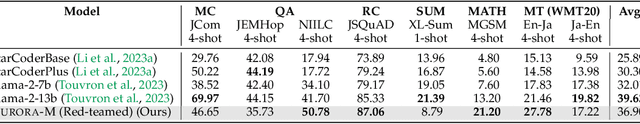
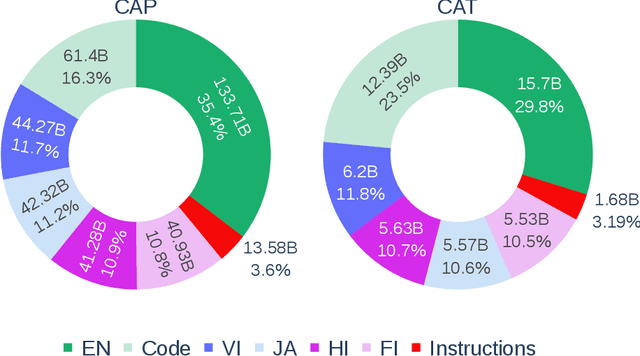
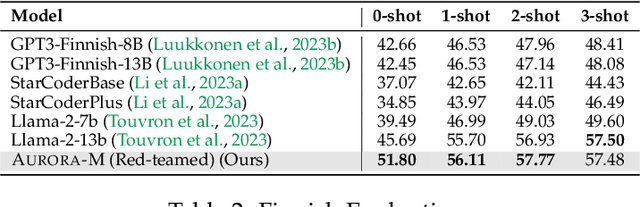
Abstract:Pretrained language models underpin several AI applications, but their high computational cost for training limits accessibility. Initiatives such as BLOOM and StarCoder aim to democratize access to pretrained models for collaborative community development. However, such existing models face challenges: limited multilingual capabilities, continual pretraining causing catastrophic forgetting, whereas pretraining from scratch is computationally expensive, and compliance with AI safety and development laws. This paper presents Aurora-M, a 15B parameter multilingual open-source model trained on English, Finnish, Hindi, Japanese, Vietnamese, and code. Continually pretrained from StarCoderPlus on 435 billion additional tokens, Aurora-M surpasses 2 trillion tokens in total training token count. It is the first open-source multilingual model fine-tuned on human-reviewed safety instructions, thus aligning its development not only with conventional red-teaming considerations, but also with the specific concerns articulated in the Biden-Harris Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence. Aurora-M is rigorously evaluated across various tasks and languages, demonstrating robustness against catastrophic forgetting and outperforming alternatives in multilingual settings, particularly in safety evaluations. To promote responsible open-source LLM development, Aurora-M and its variants are released at https://huggingface.co/collections/aurora-m/aurora-m-models-65fdfdff62471e09812f5407 .
FinGPT: Large Generative Models for a Small Language
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in many tasks in NLP and beyond, but most open models have very limited coverage of smaller languages and LLM work tends to focus on languages where nearly unlimited data is available for pretraining. In this work, we study the challenges of creating LLMs for Finnish, a language spoken by less than 0.1% of the world population. We compile an extensive dataset of Finnish combining web crawls, news, social media and eBooks. We pursue two approaches to pretrain models: 1) we train seven monolingual models from scratch (186M to 13B parameters) dubbed FinGPT, 2) we continue the pretraining of the multilingual BLOOM model on a mix of its original training data and Finnish, resulting in a 176 billion parameter model we call BLUUMI. For model evaluation, we introduce FIN-bench, a version of BIG-bench with Finnish tasks. We also assess other model qualities such as toxicity and bias. Our models and tools are openly available at https://turkunlp.org/gpt3-finnish.
BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
Explaining Classes through Word Attribution
Aug 31, 2021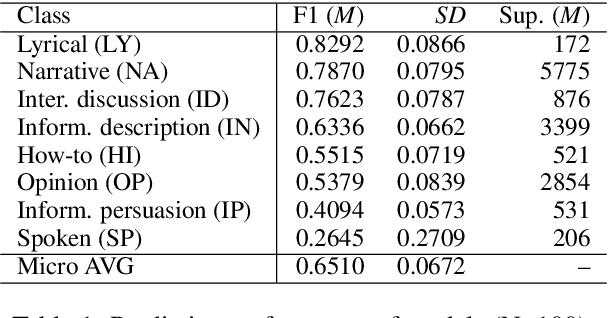
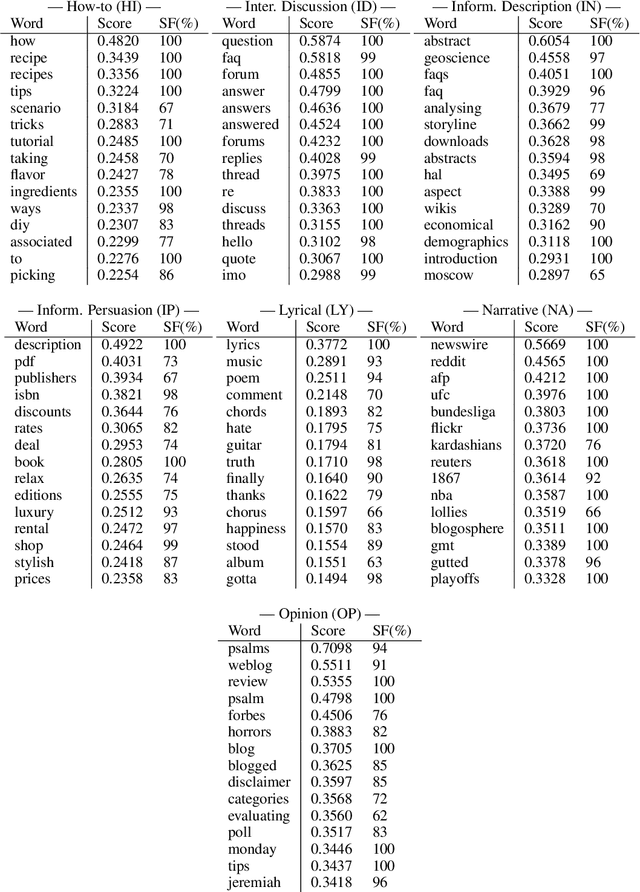
Abstract:In recent years, several methods have been proposed for explaining individual predictions of deep learning models, yet there has been little study of how to aggregate these predictions to explain how such models view classes as a whole in text classification tasks. In this work, we propose a method for explaining classes using deep learning models and the Integrated Gradients feature attribution technique by aggregating explanations of individual examples in text classification to general descriptions of the classes. We demonstrate the approach on Web register (genre) classification using the XML-R model and the Corpus of Online Registers of English (CORE), finding that the method identifies plausible and discriminative keywords characterizing all but the smallest class.
Beyond the English Web: Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual and Lightweight Monolingual Classification of Registers
Feb 15, 2021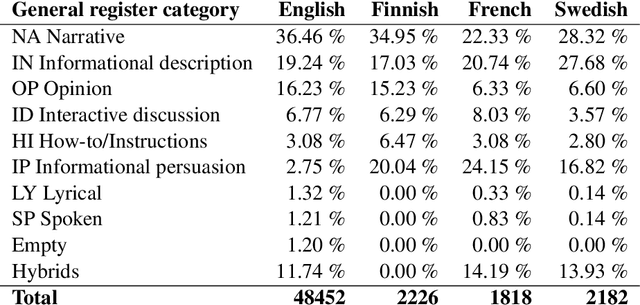
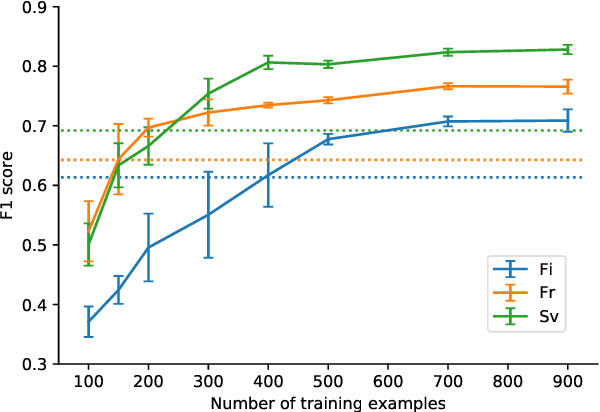
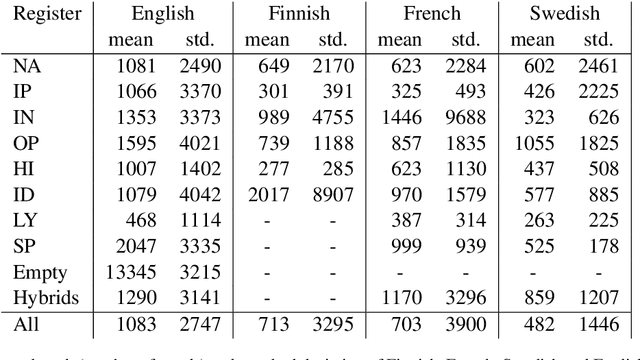
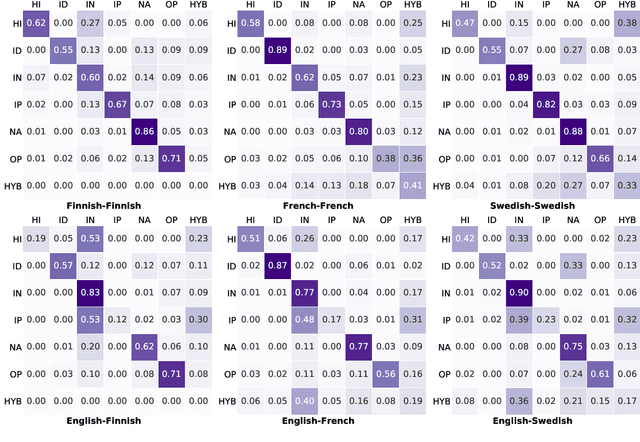
Abstract:We explore cross-lingual transfer of register classification for web documents. Registers, that is, text varieties such as blogs or news are one of the primary predictors of linguistic variation and thus affect the automatic processing of language. We introduce two new register annotated corpora, FreCORE and SweCORE, for French and Swedish. We demonstrate that deep pre-trained language models perform strongly in these languages and outperform previous state-of-the-art in English and Finnish. Specifically, we show 1) that zero-shot cross-lingual transfer from the large English CORE corpus can match or surpass previously published monolingual models, and 2) that lightweight monolingual classification requiring very little training data can reach or surpass our zero-shot performance. We further analyse classification results finding that certain registers continue to pose challenges in particular for cross-lingual transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge