Sweta Priyadarshi
Quantization-Aware Distillation for NVFP4 Inference Accuracy Recovery
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:This technical report presents quantization-aware distillation (QAD) and our best practices for recovering accuracy of NVFP4-quantized large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs). QAD distills a full-precision teacher model into a quantized student model using a KL divergence loss. While applying distillation to quantized models is not a new idea, we observe key advantages of QAD for today's LLMs: 1. It shows remarkable effectiveness and stability for models trained through multi-stage post-training pipelines, including supervised fine-tuning (SFT), reinforcement learning (RL), and model merging, where traditional quantization-aware training (QAT) suffers from engineering complexity and training instability; 2. It is robust to data quality and coverage, enabling accuracy recovery without full training data. We evaluate QAD across multiple post-trained models including AceReason Nemotron, Nemotron 3 Nano, Nemotron Nano V2, Nemotron Nano V2 VL (VLM), and Llama Nemotron Super v1, showing consistent recovery to near-BF16 accuracy.
NVIDIA Nemotron 3: Efficient and Open Intelligence
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:We introduce the Nemotron 3 family of models - Nano, Super, and Ultra. These models deliver strong agentic, reasoning, and conversational capabilities. The Nemotron 3 family uses a Mixture-of-Experts hybrid Mamba-Transformer architecture to provide best-in-class throughput and context lengths of up to 1M tokens. Super and Ultra models are trained with NVFP4 and incorporate LatentMoE, a novel approach that improves model quality. The two larger models also include MTP layers for faster text generation. All Nemotron 3 models are post-trained using multi-environment reinforcement learning enabling reasoning, multi-step tool use, and support granular reasoning budget control. Nano, the smallest model, outperforms comparable models in accuracy while remaining extremely cost-efficient for inference. Super is optimized for collaborative agents and high-volume workloads such as IT ticket automation. Ultra, the largest model, provides state-of-the-art accuracy and reasoning performance. Nano is released together with its technical report and this white paper, while Super and Ultra will follow in the coming months. We will openly release the model weights, pre- and post-training software, recipes, and all data for which we hold redistribution rights.
Nemotron 3 Nano: Open, Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Model for Agentic Reasoning
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:We present Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B, a Mixture-of-Experts hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model. Nemotron 3 Nano was pretrained on 25 trillion text tokens, including more than 3 trillion new unique tokens over Nemotron 2, followed by supervised fine tuning and large-scale RL on diverse environments. Nemotron 3 Nano achieves better accuracy than our previous generation Nemotron 2 Nano while activating less than half of the parameters per forward pass. It achieves up to 3.3x higher inference throughput than similarly-sized open models like GPT-OSS-20B and Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507, while also being more accurate on popular benchmarks. Nemotron 3 Nano demonstrates enhanced agentic, reasoning, and chat abilities and supports context lengths up to 1M tokens. We release both our pretrained Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B Base and post-trained Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B checkpoints on Hugging Face.
Rapid Switching and Multi-Adapter Fusion via Sparse High Rank Adapters
Jul 22, 2024


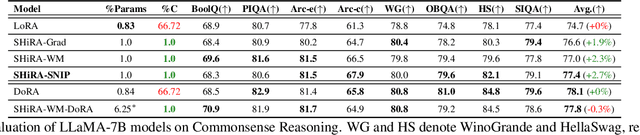
Abstract:In this paper, we propose Sparse High Rank Adapters (SHiRA) that directly finetune 1-2% of the base model weights while leaving others unchanged, thus, resulting in a highly sparse adapter. This high sparsity incurs no inference overhead, enables rapid switching directly in the fused mode, and significantly reduces concept-loss during multi-adapter fusion. Our extensive experiments on LVMs and LLMs demonstrate that finetuning merely 1-2% parameters in the base model is sufficient for many adapter tasks and significantly outperforms Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA). We also show that SHiRA is orthogonal to advanced LoRA methods such as DoRA and can be easily combined with existing techniques.
Sparse High Rank Adapters
Jun 19, 2024
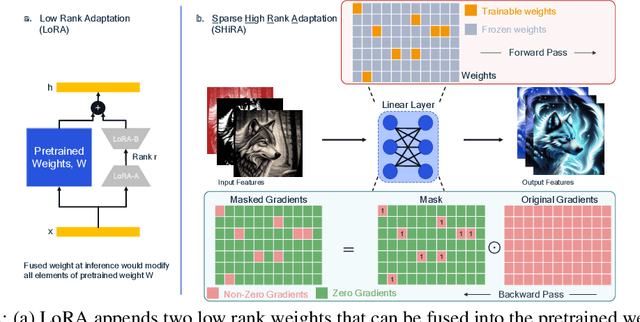
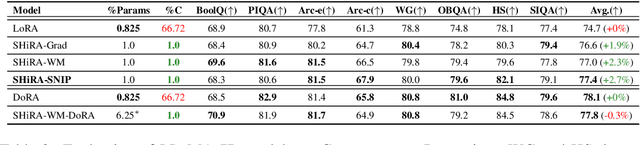
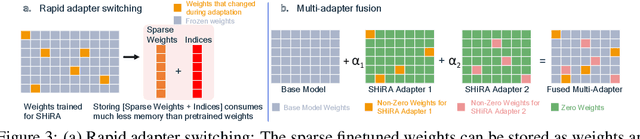
Abstract:Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has gained massive attention in the recent generative AI research. One of the main advantages of LoRA is its ability to be fused with pretrained models adding no overhead during inference. However, from a mobile deployment standpoint, we can either avoid inference overhead in the fused mode but lose the ability to switch adapters rapidly, or suffer significant (up to 30% higher) inference latency while enabling rapid switching in the unfused mode. LoRA also exhibits concept-loss when multiple adapters are used concurrently. In this paper, we propose Sparse High Rank Adapters (SHiRA), a new paradigm which incurs no inference overhead, enables rapid switching, and significantly reduces concept-loss. Specifically, SHiRA can be trained by directly tuning only 1-2% of the base model weights while leaving others unchanged. This results in a highly sparse adapter which can be switched directly in the fused mode. We further provide theoretical and empirical insights on how high sparsity in SHiRA can aid multi-adapter fusion by reducing concept loss. Our extensive experiments on LVMs and LLMs demonstrate that finetuning only a small fraction of the parameters in the base model is sufficient for many tasks while enabling both rapid switching and multi-adapter fusion. Finally, we provide a latency- and memory-efficient SHiRA implementation based on Parameter-Efficient Finetuning (PEFT) Library. This implementation trains at nearly the same speed as LoRA while consuming lower peak GPU memory, thus making SHiRA easy to adopt for practical use cases.
FouRA: Fourier Low Rank Adaptation
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:While Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has proven beneficial for efficiently fine-tuning large models, LoRA fine-tuned text-to-image diffusion models lack diversity in the generated images, as the model tends to copy data from the observed training samples. This effect becomes more pronounced at higher values of adapter strength and for adapters with higher ranks which are fine-tuned on smaller datasets. To address these challenges, we present FouRA, a novel low-rank method that learns projections in the Fourier domain along with learning a flexible input-dependent adapter rank selection strategy. Through extensive experiments and analysis, we show that FouRA successfully solves the problems related to data copying and distribution collapse while significantly improving the generated image quality. We demonstrate that FouRA enhances the generalization of fine-tuned models thanks to its adaptive rank selection. We further show that the learned projections in the frequency domain are decorrelated and prove effective when merging multiple adapters. While FouRA is motivated for vision tasks, we also demonstrate its merits for language tasks on the GLUE benchmark.
Oh! We Freeze: Improving Quantized Knowledge Distillation via Signal Propagation Analysis for Large Language Models
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Large generative models such as large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models have revolutionized the fields of NLP and computer vision respectively. However, their slow inference, high computation and memory requirement makes it challenging to deploy them on edge devices. In this study, we propose a light-weight quantization aware fine tuning technique using knowledge distillation (KD-QAT) to improve the performance of 4-bit weight quantized LLMs using commonly available datasets to realize a popular language use case, on device chat applications. To improve this paradigm of finetuning, as main contributions, we provide insights into stability of KD-QAT by empirically studying the gradient propagation during training to better understand the vulnerabilities of KD-QAT based approaches to low-bit quantization errors. Based on our insights, we propose ov-freeze, a simple technique to stabilize the KD-QAT process. Finally, we experiment with the popular 7B LLaMAv2-Chat model at 4-bit quantization level and demonstrate that ov-freeze results in near floating point precision performance, i.e., less than 0.7% loss of accuracy on Commonsense Reasoning benchmarks.
ZiCo-BC: A Bias Corrected Zero-Shot NAS for Vision Tasks
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Zero-Shot Neural Architecture Search (NAS) approaches propose novel training-free metrics called zero-shot proxies to substantially reduce the search time compared to the traditional training-based NAS. Despite the success on image classification, the effectiveness of zero-shot proxies is rarely evaluated on complex vision tasks such as semantic segmentation and object detection. Moreover, existing zero-shot proxies are shown to be biased towards certain model characteristics which restricts their broad applicability. In this paper, we empirically study the bias of state-of-the-art (SOTA) zero-shot proxy ZiCo across multiple vision tasks and observe that ZiCo is biased towards thinner and deeper networks, leading to sub-optimal architectures. To solve the problem, we propose a novel bias correction on ZiCo, called ZiCo-BC. Our extensive experiments across various vision tasks (image classification, object detection and semantic segmentation) show that our approach can successfully search for architectures with higher accuracy and significantly lower latency on Samsung Galaxy S10 devices.
DONNAv2 -- Lightweight Neural Architecture Search for Vision tasks
Sep 26, 2023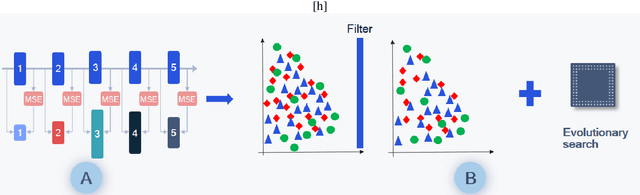
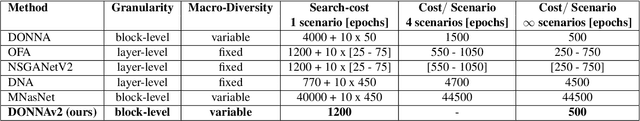
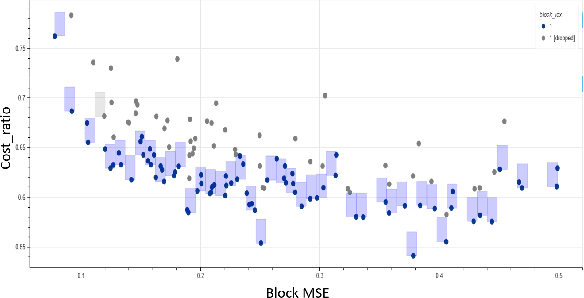
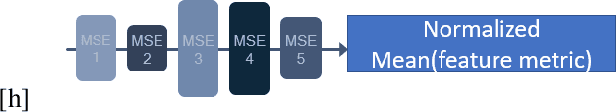
Abstract:With the growing demand for vision applications and deployment across edge devices, the development of hardware-friendly architectures that maintain performance during device deployment becomes crucial. Neural architecture search (NAS) techniques explore various approaches to discover efficient architectures for diverse learning tasks in a computationally efficient manner. In this paper, we present the next-generation neural architecture design for computationally efficient neural architecture distillation - DONNAv2 . Conventional NAS algorithms rely on a computationally extensive stage where an accuracy predictor is learned to estimate model performance within search space. This building of accuracy predictors helps them predict the performance of models that are not being finetuned. Here, we have developed an elegant approach to eliminate building the accuracy predictor and extend DONNA to a computationally efficient setting. The loss metric of individual blocks forming the network serves as the surrogate performance measure for the sampled models in the NAS search stage. To validate the performance of DONNAv2 we have performed extensive experiments involving a range of diverse vision tasks including classification, object detection, image denoising, super-resolution, and panoptic perception network (YOLOP). The hardware-in-the-loop experiments were carried out using the Samsung Galaxy S10 mobile platform. Notably, DONNAv2 reduces the computational cost of DONNA by 10x for the larger datasets. Furthermore, to improve the quality of NAS search space, DONNAv2 leverages a block knowledge distillation filter to remove blocks with high inference costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge