Hanna-Mari Kupari
FinGPT: Large Generative Models for a Small Language
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in many tasks in NLP and beyond, but most open models have very limited coverage of smaller languages and LLM work tends to focus on languages where nearly unlimited data is available for pretraining. In this work, we study the challenges of creating LLMs for Finnish, a language spoken by less than 0.1% of the world population. We compile an extensive dataset of Finnish combining web crawls, news, social media and eBooks. We pursue two approaches to pretrain models: 1) we train seven monolingual models from scratch (186M to 13B parameters) dubbed FinGPT, 2) we continue the pretraining of the multilingual BLOOM model on a mix of its original training data and Finnish, resulting in a 176 billion parameter model we call BLUUMI. For model evaluation, we introduce FIN-bench, a version of BIG-bench with Finnish tasks. We also assess other model qualities such as toxicity and bias. Our models and tools are openly available at https://turkunlp.org/gpt3-finnish.
Annotation Guidelines for the Turku Paraphrase Corpus
Aug 19, 2021Abstract:This document describes the annotation guidelines used to construct the Turku Paraphrase Corpus. These guidelines were developed together with the corpus annotation, revising and extending the guidelines regularly during the annotation work. Our paraphrase annotation scheme uses the base scale 1-4, where labels 1 and 2 are used for negative candidates (not paraphrases), while labels 3 and 4 are paraphrases at least in the given context if not everywhere. In addition to base labeling, the scheme is enriched with additional subcategories (flags) for categorizing different types of paraphrases inside the two positive labels, making the annotation scheme suitable for more fine-grained paraphrase categorization. The annotation scheme is used to annotate over 100,000 Finnish paraphrase pairs.
Finnish Paraphrase Corpus
Mar 24, 2021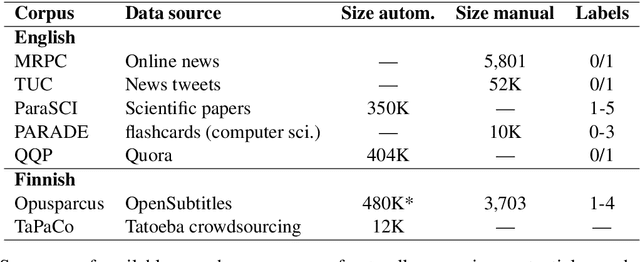
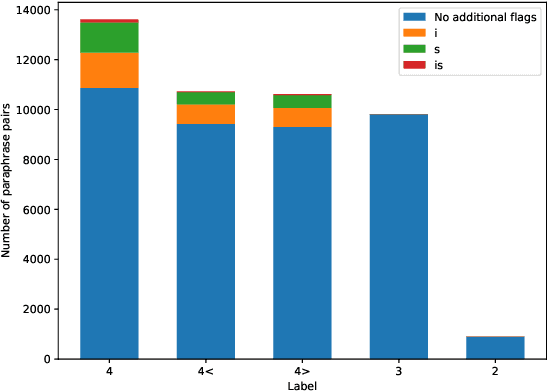

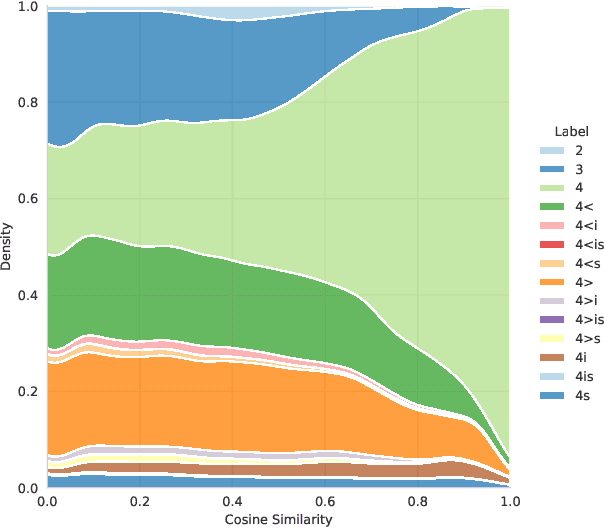
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the first fully manually annotated paraphrase corpus for Finnish containing 53,572 paraphrase pairs harvested from alternative subtitles and news headings. Out of all paraphrase pairs in our corpus 98% are manually classified to be paraphrases at least in their given context, if not in all contexts. Additionally, we establish a manual candidate selection method and demonstrate its feasibility in high quality paraphrase selection in terms of both cost and quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge