Tianqi Xu
Preferred Elements, Inc.
PLaMo 2 Technical Report
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce PLaMo 2, a series of Japanese-focused large language models featuring a hybrid Samba-based architecture that transitions to full attention via continual pre-training to support 32K token contexts. Training leverages extensive synthetic corpora to overcome data scarcity, while computational efficiency is achieved through weight reuse and structured pruning. This efficient pruning methodology produces an 8B model that achieves performance comparable to our previous 100B model. Post-training further refines the models using a pipeline of supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and direct preference optimization (DPO), enhanced by synthetic Japanese instruction data and model merging techniques. Optimized for inference using vLLM and quantization with minimal accuracy loss, the PLaMo 2 models achieve state-of-the-art results on Japanese benchmarks, outperforming similarly-sized open models in instruction-following, language fluency, and Japanese-specific knowledge.
BOLT: Boost Large Vision-Language Model Without Training for Long-form Video Understanding
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Large video-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated promising progress in various video understanding tasks. However, their effectiveness in long-form video analysis is constrained by limited context windows. Traditional approaches, such as uniform frame sampling, often inevitably allocate resources to irrelevant content, diminishing their effectiveness in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we introduce BOLT, a method to BOost Large VLMs without additional Training through a comprehensive study of frame selection strategies. First, to enable a more realistic evaluation of VLMs in long-form video understanding, we propose a multi-source retrieval evaluation setting. Our findings reveal that uniform sampling performs poorly in noisy contexts, underscoring the importance of selecting the right frames. Second, we explore several frame selection strategies based on query-frame similarity and analyze their effectiveness at inference time. Our results show that inverse transform sampling yields the most significant performance improvement, increasing accuracy on the Video-MME benchmark from 53.8% to 56.1% and MLVU benchmark from 58.9% to 63.4%. Our code is available at https://github.com/sming256/BOLT.
Uncertainty-aware Knowledge Tracing
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Tracing (KT) is crucial in education assessment, which focuses on depicting students' learning states and assessing students' mastery of subjects. With the rise of modern online learning platforms, particularly massive open online courses (MOOCs), an abundance of interaction data has greatly advanced the development of the KT technology. Previous research commonly adopts deterministic representation to capture students' knowledge states, which neglects the uncertainty during student interactions and thus fails to model the true knowledge state in learning process. In light of this, we propose an Uncertainty-Aware Knowledge Tracing model (UKT) which employs stochastic distribution embeddings to represent the uncertainty in student interactions, with a Wasserstein self-attention mechanism designed to capture the transition of state distribution in student learning behaviors. Additionally, we introduce the aleatory uncertainty-aware contrastive learning loss, which strengthens the model's robustness towards different types of uncertainties. Extensive experiments on six real-world datasets demonstrate that UKT not only significantly surpasses existing deep learning-based models in KT prediction, but also shows unique advantages in handling the uncertainty of student interactions.
$\textbf{EMOS}$: $\textbf{E}$mbodiment-aware Heterogeneous $\textbf{M}$ulti-robot $\textbf{O}$perating $\textbf{S}$ystem with LLM Agents
Oct 30, 2024

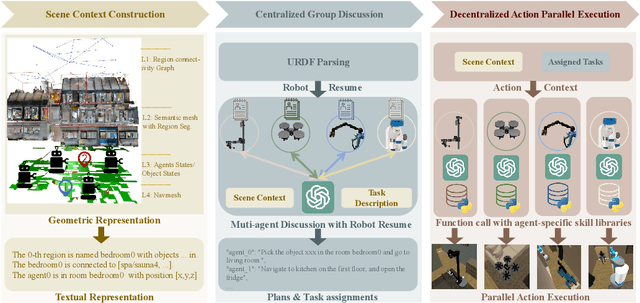

Abstract:Heterogeneous multi-robot systems (HMRS) have emerged as a powerful approach for tackling complex tasks that single robots cannot manage alone. Current large-language-model-based multi-agent systems (LLM-based MAS) have shown success in areas like software development and operating systems, but applying these systems to robot control presents unique challenges. In particular, the capabilities of each agent in a multi-robot system are inherently tied to the physical composition of the robots, rather than predefined roles. To address this issue, we introduce a novel multi-agent framework designed to enable effective collaboration among heterogeneous robots with varying embodiments and capabilities, along with a new benchmark named Habitat-MAS. One of our key designs is $\textit{Robot Resume}$: Instead of adopting human-designed role play, we propose a self-prompted approach, where agents comprehend robot URDF files and call robot kinematics tools to generate descriptions of their physics capabilities to guide their behavior in task planning and action execution. The Habitat-MAS benchmark is designed to assess how a multi-agent framework handles tasks that require embodiment-aware reasoning, which includes 1) manipulation, 2) perception, 3) navigation, and 4) comprehensive multi-floor object rearrangement. The experimental results indicate that the robot's resume and the hierarchical design of our multi-agent system are essential for the effective operation of the heterogeneous multi-robot system within this intricate problem context.
PLaMo-100B: A Ground-Up Language Model Designed for Japanese Proficiency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PLaMo-100B, a large-scale language model designed for Japanese proficiency. The model was trained from scratch using 2 trillion tokens, with architecture such as QK Normalization and Z-Loss to ensure training stability during the training process. Post-training techniques, including Supervised Fine-Tuning and Direct Preference Optimization, were applied to refine the model's performance. Benchmark evaluations suggest that PLaMo-100B performs well, particularly in Japanese-specific tasks, achieving results that are competitive with frontier models like GPT-4.
CRAB: Cross-environment Agent Benchmark for Multimodal Language Model Agents
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:The development of autonomous agents increasingly relies on Multimodal Language Models (MLMs) to perform tasks described in natural language with GUI environments, such as websites, desktop computers, or mobile phones. Existing benchmarks for MLM agents in interactive environments are limited by their focus on a single environment, lack of detailed and generalized evaluation methods, and the complexities of constructing tasks and evaluators. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Crab, the first agent benchmark framework designed to support cross-environment tasks, incorporating a graph-based fine-grained evaluation method and an efficient mechanism for task and evaluator construction. Our framework supports multiple devices and can be easily extended to any environment with a Python interface. Leveraging Crab, we developed a cross-platform Crab Benchmark-v0 comprising 100 tasks in computer desktop and mobile phone environments. We evaluated four advanced MLMs using different single and multi-agent system configurations on this benchmark. The experimental results demonstrate that the single agent with GPT-4o achieves the best completion ratio of 35.26%. All framework code, agent code, and task datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/camel-ai/crab.
Rapid detection and recognition of whole brain activity in a freely behaving Caenorhabditis elegans
Sep 23, 2021



Abstract:Advanced volumetric imaging methods and genetically encoded activity indicators have permitted a comprehensive characterization of whole brain activity at single neuron resolution in \textit{Caenorhabditis elegans}. The constant motion and deformation of the mollusc nervous system, however, impose a great challenge for a consistent identification of densely packed neurons in a behaving animal. Here, we propose a cascade solution for long-term and rapid recognition of head ganglion neurons in a freely moving \textit{C. elegans}. First, potential neuronal regions from a stack of fluorescence images are detected by a deep learning algorithm. Second, 2 dimensional neuronal regions are fused into 3 dimensional neuron entities. Third, by exploiting the neuronal density distribution surrounding a neuron and relative positional information between neurons, a multi-class artificial neural network transforms engineered neuronal feature vectors into digital neuronal identities. Under the constraint of a small number (20-40 volumes) of training samples, our bottom-up approach is able to process each volume - $1024 \times 1024 \times 18$ in voxels - in less than 1 second and achieves an accuracy of $91\%$ in neuronal detection and $74\%$ in neuronal recognition. Our work represents an important development towards a rapid and fully automated algorithm for decoding whole brain activity underlying natural animal behaviors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge