Lun-Wei Ku
Academia Sinica, Taiwan
Beyond Many-Shot Translation: Scaling In-Context Demonstrations For Low-Resource Machine Translation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Building machine translation (MT) systems for low-resource languages is notably difficult due to the scarcity of high-quality data. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) have improved MT system performance, adapting them to lesser-represented languages remains challenging. In-context learning (ICL) may offer novel ways to adapt LLMs for low-resource MT by conditioning models on demonstration at inference time. In this study, we explore scaling low-resource machine translation ICL beyond the few-shot setting to thousands of examples with long-context models. We scale in-context token budget to 1M tokens and compare three types of training corpora used as in-context supervision: monolingual unsupervised data, instruction-style data, and parallel data (English--target and Indonesian--target). Our experiments on Javanese and Sundanese show that gains from additional context saturate quickly and can degrade near the maximum context window, with scaling behavior strongly dependent on corpus type. Notably, some forms of monolingual supervision can be competitive with parallel data, despite the latter offering additional supervision. Overall, our results characterize the effective limits and corpus-type sensitivity of long-context ICL for low-resource MT, highlighting that larger context windows do not necessarily yield proportional quality gains.
Do Large Multimodal Models Solve Caption Generation for Scientific Figures? Lessons Learned from SCICAP Challenge 2023
Jan 31, 2025
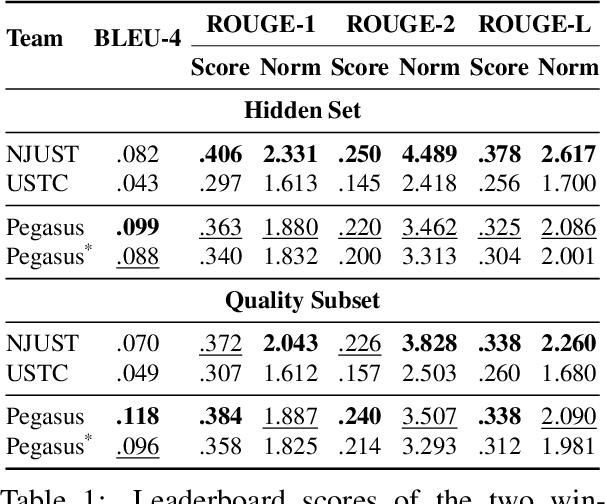
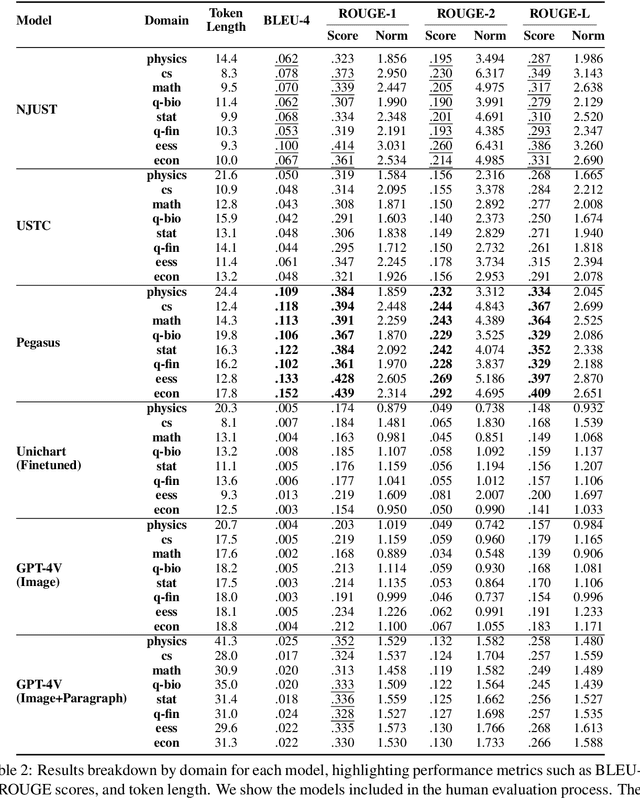
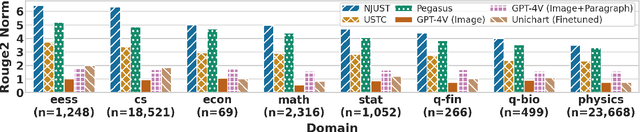
Abstract:Since the SCICAP datasets launch in 2021, the research community has made significant progress in generating captions for scientific figures in scholarly articles. In 2023, the first SCICAP Challenge took place, inviting global teams to use an expanded SCICAP dataset to develop models for captioning diverse figure types across various academic fields. At the same time, text generation models advanced quickly, with many powerful pre-trained large multimodal models (LMMs) emerging that showed impressive capabilities in various vision-and-language tasks. This paper presents an overview of the first SCICAP Challenge and details the performance of various models on its data, capturing a snapshot of the fields state. We found that professional editors overwhelmingly preferred figure captions generated by GPT-4V over those from all other models and even the original captions written by authors. Following this key finding, we conducted detailed analyses to answer this question: Have advanced LMMs solved the task of generating captions for scientific figures?
YourSkatingCoach: A Figure Skating Video Benchmark for Fine-Grained Element Analysis
Oct 27, 2024Abstract:Combining sports and machine learning involves leveraging ML algorithms and techniques to extract insight from sports-related data such as player statistics, game footage, and other relevant information. However, datasets related to figure skating in the literature focus primarily on element classification and are currently unavailable or exhibit only limited access, which greatly raise the entry barrier to developing visual sports technology for it. Moreover, when using such data to help athletes improve their skills, we find they are very coarse-grained: they work for learning what an element is, but they are poorly suited to learning whether the element is good or bad. Here we propose air time detection, a novel motion analysis task, the goal of which is to accurately detect the duration of the air time of a jump. We present YourSkatingCoach, a large, novel figure skating dataset which contains 454 videos of jump elements, the detected skater skeletons in each video, along with the gold labels of the start and ending frames of each jump, together as a video benchmark for figure skating. In addition, although this type of task is often viewed as classification, we cast it as a sequential labeling problem and propose a Transformer-based model to calculate the duration. Experimental results show that the proposed model yields a favorable results for a strong baseline. To further verify the generalizability of the fine-grained labels, we apply the same process to other sports as cross-sports tasks but for coarse-grained task action classification. Here we fine-tune the classification to demonstrate that figure skating, as it contains the essential body movements, constitutes a strong foundation for adaptation to other sports.
SocialNLP Fake-EmoReact 2021 Challenge Overview: Predicting Fake Tweets from Their Replies and GIFs
May 31, 2024

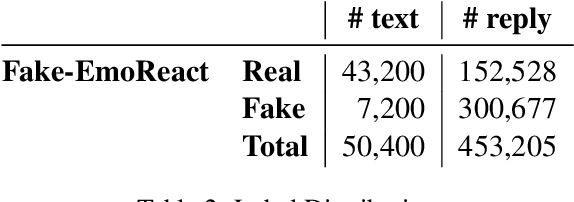

Abstract:This paper provides an overview of the Fake-EmoReact 2021 Challenge, held at the 9th SocialNLP Workshop, in conjunction with NAACL 2021. The challenge requires predicting the authenticity of tweets using reply context and augmented GIF categories from EmotionGIF dataset. We offer the Fake-EmoReact dataset with more than 453k as the experimental materials, where every tweet is labeled with authenticity. Twenty-four teams registered to participate in this challenge, and 5 submitted their results successfully in the evaluation phase. The best team achieves 93.9 on Fake-EmoReact 2021 dataset using F1 score. In addition, we show the definition of share task, data collection, and the teams' performance that joined this challenge and their approaches.
MAAIG: Motion Analysis And Instruction Generation
Nov 02, 2023Abstract:Many people engage in self-directed sports training at home but lack the real-time guidance of professional coaches, making them susceptible to injuries or the development of incorrect habits. In this paper, we propose a novel application framework called MAAIG(Motion Analysis And Instruction Generation). It can generate embedding vectors for each frame based on user-provided sports action videos. These embedding vectors are associated with the 3D skeleton of each frame and are further input into a pretrained T5 model. Ultimately, our model utilizes this information to generate specific sports instructions. It has the capability to identify potential issues and provide real-time guidance in a manner akin to professional coaches, helping users improve their sports skills and avoid injuries.
Is Explanation the Cure? Misinformation Mitigation in the Short Term and Long Term
Oct 26, 2023
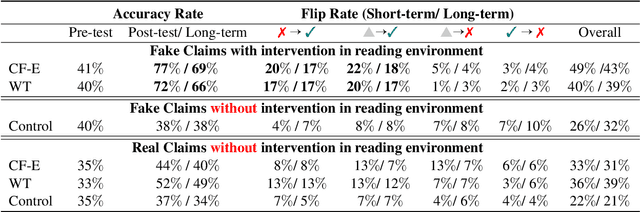
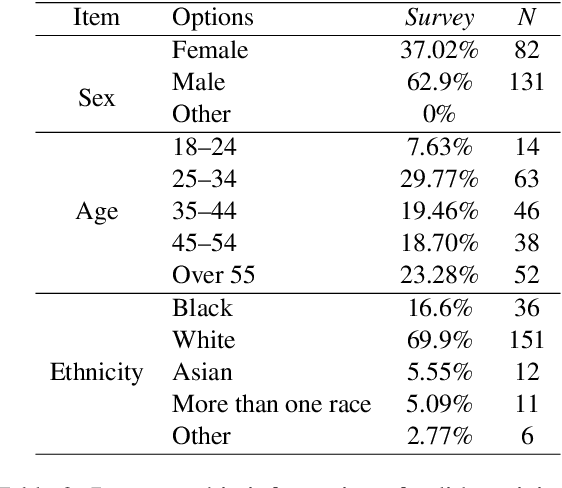
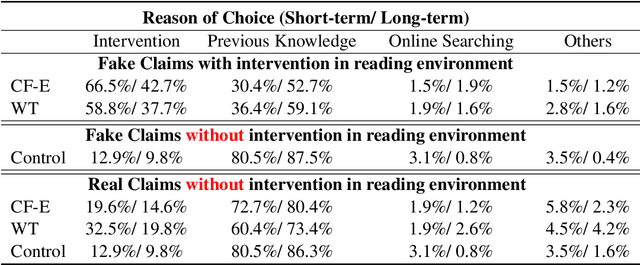
Abstract:With advancements in natural language processing (NLP) models, automatic explanation generation has been proposed to mitigate misinformation on social media platforms in addition to adding warning labels to identified fake news. While many researchers have focused on generating good explanations, how these explanations can really help humans combat fake news is under-explored. In this study, we compare the effectiveness of a warning label and the state-of-the-art counterfactual explanations generated by GPT-4 in debunking misinformation. In a two-wave, online human-subject study, participants (N = 215) were randomly assigned to a control group in which false contents are shown without any intervention, a warning tag group in which the false claims were labeled, or an explanation group in which the false contents were accompanied by GPT-4 generated explanations. Our results show that both interventions significantly decrease participants' self-reported belief in fake claims in an equivalent manner for the short-term and long-term. We discuss the implications of our findings and directions for future NLP-based misinformation debunking strategies.
Location-Aware Visual Question Generation with Lightweight Models
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:This work introduces a novel task, location-aware visual question generation (LocaVQG), which aims to generate engaging questions from data relevant to a particular geographical location. Specifically, we represent such location-aware information with surrounding images and a GPS coordinate. To tackle this task, we present a dataset generation pipeline that leverages GPT-4 to produce diverse and sophisticated questions. Then, we aim to learn a lightweight model that can address the LocaVQG task and fit on an edge device, such as a mobile phone. To this end, we propose a method which can reliably generate engaging questions from location-aware information. Our proposed method outperforms baselines regarding human evaluation (e.g., engagement, grounding, coherence) and automatic evaluation metrics (e.g., BERTScore, ROUGE-2). Moreover, we conduct extensive ablation studies to justify our proposed techniques for both generating the dataset and solving the task.
LLM-in-the-loop: Leveraging Large Language Model for Thematic Analysis
Oct 23, 2023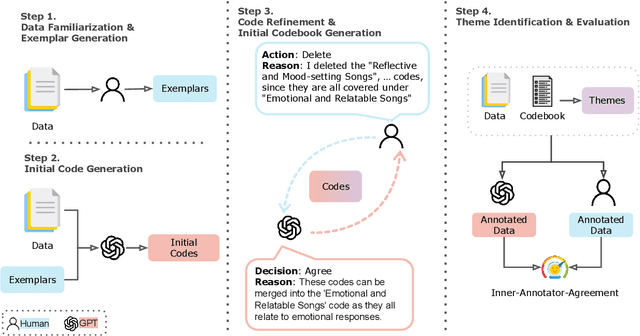
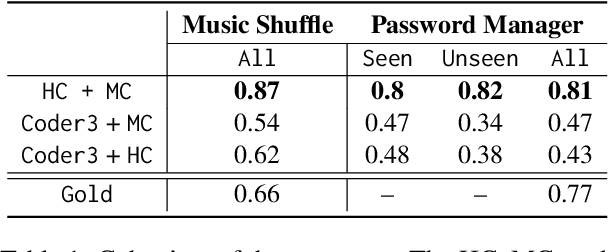

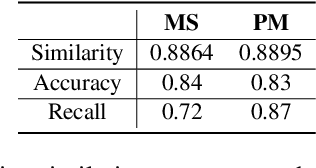
Abstract:Thematic analysis (TA) has been widely used for analyzing qualitative data in many disciplines and fields. To ensure reliable analysis, the same piece of data is typically assigned to at least two human coders. Moreover, to produce meaningful and useful analysis, human coders develop and deepen their data interpretation and coding over multiple iterations, making TA labor-intensive and time-consuming. Recently the emerging field of large language models (LLMs) research has shown that LLMs have the potential replicate human-like behavior in various tasks: in particular, LLMs outperform crowd workers on text-annotation tasks, suggesting an opportunity to leverage LLMs on TA. We propose a human-LLM collaboration framework (i.e., LLM-in-the-loop) to conduct TA with in-context learning (ICL). This framework provides the prompt to frame discussions with a LLM (e.g., GPT-3.5) to generate the final codebook for TA. We demonstrate the utility of this framework using survey datasets on the aspects of the music listening experience and the usage of a password manager. Results of the two case studies show that the proposed framework yields similar coding quality to that of human coders but reduces TA's labor and time demands.
Label-Aware Hyperbolic Embeddings for Fine-grained Emotion Classification
Jun 26, 2023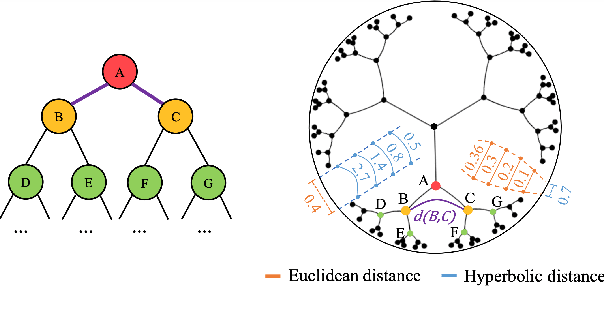
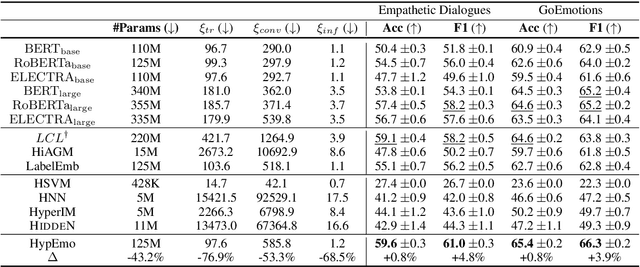
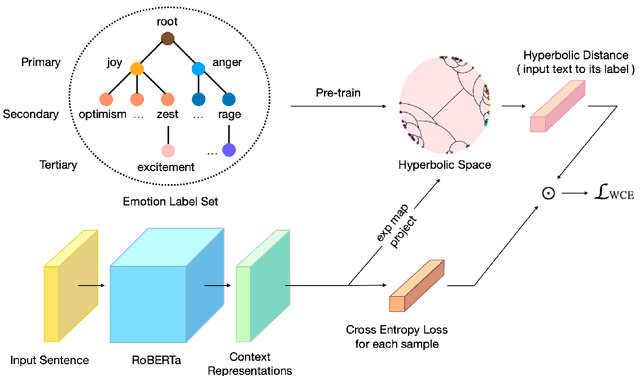
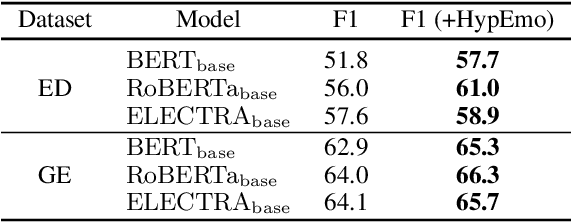
Abstract:Fine-grained emotion classification (FEC) is a challenging task. Specifically, FEC needs to handle subtle nuance between labels, which can be complex and confusing. Most existing models only address text classification problem in the euclidean space, which we believe may not be the optimal solution as labels of close semantic (e.g., afraid and terrified) may not be differentiated in such space, which harms the performance. In this paper, we propose HypEmo, a novel framework that can integrate hyperbolic embeddings to improve the FEC task. First, we learn label embeddings in the hyperbolic space to better capture their hierarchical structure, and then our model projects contextualized representations to the hyperbolic space to compute the distance between samples and labels. Experimental results show that incorporating such distance to weight cross entropy loss substantially improves the performance with significantly higher efficiency. We evaluate our proposed model on two benchmark datasets and found 4.8% relative improvement compared to the previous state of the art with 43.2% fewer parameters and 76.9% less training time. Code is available at https: //github.com/dinobby/HypEmo.
HonestBait: Forward References for Attractive but Faithful Headline Generation
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Current methods for generating attractive headlines often learn directly from data, which bases attractiveness on the number of user clicks and views. Although clicks or views do reflect user interest, they can fail to reveal how much interest is raised by the writing style and how much is due to the event or topic itself. Also, such approaches can lead to harmful inventions by over-exaggerating the content, aggravating the spread of false information. In this work, we propose HonestBait, a novel framework for solving these issues from another aspect: generating headlines using forward references (FRs), a writing technique often used for clickbait. A self-verification process is included during training to avoid spurious inventions. We begin with a preliminary user study to understand how FRs affect user interest, after which we present PANCO1, an innovative dataset containing pairs of fake news with verified news for attractive but faithful news headline generation. Automatic metrics and human evaluations show that our framework yields more attractive results (+11.25% compared to human-written verified news headlines) while maintaining high veracity, which helps promote real information to fight against fake news.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge