Suvir Mirchandani
RoboCade: Gamifying Robot Data Collection
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Imitation learning from human demonstrations has become a dominant approach for training autonomous robot policies. However, collecting demonstration datasets is costly: it often requires access to robots and needs sustained effort in a tedious, long process. These factors limit the scale of data available for training policies. We aim to address this scalability challenge by involving a broader audience in a gamified data collection experience that is both accessible and motivating. Specifically, we develop a gamified remote teleoperation platform, RoboCade, to engage general users in collecting data that is beneficial for downstream policy training. To do this, we embed gamification strategies into the design of the system interface and data collection tasks. In the system interface, we include components such as visual feedback, sound effects, goal visualizations, progress bars, leaderboards, and badges. We additionally propose principles for constructing gamified tasks that have overlapping structure with useful downstream target tasks. We instantiate RoboCade on three manipulation tasks -- including spatial arrangement, scanning, and insertion. To illustrate the viability of gamified robot data collection, we collect a demonstration dataset through our platform, and show that co-training robot policies with this data can improve success rate on non-gamified target tasks (+16-56%). Further, we conduct a user study to validate that novice users find the gamified platform significantly more enjoyable than a standard non-gamified platform (+24%). These results highlight the promise of gamified data collection as a scalable, accessible, and engaging method for collecting demonstration data.
Training Strategies for Efficient Embodied Reasoning
May 13, 2025Abstract:Robot chain-of-thought reasoning (CoT) -- wherein a model predicts helpful intermediate representations before choosing actions -- provides an effective method for improving the generalization and performance of robot policies, especially vision-language-action models (VLAs). While such approaches have been shown to improve performance and generalization, they suffer from core limitations, like needing specialized robot reasoning data and slow inference speeds. To design new robot reasoning approaches that address these issues, a more complete characterization of why reasoning helps policy performance is critical. We hypothesize several mechanisms by which robot reasoning improves policies -- (1) better representation learning, (2) improved learning curricularization, and (3) increased expressivity -- then devise simple variants of robot CoT reasoning to isolate and test each one. We find that learning to generate reasonings does lead to better VLA representations, while attending to the reasonings aids in actually leveraging these features for improved action prediction. Our results provide us with a better understanding of why CoT reasoning helps VLAs, which we use to introduce two simple and lightweight alternative recipes for robot reasoning. Our proposed approaches achieve significant performance gains over non-reasoning policies, state-of-the-art results on the LIBERO-90 benchmark, and a 3x inference speedup compared to standard robot reasoning.
What Matters for Batch Online Reinforcement Learning in Robotics?
May 12, 2025Abstract:The ability to learn from large batches of autonomously collected data for policy improvement -- a paradigm we refer to as batch online reinforcement learning -- holds the promise of enabling truly scalable robot learning by significantly reducing the need for human effort of data collection while getting benefits from self-improvement. Yet, despite the promise of this paradigm, it remains challenging to achieve due to algorithms not being able to learn effectively from the autonomous data. For example, prior works have applied imitation learning and filtered imitation learning methods to the batch online RL problem, but these algorithms often fail to efficiently improve from the autonomously collected data or converge quickly to a suboptimal point. This raises the question of what matters for effective batch online RL in robotics. Motivated by this question, we perform a systematic empirical study of three axes -- (i) algorithm class, (ii) policy extraction methods, and (iii) policy expressivity -- and analyze how these axes affect performance and scaling with the amount of autonomous data. Through our analysis, we make several observations. First, we observe that the use of Q-functions to guide batch online RL significantly improves performance over imitation-based methods. Building on this, we show that an implicit method of policy extraction -- via choosing the best action in the distribution of the policy -- is necessary over traditional policy extraction methods from offline RL. Next, we show that an expressive policy class is preferred over less expressive policy classes. Based on this analysis, we propose a general recipe for effective batch online RL. We then show a simple addition to the recipe of using temporally-correlated noise to obtain more diversity results in further performance gains. Our recipe obtains significantly better performance and scaling compared to prior methods.
Robot Data Curation with Mutual Information Estimators
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:The performance of imitation learning policies often hinges on the datasets with which they are trained. Consequently, investment in data collection for robotics has grown across both industrial and academic labs. However, despite the marked increase in the quantity of demonstrations collected, little work has sought to assess the quality of said data despite mounting evidence of its importance in other areas such as vision and language. In this work, we take a critical step towards addressing the data quality in robotics. Given a dataset of demonstrations, we aim to estimate the relative quality of individual demonstrations in terms of both state diversity and action predictability. To do so, we estimate the average contribution of a trajectory towards the mutual information between states and actions in the entire dataset, which precisely captures both the entropy of the state distribution and the state-conditioned entropy of actions. Though commonly used mutual information estimators require vast amounts of data often beyond the scale available in robotics, we introduce a novel technique based on k-nearest neighbor estimates of mutual information on top of simple VAE embeddings of states and actions. Empirically, we demonstrate that our approach is able to partition demonstration datasets by quality according to human expert scores across a diverse set of benchmarks spanning simulation and real world environments. Moreover, training policies based on data filtered by our method leads to a 5-10% improvement in RoboMimic and better performance on real ALOHA and Franka setups.
Action-Free Reasoning for Policy Generalization
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:End-to-end imitation learning offers a promising approach for training robot policies. However, generalizing to new settings remains a significant challenge. Although large-scale robot demonstration datasets have shown potential for inducing generalization, they are resource-intensive to scale. In contrast, human video data is abundant and diverse, presenting an attractive alternative. Yet, these human-video datasets lack action labels, complicating their use in imitation learning. Existing methods attempt to extract grounded action representations (e.g., hand poses), but resulting policies struggle to bridge the embodiment gap between human and robot actions. We propose an alternative approach: leveraging language-based reasoning from human videos-essential for guiding robot actions-to train generalizable robot policies. Building on recent advances in reasoning-based policy architectures, we introduce Reasoning through Action-free Data (RAD). RAD learns from both robot demonstration data (with reasoning and action labels) and action-free human video data (with only reasoning labels). The robot data teaches the model to map reasoning to low-level actions, while the action-free data enhances reasoning capabilities. Additionally, we will release a new dataset of 3,377 human-hand demonstrations with reasoning annotations compatible with the Bridge V2 benchmark and aimed at facilitating future research on reasoning-driven robot learning. Our experiments show that RAD enables effective transfer across the embodiment gap, allowing robots to perform tasks seen only in action-free data. Furthermore, scaling up action-free reasoning data significantly improves policy performance and generalization to novel tasks. These results highlight the promise of reasoning-driven learning from action-free datasets for advancing generalizable robot control. Project page: https://rad-generalization.github.io
Vocal Sandbox: Continual Learning and Adaptation for Situated Human-Robot Collaboration
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Vocal Sandbox, a framework for enabling seamless human-robot collaboration in situated environments. Systems in our framework are characterized by their ability to adapt and continually learn at multiple levels of abstraction from diverse teaching modalities such as spoken dialogue, object keypoints, and kinesthetic demonstrations. To enable such adaptation, we design lightweight and interpretable learning algorithms that allow users to build an understanding and co-adapt to a robot's capabilities in real-time, as they teach new behaviors. For example, after demonstrating a new low-level skill for "tracking around" an object, users are provided with trajectory visualizations of the robot's intended motion when asked to track a new object. Similarly, users teach high-level planning behaviors through spoken dialogue, using pretrained language models to synthesize behaviors such as "packing an object away" as compositions of low-level skills $-$ concepts that can be reused and built upon. We evaluate Vocal Sandbox in two settings: collaborative gift bag assembly and LEGO stop-motion animation. In the first setting, we run systematic ablations and user studies with 8 non-expert participants, highlighting the impact of multi-level teaching. Across 23 hours of total robot interaction time, users teach 17 new high-level behaviors with an average of 16 novel low-level skills, requiring 22.1% less active supervision compared to baselines and yielding more complex autonomous performance (+19.7%) with fewer failures (-67.1%). Qualitatively, users strongly prefer Vocal Sandbox systems due to their ease of use (+20.6%) and overall performance (+13.9%). Finally, we pair an experienced system-user with a robot to film a stop-motion animation; over two hours of continuous collaboration, the user teaches progressively more complex motion skills to shoot a 52 second (232 frame) movie.
So You Think You Can Scale Up Autonomous Robot Data Collection?
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:A long-standing goal in robot learning is to develop methods for robots to acquire new skills autonomously. While reinforcement learning (RL) comes with the promise of enabling autonomous data collection, it remains challenging to scale in the real-world partly due to the significant effort required for environment design and instrumentation, including the need for designing reset functions or accurate success detectors. On the other hand, imitation learning (IL) methods require little to no environment design effort, but instead require significant human supervision in the form of collected demonstrations. To address these shortcomings, recent works in autonomous IL start with an initial seed dataset of human demonstrations that an autonomous policy can bootstrap from. While autonomous IL approaches come with the promise of addressing the challenges of autonomous RL as well as pure IL strategies, in this work, we posit that such techniques do not deliver on this promise and are still unable to scale up autonomous data collection in the real world. Through a series of real-world experiments, we demonstrate that these approaches, when scaled up to realistic settings, face much of the same scaling challenges as prior attempts in RL in terms of environment design. Further, we perform a rigorous study of autonomous IL methods across different data scales and 7 simulation and real-world tasks, and demonstrate that while autonomous data collection can modestly improve performance, simply collecting more human data often provides significantly more improvement. Our work suggests a negative result: that scaling up autonomous data collection for learning robot policies for real-world tasks is more challenging and impractical than what is suggested in prior work. We hope these insights about the core challenges of scaling up data collection help inform future efforts in autonomous learning.
RoboCrowd: Scaling Robot Data Collection through Crowdsourcing
Nov 04, 2024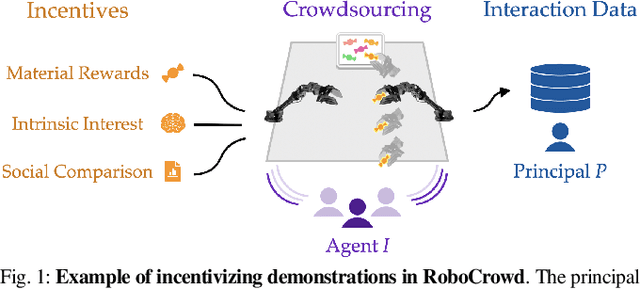
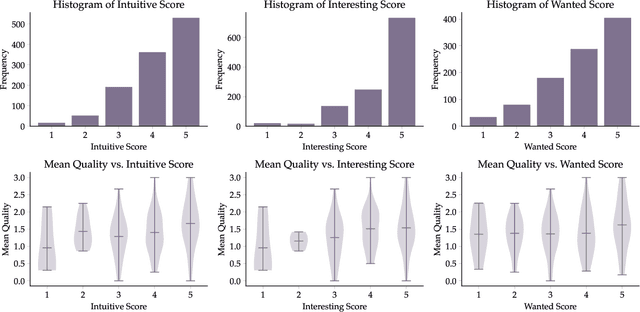
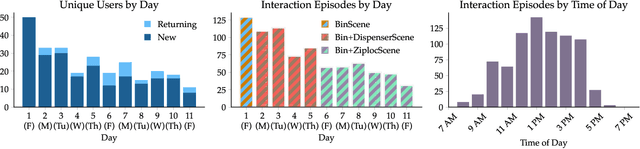
Abstract:In recent years, imitation learning from large-scale human demonstrations has emerged as a promising paradigm for training robot policies. However, the burden of collecting large quantities of human demonstrations is significant in terms of collection time and the need for access to expert operators. We introduce a new data collection paradigm, RoboCrowd, which distributes the workload by utilizing crowdsourcing principles and incentive design. RoboCrowd helps enable scalable data collection and facilitates more efficient learning of robot policies. We build RoboCrowd on top of ALOHA (Zhao et al. 2023) -- a bimanual platform that supports data collection via puppeteering -- to explore the design space for crowdsourcing in-person demonstrations in a public environment. We propose three classes of incentive mechanisms to appeal to users' varying sources of motivation for interacting with the system: material rewards, intrinsic interest, and social comparison. We instantiate these incentives through tasks that include physical rewards, engaging or challenging manipulations, as well as gamification elements such as a leaderboard. We conduct a large-scale, two-week field experiment in which the platform is situated in a university cafe. We observe significant engagement with the system -- over 200 individuals independently volunteered to provide a total of over 800 interaction episodes. Our findings validate the proposed incentives as mechanisms for shaping users' data quantity and quality. Further, we demonstrate that the crowdsourced data can serve as useful pre-training data for policies fine-tuned on expert demonstrations -- boosting performance up to 20% compared to when this data is not available. These results suggest the potential for RoboCrowd to reduce the burden of robot data collection by carefully implementing crowdsourcing and incentive design principles.
DROID: A Large-Scale In-The-Wild Robot Manipulation Dataset
Mar 19, 2024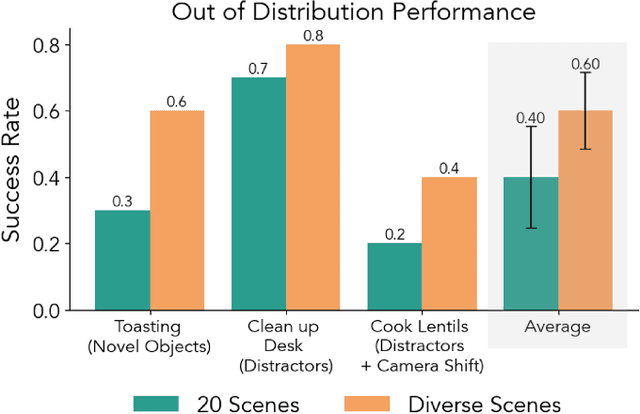
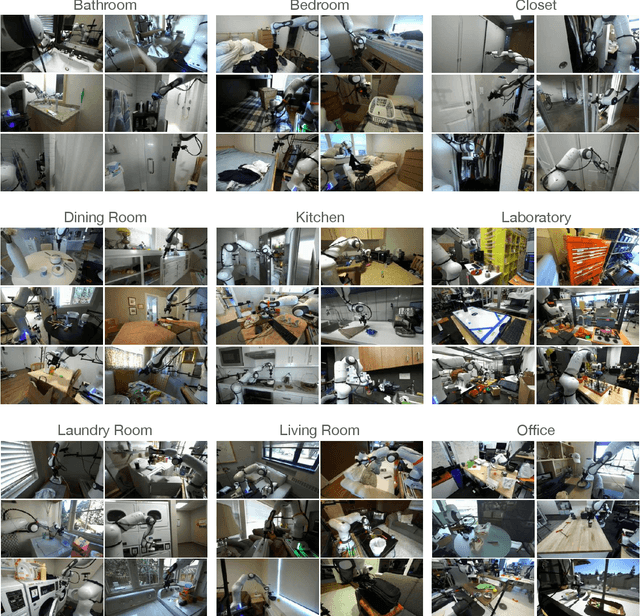


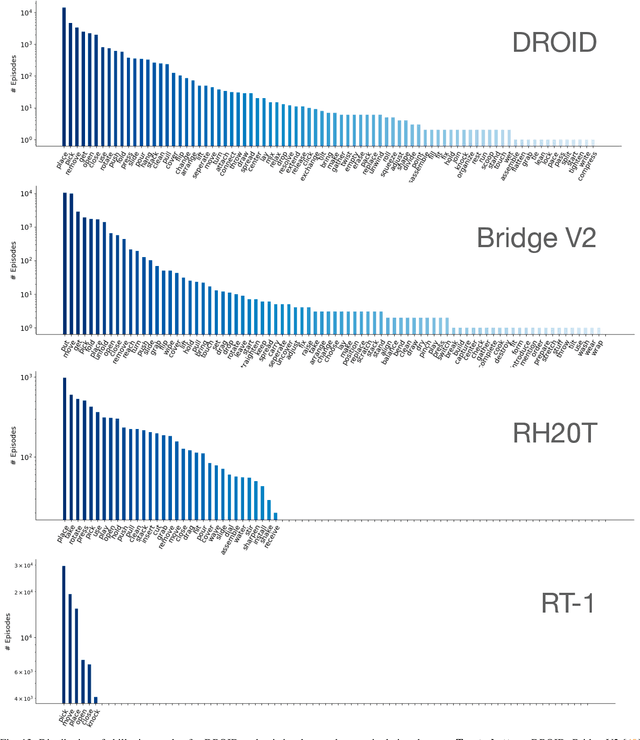
Abstract:The creation of large, diverse, high-quality robot manipulation datasets is an important stepping stone on the path toward more capable and robust robotic manipulation policies. However, creating such datasets is challenging: collecting robot manipulation data in diverse environments poses logistical and safety challenges and requires substantial investments in hardware and human labour. As a result, even the most general robot manipulation policies today are mostly trained on data collected in a small number of environments with limited scene and task diversity. In this work, we introduce DROID (Distributed Robot Interaction Dataset), a diverse robot manipulation dataset with 76k demonstration trajectories or 350 hours of interaction data, collected across 564 scenes and 84 tasks by 50 data collectors in North America, Asia, and Europe over the course of 12 months. We demonstrate that training with DROID leads to policies with higher performance and improved generalization ability. We open source the full dataset, policy learning code, and a detailed guide for reproducing our robot hardware setup.
Imitation Bootstrapped Reinforcement Learning
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:Despite the considerable potential of reinforcement learning (RL), robotics control tasks predominantly rely on imitation learning (IL) owing to its better sample efficiency. However, given the high cost of collecting extensive demonstrations, RL is still appealing if it can utilize limited imitation data for efficient autonomous self-improvement. Existing RL methods that utilize demonstrations either initialize the replay buffer with demonstrations and oversample them during RL training, which does not benefit from the generalization potential of modern IL methods, or pretrain the RL policy with IL on the demonstrations, which requires additional mechanisms to prevent catastrophic forgetting during RL fine-tuning. We propose imitation bootstrapped reinforcement learning (IBRL), a novel framework that first trains an IL policy on a limited number of demonstrations and then uses it to propose alternative actions for both online exploration and target value bootstrapping. IBRL achieves SoTA performance and sample efficiency on 7 challenging sparse reward continuous control tasks in simulation while learning directly from pixels. As a highlight of our method, IBRL achieves $6.4\times$ higher success rate than RLPD, a strong method that combines the idea of oversampling demonstrations with modern RL improvements, under the budget of 10 demos and 100K interactions in the challenging PickPlaceCan task in the Robomimic benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge