Shaurya Rohatgi
Pre-review to Peer review: Pitfalls of Automating Reviews using Large Language Models
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models are versatile general-task solvers, and their capabilities can truly assist people with scholarly peer review as \textit{pre-review} agents, if not as fully autonomous \textit{peer-review} agents. While incredibly beneficial, automating academic peer-review, as a concept, raises concerns surrounding safety, research integrity, and the validity of the academic peer-review process. The majority of the studies performing a systematic evaluation of frontier LLMs generating reviews across science disciplines miss the mark on addressing the alignment/misalignment of reviews along with the utility of LLM generated reviews when compared against publication outcomes such as \textbf{Citations}, \textbf{Hit-papers}, \textbf{Novelty}, and \textbf{Disruption}. This paper presents an experimental study in which we gathered ground-truth reviewer ratings from OpenReview and used various frontier open-weight LLMs to generate reviews of papers to gauge the safety and reliability of incorporating LLMs into the scientific review pipeline. Our findings demonstrate the utility of frontier open-weight LLMs as pre-review screening agents despite highlighting fundamental misalignment risks when deployed as autonomous reviewers. Our results show that all models exhibit weak correlation with human peer reviewers (0.15), with systematic overestimation bias of 3-5 points and uniformly high confidence scores (8.0-9.0/10) despite prediction errors. However, we also observed that LLM reviews correlate more strongly with post-publication metrics than with human scores, suggesting potential utility as pre-review screening tools. Our findings highlight the potential and address the pitfalls of automating peer reviews with language models. We open-sourced our dataset $D_{LMRSD}$ to help the research community expand the safety framework of automating scientific reviews.
Do Large Multimodal Models Solve Caption Generation for Scientific Figures? Lessons Learned from SCICAP Challenge 2023
Jan 31, 2025
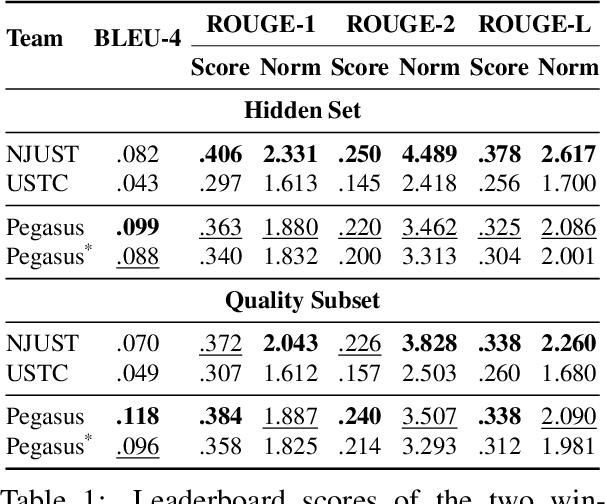
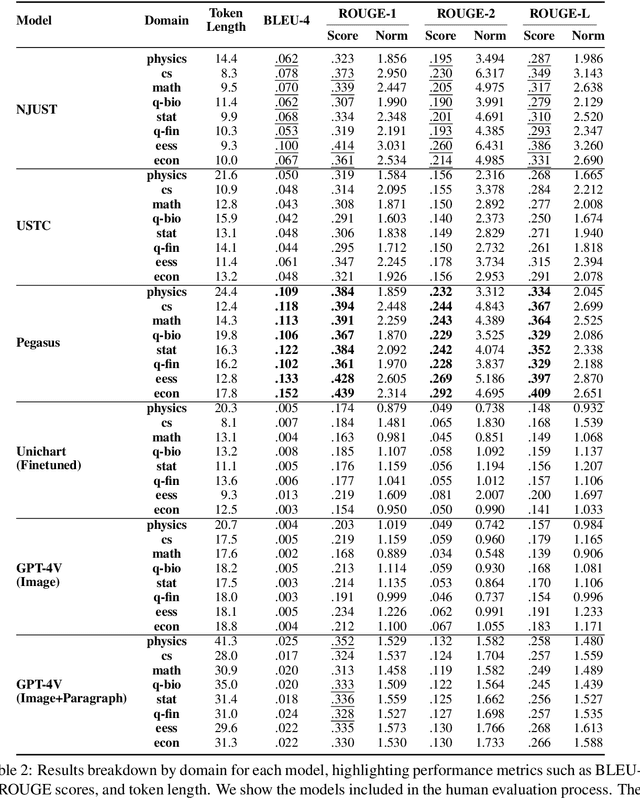
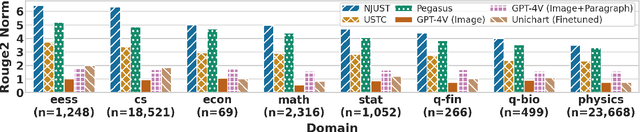
Abstract:Since the SCICAP datasets launch in 2021, the research community has made significant progress in generating captions for scientific figures in scholarly articles. In 2023, the first SCICAP Challenge took place, inviting global teams to use an expanded SCICAP dataset to develop models for captioning diverse figure types across various academic fields. At the same time, text generation models advanced quickly, with many powerful pre-trained large multimodal models (LMMs) emerging that showed impressive capabilities in various vision-and-language tasks. This paper presents an overview of the first SCICAP Challenge and details the performance of various models on its data, capturing a snapshot of the fields state. We found that professional editors overwhelmingly preferred figure captions generated by GPT-4V over those from all other models and even the original captions written by authors. Following this key finding, we conducted detailed analyses to answer this question: Have advanced LMMs solved the task of generating captions for scientific figures?
If in a Crowdsourced Data Annotation Pipeline, a GPT-4
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies indicated GPT-4 outperforms online crowd workers in data labeling accuracy, notably workers from Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk). However, these studies were criticized for deviating from standard crowdsourcing practices and emphasizing individual workers' performances over the whole data-annotation process. This paper compared GPT-4 and an ethical and well-executed MTurk pipeline, with 415 workers labeling 3,177 sentence segments from 200 scholarly articles using the CODA-19 scheme. Two worker interfaces yielded 127,080 labels, which were then used to infer the final labels through eight label-aggregation algorithms. Our evaluation showed that despite best practices, MTurk pipeline's highest accuracy was 81.5%, whereas GPT-4 achieved 83.6%. Interestingly, when combining GPT-4's labels with crowd labels collected via an advanced worker interface for aggregation, 2 out of the 8 algorithms achieved an even higher accuracy (87.5%, 87.0%). Further analysis suggested that, when the crowd's and GPT-4's labeling strengths are complementary, aggregating them could increase labeling accuracy.
Fighting Fire with Fire: The Dual Role of LLMs in Crafting and Detecting Elusive Disinformation
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Recent ubiquity and disruptive impacts of large language models (LLMs) have raised concerns about their potential to be misused (.i.e, generating large-scale harmful and misleading content). To combat this emerging risk of LLMs, we propose a novel "Fighting Fire with Fire" (F3) strategy that harnesses modern LLMs' generative and emergent reasoning capabilities to counter human-written and LLM-generated disinformation. First, we leverage GPT-3.5-turbo to synthesize authentic and deceptive LLM-generated content through paraphrase-based and perturbation-based prefix-style prompts, respectively. Second, we apply zero-shot in-context semantic reasoning techniques with cloze-style prompts to discern genuine from deceptive posts and news articles. In our extensive experiments, we observe GPT-3.5-turbo's zero-shot superiority for both in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets, where GPT-3.5-turbo consistently achieved accuracy at 68-72%, unlike the decline observed in previous customized and fine-tuned disinformation detectors. Our codebase and dataset are available at https://github.com/mickeymst/F3.
The ACL OCL Corpus: advancing Open science in Computational Linguistics
May 24, 2023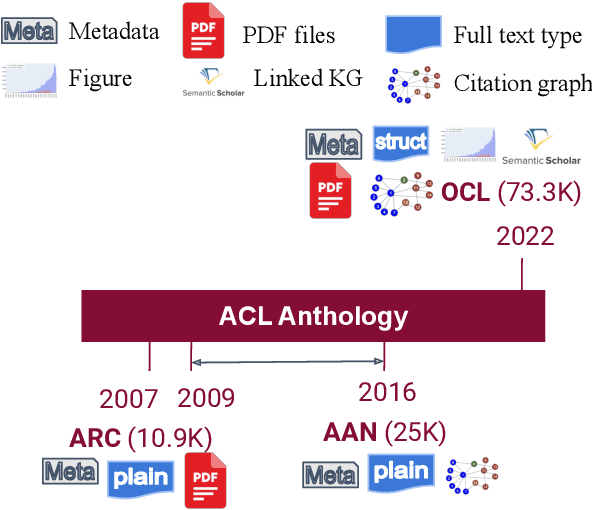
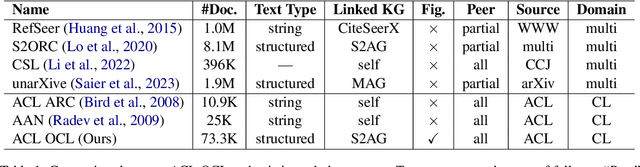

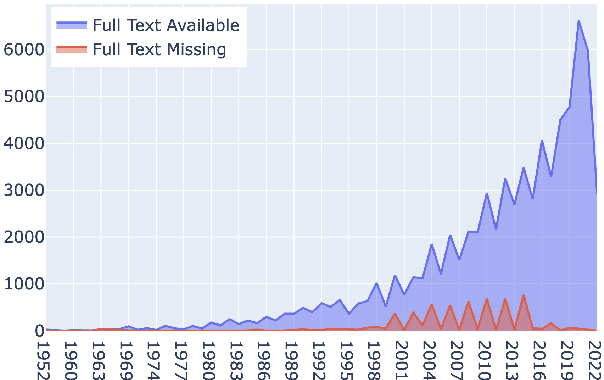
Abstract:We present a scholarly corpus from the ACL Anthology to assist Open scientific research in the Computational Linguistics domain, named as ACL OCL. Compared with previous ARC and AAN versions, ACL OCL includes structured full-texts with logical sections, references to figures, and links to a large knowledge resource (semantic scholar). ACL OCL contains 74k scientific papers, together with 210k figures extracted up to September 2022. To observe the development in the computational linguistics domain, we detect the topics of all OCL papers with a supervised neural model. We observe ''Syntax: Tagging, Chunking and Parsing'' topic is significantly shrinking and ''Natural Language Generation'' is resurging. Our dataset is open and available to download from HuggingFace in https://huggingface.co/datasets/ACL-OCL/ACL-OCL-Corpus.
ACL-Fig: A Dataset for Scientific Figure Classification
Jan 28, 2023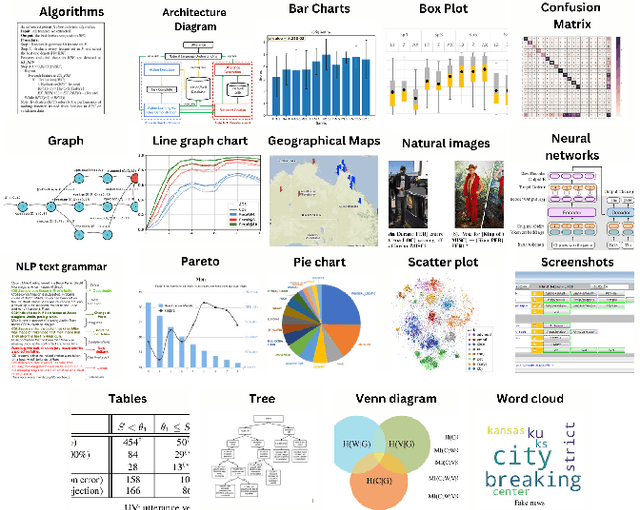
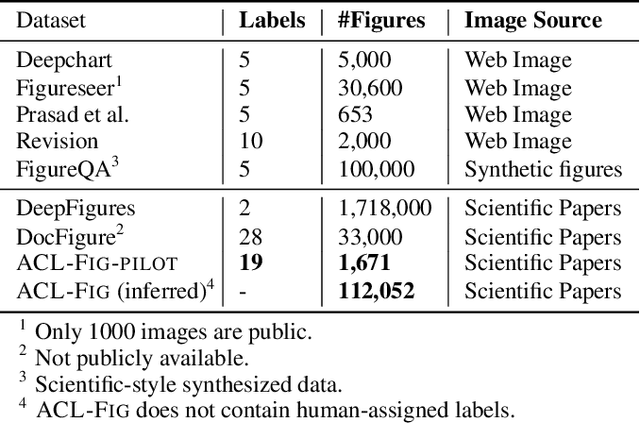
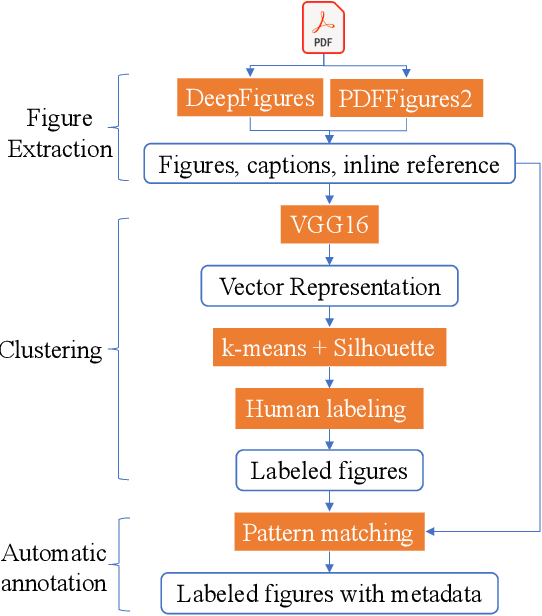

Abstract:Most existing large-scale academic search engines are built to retrieve text-based information. However, there are no large-scale retrieval services for scientific figures and tables. One challenge for such services is understanding scientific figures' semantics, such as their types and purposes. A key obstacle is the need for datasets containing annotated scientific figures and tables, which can then be used for classification, question-answering, and auto-captioning. Here, we develop a pipeline that extracts figures and tables from the scientific literature and a deep-learning-based framework that classifies scientific figures using visual features. Using this pipeline, we built the first large-scale automatically annotated corpus, ACL-Fig, consisting of 112,052 scientific figures extracted from ~56K research papers in the ACL Anthology. The ACL-Fig-Pilot dataset contains 1,671 manually labeled scientific figures belonging to 19 categories. The dataset is accessible at https://huggingface.co/datasets/citeseerx/ACL-fig under a CC BY-NC license.
The Semantic Scholar Open Data Platform
Jan 24, 2023



Abstract:The volume of scientific output is creating an urgent need for automated tools to help scientists keep up with developments in their field. Semantic Scholar (S2) is an open data platform and website aimed at accelerating science by helping scholars discover and understand scientific literature. We combine public and proprietary data sources using state-of-the-art techniques for scholarly PDF content extraction and automatic knowledge graph construction to build the Semantic Scholar Academic Graph, the largest open scientific literature graph to-date, with 200M+ papers, 80M+ authors, 550M+ paper-authorship edges, and 2.4B+ citation edges. The graph includes advanced semantic features such as structurally parsed text, natural language summaries, and vector embeddings. In this paper, we describe the components of the S2 data processing pipeline and the associated APIs offered by the platform. We will update this living document to reflect changes as we add new data offerings and improve existing services.
Large Scale Subject Category Classification of Scholarly Papers with Deep Attentive Neural Networks
Jul 27, 2020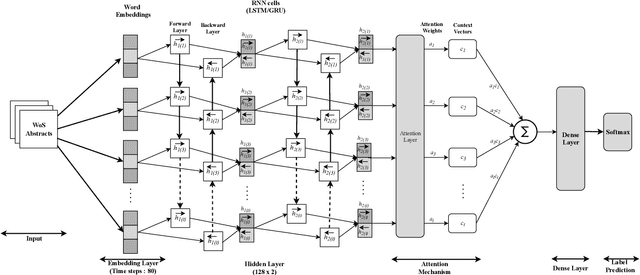
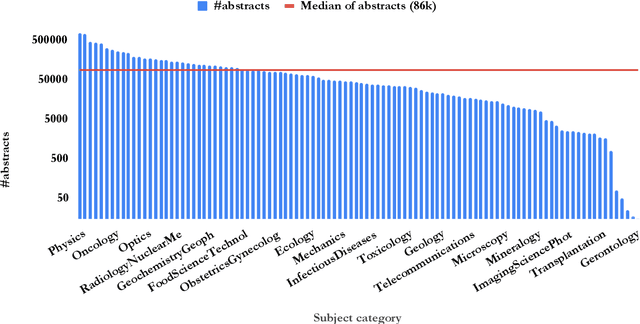
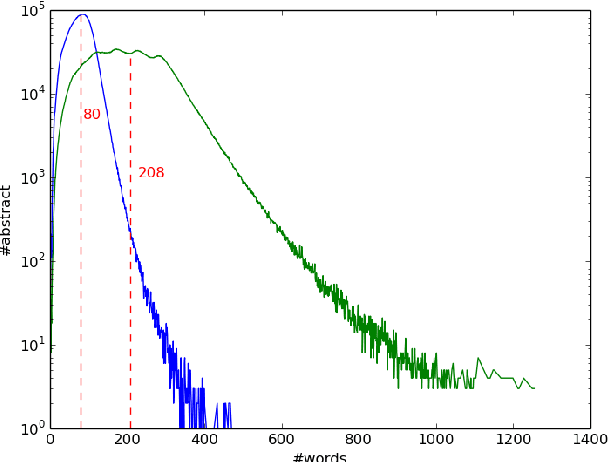
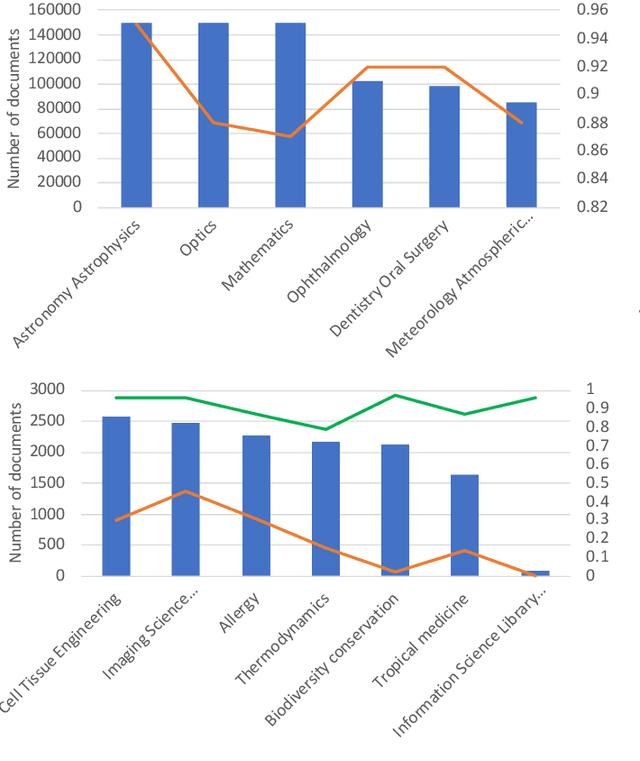
Abstract:Subject categories of scholarly papers generally refer to the knowledge domain(s) to which the papers belong, examples being computer science or physics. Subject category information can be used for building faceted search for digital library search engines. This can significantly assist users in narrowing down their search space of relevant documents. Unfortunately, many academic papers do not have such information as part of their metadata. Existing methods for solving this task usually focus on unsupervised learning that often relies on citation networks. However, a complete list of papers citing the current paper may not be readily available. In particular, new papers that have few or no citations cannot be classified using such methods. Here, we propose a deep attentive neural network (DANN) that classifies scholarly papers using only their abstracts. The network is trained using 9 million abstracts from Web of Science (WoS). We also use the WoS schema that covers 104 subject categories. The proposed network consists of two bi-directional recurrent neural networks followed by an attention layer. We compare our model against baselines by varying the architecture and text representation. Our best model achieves micro-F1 measure of 0.76 with F1 of individual subject categories ranging from 0.50-0.95. The results showed the importance of retraining word embedding models to maximize the vocabulary overlap and the effectiveness of the attention mechanism. The combination of word vectors with TFIDF outperforms character and sentence level embedding models. We discuss imbalanced samples and overlapping categories and suggest possible strategies for mitigation. We also determine the subject category distribution in CiteSeerX by classifying a random sample of one million academic papers.
DeepNorm-A Deep Learning Approach to Text Normalization
Dec 17, 2017



Abstract:This paper presents an simple yet sophisticated approach to the challenge by Sproat and Jaitly (2016)- given a large corpus of written text aligned to its normalized spoken form, train an RNN to learn the correct normalization function. Text normalization for a token seems very straightforward without it's context. But given the context of the used token and then normalizing becomes tricky for some classes. We present a novel approach in which the prediction of our classification algorithm is used by our sequence to sequence model to predict the normalized text of the input token. Our approach takes very less time to learn and perform well unlike what has been reported by Google (5 days on their GPU cluster). We have achieved an accuracy of 97.62 which is impressive given the resources we use. Our approach is using the best of both worlds, gradient boosting - state of the art in most classification tasks and sequence to sequence learning - state of the art in machine translation. We present our experiments and report results with various parameter settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge