Risheek Garrepalli
Generative Scenario Rollouts for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are emerging as highly effective planning models for end-to-end autonomous driving systems. However, current works mostly rely on imitation learning from sparse trajectory annotations and under-utilize their potential as generative models. We propose Generative Scenario Rollouts (GeRo), a plug-and-play framework for VLA models that jointly performs planning and generation of language-grounded future traffic scenes through an autoregressive rollout strategy. First, a VLA model is trained to encode ego vehicle and agent dynamics into latent tokens under supervision from planning, motion, and language tasks, facilitating text-aligned generation. Next, GeRo performs language-conditioned autoregressive generation. Given multi-view images, a scenario description, and ego-action questions, it generates future latent tokens and textual responses to guide long-horizon rollouts. A rollout-consistency loss stabilizes predictions using ground truth or pseudo-labels, mitigating drift and preserving text-action alignment. This design enables GeRo to perform temporally consistent, language-grounded rollouts that support long-horizon reasoning and multi-agent planning. On Bench2Drive, GeRo improves driving score and success rate by +15.7 and +26.2, respectively. By integrating reinforcement learning with generative rollouts, GeRo achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop and open-loop performance, demonstrating strong zero-shot robustness. These results highlight the promise of generative, language-conditioned reasoning as a foundation for safer and more interpretable end-to-end autonomous driving.
MultiHuman-Testbench: Benchmarking Image Generation for Multiple Humans
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Generation of images containing multiple humans, performing complex actions, while preserving their facial identities, is a significant challenge. A major factor contributing to this is the lack of a a dedicated benchmark. To address this, we introduce MultiHuman-Testbench, a novel benchmark for rigorously evaluating generative models for multi-human generation. The benchmark comprises 1800 samples, including carefully curated text prompts, describing a range of simple to complex human actions. These prompts are matched with a total of 5,550 unique human face images, sampled uniformly to ensure diversity across age, ethnic background, and gender. Alongside captions, we provide human-selected pose conditioning images which accurately match the prompt. We propose a multi-faceted evaluation suite employing four key metrics to quantify face count, ID similarity, prompt alignment, and action detection. We conduct a thorough evaluation of a diverse set of models, including zero-shot approaches and training-based methods, with and without regional priors. We also propose novel techniques to incorporate image and region isolation using human segmentation and Hungarian matching, significantly improving ID similarity. Our proposed benchmark and key findings provide valuable insights and a standardized tool for advancing research in multi-human image generation.
RoCA: Robust Cross-Domain End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving has recently emerged as a new paradigm, offering significant potential. However, few studies have looked into the practical challenge of deployment across domains (e.g., cities). Although several works have incorporated Large Language Models (LLMs) to leverage their open-world knowledge, LLMs do not guarantee cross-domain driving performance and may incur prohibitive retraining costs during domain adaptation. In this paper, we propose RoCA, a novel framework for robust cross-domain E2E autonomous driving. RoCA formulates the joint probabilistic distribution over the tokens that encode ego and surrounding vehicle information in the E2E pipeline. Instantiating with a Gaussian process (GP), RoCA learns a set of basis tokens with corresponding trajectories, which span diverse driving scenarios. Then, given any driving scene, it is able to probabilistically infer the future trajectory. By using RoCA together with a base E2E model in source-domain training, we improve the generalizability of the base model, without requiring extra inference computation. In addition, RoCA enables robust adaptation on new target domains, significantly outperforming direct finetuning. We extensively evaluate RoCA on various cross-domain scenarios and show that it achieves strong domain generalization and adaptation performance.
Distilling Multi-modal Large Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Jan 16, 2025
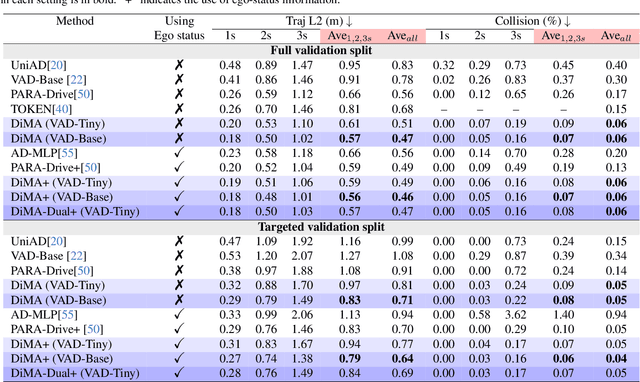

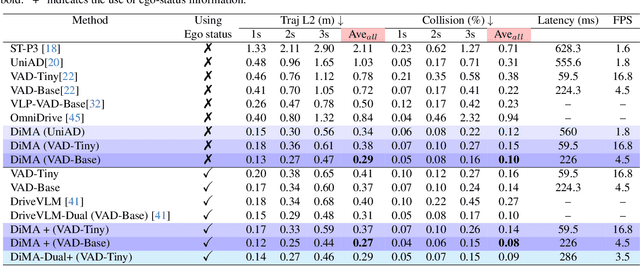
Abstract:Autonomous driving demands safe motion planning, especially in critical "long-tail" scenarios. Recent end-to-end autonomous driving systems leverage large language models (LLMs) as planners to improve generalizability to rare events. However, using LLMs at test time introduces high computational costs. To address this, we propose DiMA, an end-to-end autonomous driving system that maintains the efficiency of an LLM-free (or vision-based) planner while leveraging the world knowledge of an LLM. DiMA distills the information from a multi-modal LLM to a vision-based end-to-end planner through a set of specially designed surrogate tasks. Under a joint training strategy, a scene encoder common to both networks produces structured representations that are semantically grounded as well as aligned to the final planning objective. Notably, the LLM is optional at inference, enabling robust planning without compromising on efficiency. Training with DiMA results in a 37% reduction in the L2 trajectory error and an 80% reduction in the collision rate of the vision-based planner, as well as a 44% trajectory error reduction in longtail scenarios. DiMA also achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes planning benchmark.
DDIL: Improved Diffusion Distillation With Imitation Learning
Oct 15, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models excel at generative modeling (e.g., text-to-image) but sampling requires multiple denoising network passes, limiting practicality. Efforts such as progressive distillation or consistency distillation have shown promise by reducing the number of passes at the expense of quality of the generated samples. In this work we identify co-variate shift as one of reason for poor performance of multi-step distilled models from compounding error at inference time. To address co-variate shift, we formulate diffusion distillation within imitation learning (DDIL) framework and enhance training distribution for distilling diffusion models on both data distribution (forward diffusion) and student induced distributions (backward diffusion). Training on data distribution helps to diversify the generations by preserving marginal data distribution and training on student distribution addresses compounding error by correcting covariate shift. In addition, we adopt reflected diffusion formulation for distillation and demonstrate improved performance, stable training across different distillation methods. We show that DDIL consistency improves on baseline algorithms of progressive distillation (PD), Latent consistency models (LCM) and Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD2).
Rapid Switching and Multi-Adapter Fusion via Sparse High Rank Adapters
Jul 22, 2024


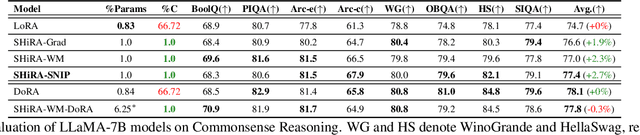
Abstract:In this paper, we propose Sparse High Rank Adapters (SHiRA) that directly finetune 1-2% of the base model weights while leaving others unchanged, thus, resulting in a highly sparse adapter. This high sparsity incurs no inference overhead, enables rapid switching directly in the fused mode, and significantly reduces concept-loss during multi-adapter fusion. Our extensive experiments on LVMs and LLMs demonstrate that finetuning merely 1-2% parameters in the base model is sufficient for many adapter tasks and significantly outperforms Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA). We also show that SHiRA is orthogonal to advanced LoRA methods such as DoRA and can be easily combined with existing techniques.
Sparse High Rank Adapters
Jun 19, 2024
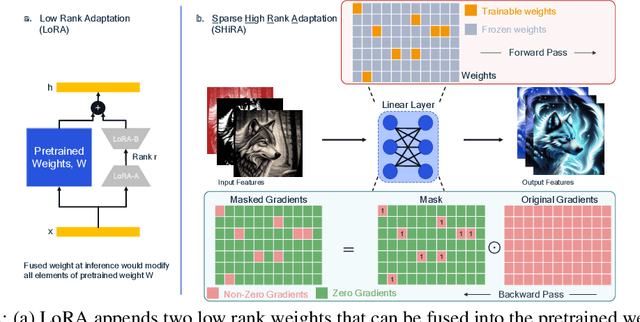
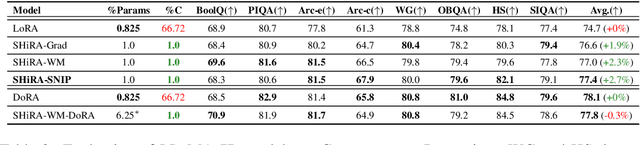
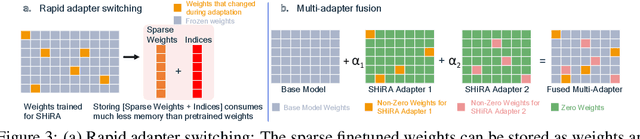
Abstract:Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has gained massive attention in the recent generative AI research. One of the main advantages of LoRA is its ability to be fused with pretrained models adding no overhead during inference. However, from a mobile deployment standpoint, we can either avoid inference overhead in the fused mode but lose the ability to switch adapters rapidly, or suffer significant (up to 30% higher) inference latency while enabling rapid switching in the unfused mode. LoRA also exhibits concept-loss when multiple adapters are used concurrently. In this paper, we propose Sparse High Rank Adapters (SHiRA), a new paradigm which incurs no inference overhead, enables rapid switching, and significantly reduces concept-loss. Specifically, SHiRA can be trained by directly tuning only 1-2% of the base model weights while leaving others unchanged. This results in a highly sparse adapter which can be switched directly in the fused mode. We further provide theoretical and empirical insights on how high sparsity in SHiRA can aid multi-adapter fusion by reducing concept loss. Our extensive experiments on LVMs and LLMs demonstrate that finetuning only a small fraction of the parameters in the base model is sufficient for many tasks while enabling both rapid switching and multi-adapter fusion. Finally, we provide a latency- and memory-efficient SHiRA implementation based on Parameter-Efficient Finetuning (PEFT) Library. This implementation trains at nearly the same speed as LoRA while consuming lower peak GPU memory, thus making SHiRA easy to adopt for practical use cases.
FouRA: Fourier Low Rank Adaptation
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:While Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has proven beneficial for efficiently fine-tuning large models, LoRA fine-tuned text-to-image diffusion models lack diversity in the generated images, as the model tends to copy data from the observed training samples. This effect becomes more pronounced at higher values of adapter strength and for adapters with higher ranks which are fine-tuned on smaller datasets. To address these challenges, we present FouRA, a novel low-rank method that learns projections in the Fourier domain along with learning a flexible input-dependent adapter rank selection strategy. Through extensive experiments and analysis, we show that FouRA successfully solves the problems related to data copying and distribution collapse while significantly improving the generated image quality. We demonstrate that FouRA enhances the generalization of fine-tuned models thanks to its adaptive rank selection. We further show that the learned projections in the frequency domain are decorrelated and prove effective when merging multiple adapters. While FouRA is motivated for vision tasks, we also demonstrate its merits for language tasks on the GLUE benchmark.
SciFlow: Empowering Lightweight Optical Flow Models with Self-Cleaning Iterations
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Optical flow estimation is crucial to a variety of vision tasks. Despite substantial recent advancements, achieving real-time on-device optical flow estimation remains a complex challenge. First, an optical flow model must be sufficiently lightweight to meet computation and memory constraints to ensure real-time performance on devices. Second, the necessity for real-time on-device operation imposes constraints that weaken the model's capacity to adequately handle ambiguities in flow estimation, thereby intensifying the difficulty of preserving flow accuracy. This paper introduces two synergistic techniques, Self-Cleaning Iteration (SCI) and Regression Focal Loss (RFL), designed to enhance the capabilities of optical flow models, with a focus on addressing optical flow regression ambiguities. These techniques prove particularly effective in mitigating error propagation, a prevalent issue in optical flow models that employ iterative refinement. Notably, these techniques add negligible to zero overhead in model parameters and inference latency, thereby preserving real-time on-device efficiency. The effectiveness of our proposed SCI and RFL techniques, collectively referred to as SciFlow for brevity, is demonstrated across two distinct lightweight optical flow model architectures in our experiments. Remarkably, SciFlow enables substantial reduction in error metrics (EPE and Fl-all) over the baseline models by up to 6.3% and 10.5% for in-domain scenarios and by up to 6.2% and 13.5% for cross-domain scenarios on the Sintel and KITTI 2015 datasets, respectively.
OCAI: Improving Optical Flow Estimation by Occlusion and Consistency Aware Interpolation
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:The scarcity of ground-truth labels poses one major challenge in developing optical flow estimation models that are both generalizable and robust. While current methods rely on data augmentation, they have yet to fully exploit the rich information available in labeled video sequences. We propose OCAI, a method that supports robust frame interpolation by generating intermediate video frames alongside optical flows in between. Utilizing a forward warping approach, OCAI employs occlusion awareness to resolve ambiguities in pixel values and fills in missing values by leveraging the forward-backward consistency of optical flows. Additionally, we introduce a teacher-student style semi-supervised learning method on top of the interpolated frames. Using a pair of unlabeled frames and the teacher model's predicted optical flow, we generate interpolated frames and flows to train a student model. The teacher's weights are maintained using Exponential Moving Averaging of the student. Our evaluations demonstrate perceptually superior interpolation quality and enhanced optical flow accuracy on established benchmarks such as Sintel and KITTI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge