Toshiki Kataoka
Preferred Elements, Inc.
PLaMo 2 Technical Report
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce PLaMo 2, a series of Japanese-focused large language models featuring a hybrid Samba-based architecture that transitions to full attention via continual pre-training to support 32K token contexts. Training leverages extensive synthetic corpora to overcome data scarcity, while computational efficiency is achieved through weight reuse and structured pruning. This efficient pruning methodology produces an 8B model that achieves performance comparable to our previous 100B model. Post-training further refines the models using a pipeline of supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and direct preference optimization (DPO), enhanced by synthetic Japanese instruction data and model merging techniques. Optimized for inference using vLLM and quantization with minimal accuracy loss, the PLaMo 2 models achieve state-of-the-art results on Japanese benchmarks, outperforming similarly-sized open models in instruction-following, language fluency, and Japanese-specific knowledge.
Entropy Controllable Direct Preference Optimization
Nov 12, 2024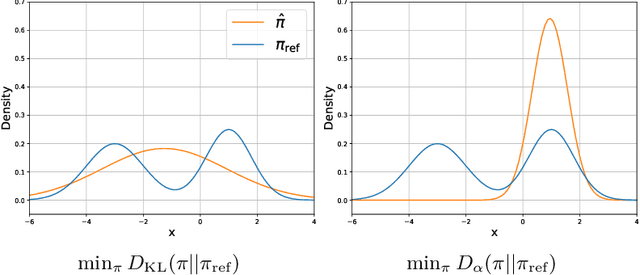
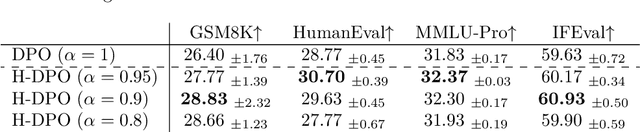
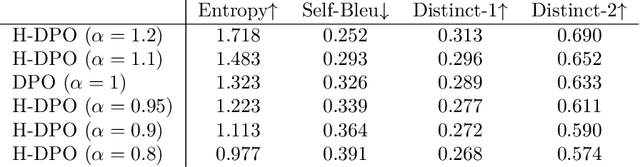
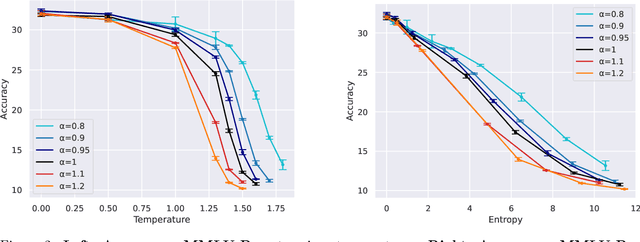
Abstract:In the post-training of large language models (LLMs), Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is an effective approach to achieve generation aligned with human preferences. Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) allows for policy training with a simple binary cross-entropy loss without a reward model. The objective of DPO is regularized by reverse KL divergence that encourages mode-seeking fitting to the reference policy. Nonetheless, we indicate that minimizing reverse KL divergence could fail to capture a mode of the reference distribution, which may hurt the policy's performance. Based on this observation, we propose a simple modification to DPO, H-DPO, which allows for control over the entropy of the resulting policy, enhancing the distribution's sharpness and thereby enabling mode-seeking fitting more effectively. In our experiments, we show that H-DPO outperformed DPO across various tasks, demonstrating superior results in pass@$k$ evaluations for mathematical tasks. Moreover, H-DPO is simple to implement, requiring only minor modifications to the loss calculation of DPO, which makes it highly practical and promising for wide-ranging applications in the training of LLMs.
PLaMo-100B: A Ground-Up Language Model Designed for Japanese Proficiency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PLaMo-100B, a large-scale language model designed for Japanese proficiency. The model was trained from scratch using 2 trillion tokens, with architecture such as QK Normalization and Z-Loss to ensure training stability during the training process. Post-training techniques, including Supervised Fine-Tuning and Direct Preference Optimization, were applied to refine the model's performance. Benchmark evaluations suggest that PLaMo-100B performs well, particularly in Japanese-specific tasks, achieving results that are competitive with frontier models like GPT-4.
ChainerRL: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Library
Dec 09, 2019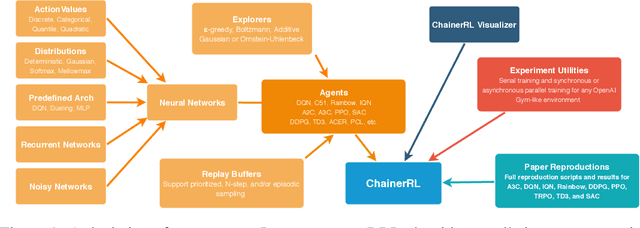
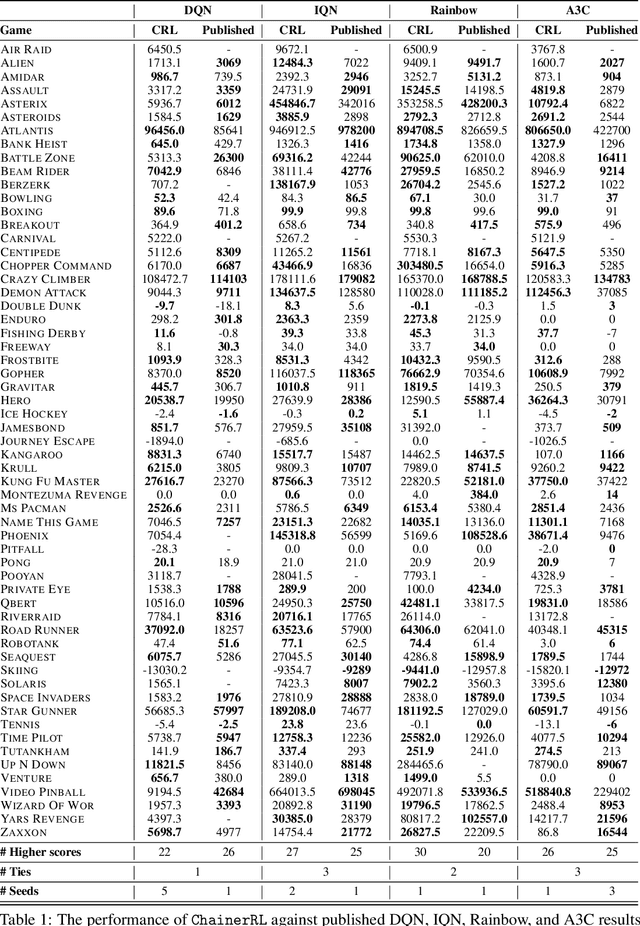
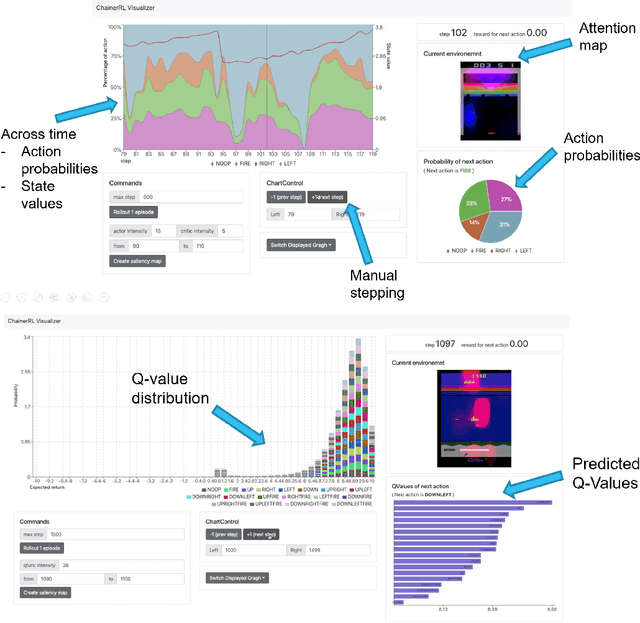

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce ChainerRL, an open-source Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) library built using Python and the Chainer deep learning framework. ChainerRL implements a comprehensive set of DRL algorithms and techniques drawn from the state-of-the-art research in the field. To foster reproducible research, and for instructional purposes, ChainerRL provides scripts that closely replicate the original papers' experimental settings and reproduce published benchmark results for several algorithms. Lastly, ChainerRL offers a visualization tool that enables the qualitative inspection of trained agents. The ChainerRL source code can be found on GitHub: https://github.com/chainer/chainerrl .
Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks
Feb 16, 2018



Abstract:One of the challenges in the study of generative adversarial networks is the instability of its training. In this paper, we propose a novel weight normalization technique called spectral normalization to stabilize the training of the discriminator. Our new normalization technique is computationally light and easy to incorporate into existing implementations. We tested the efficacy of spectral normalization on CIFAR10, STL-10, and ILSVRC2012 dataset, and we experimentally confirmed that spectrally normalized GANs (SN-GANs) is capable of generating images of better or equal quality relative to the previous training stabilization techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge