Hiroyoshi Komatsu
Preferred Elements, Inc.
PLaMo-100B: A Ground-Up Language Model Designed for Japanese Proficiency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PLaMo-100B, a large-scale language model designed for Japanese proficiency. The model was trained from scratch using 2 trillion tokens, with architecture such as QK Normalization and Z-Loss to ensure training stability during the training process. Post-training techniques, including Supervised Fine-Tuning and Direct Preference Optimization, were applied to refine the model's performance. Benchmark evaluations suggest that PLaMo-100B performs well, particularly in Japanese-specific tasks, achieving results that are competitive with frontier models like GPT-4.
The Logic for a Mildly Context-Sensitive Fragment of the Lambek-Grishin Calculus
Jan 10, 2021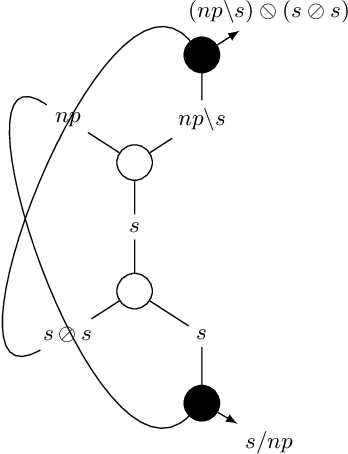
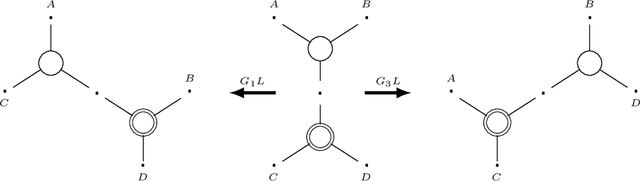
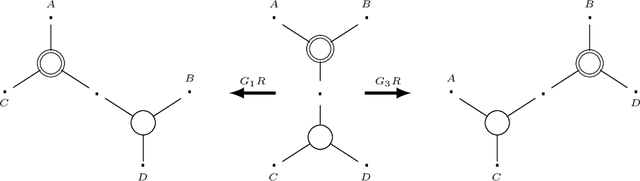
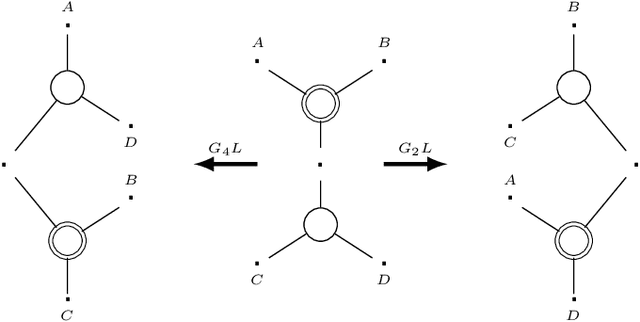
Abstract:While context-free grammars are characterized by a simple proof-theoretic grammatical formalism namely categorial grammar and its logic the Lambek calculus, no such characterizations were known for tree-adjoining grammars, and even for any mildly context-sensitive languages classes in the last forty years despite some efforts. We settle this problem in this paper. On the basis of the existing fragment of the Lambek-Grishin calculus which captures tree-adjoining languages, we present a logic called HLG: a proof-theoretic characterization of tree-adjoining languages based on the Lambek-Grishin calculus restricted to Hyperedge-replacement grammar with rank two studied by Moot. HLG is defined in display calculus with cut-admissibility. Several new techniques are introduced for the proofs, such as purely structural connectives, usefulness, and a graph-theoretic argument on proof nets for HLG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge