Hong Cai
Double-P: Hierarchical Top-P Sparse Attention for Long-Context LLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As long-context inference becomes central to large language models (LLMs), attention over growing key-value caches emerges as a dominant decoding bottleneck, motivating sparse attention for scalable inference. Fixed-budget top-k sparse attention cannot adapt to heterogeneous attention distributions across heads and layers, whereas top-p sparse attention directly preserves attention mass and provides stronger accuracy guarantees. Existing top-p methods, however, fail to jointly optimize top-p accuracy, selection overhead, and sparse attention cost, which limits their overall efficiency. We present Double-P, a hierarchical sparse attention framework that optimizes all three stages. Double-P first performs coarse-grained top-p estimation at the cluster level using size-weighted centroids, then adaptively refines computation through a second top-p stage that allocates token-level attention only when needed. Across long-context benchmarks, Double-P consistently achieves near-zero accuracy drop, reducing attention computation overhead by up to 1.8x and delivers up to 1.3x end-to-end decoding speedup over state-of-the-art fixed-budget sparse attention methods.
Generative Scenario Rollouts for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are emerging as highly effective planning models for end-to-end autonomous driving systems. However, current works mostly rely on imitation learning from sparse trajectory annotations and under-utilize their potential as generative models. We propose Generative Scenario Rollouts (GeRo), a plug-and-play framework for VLA models that jointly performs planning and generation of language-grounded future traffic scenes through an autoregressive rollout strategy. First, a VLA model is trained to encode ego vehicle and agent dynamics into latent tokens under supervision from planning, motion, and language tasks, facilitating text-aligned generation. Next, GeRo performs language-conditioned autoregressive generation. Given multi-view images, a scenario description, and ego-action questions, it generates future latent tokens and textual responses to guide long-horizon rollouts. A rollout-consistency loss stabilizes predictions using ground truth or pseudo-labels, mitigating drift and preserving text-action alignment. This design enables GeRo to perform temporally consistent, language-grounded rollouts that support long-horizon reasoning and multi-agent planning. On Bench2Drive, GeRo improves driving score and success rate by +15.7 and +26.2, respectively. By integrating reinforcement learning with generative rollouts, GeRo achieves state-of-the-art closed-loop and open-loop performance, demonstrating strong zero-shot robustness. These results highlight the promise of generative, language-conditioned reasoning as a foundation for safer and more interpretable end-to-end autonomous driving.
ViewMorpher3D: A 3D-aware Diffusion Framework for Multi-Camera Novel View Synthesis in Autonomous Driving
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Autonomous driving systems rely heavily on multi-view images to ensure accurate perception and robust decision-making. To effectively develop and evaluate perception stacks and planning algorithms, realistic closed-loop simulators are indispensable. While 3D reconstruction techniques such as Gaussian Splatting offer promising avenues for simulator construction, the rendered novel views often exhibit artifacts, particularly in extrapolated perspectives or when available observations are sparse. We introduce ViewMorpher3D, a multi-view image enhancement framework based on image diffusion models, designed to elevate photorealism and multi-view coherence in driving scenes. Unlike single-view approaches, ViewMorpher3D jointly processes a set of rendered views conditioned on camera poses, 3D geometric priors, and temporally adjacent or spatially overlapping reference views. This enables the model to infer missing details, suppress rendering artifacts, and enforce cross-view consistency. Our framework accommodates variable numbers of cameras and flexible reference/target view configurations, making it adaptable to diverse sensor setups. Experiments on real-world driving datasets demonstrate substantial improvements in image quality metrics, effectively reducing artifacts while preserving geometric fidelity.
LidarPainter: One-Step Away From Any Lidar View To Novel Guidance
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Dynamic driving scene reconstruction is of great importance in fields like digital twin system and autonomous driving simulation. However, unacceptable degradation occurs when the view deviates from the input trajectory, leading to corrupted background and vehicle models. To improve reconstruction quality on novel trajectory, existing methods are subject to various limitations including inconsistency, deformation, and time consumption. This paper proposes LidarPainter, a one-step diffusion model that recovers consistent driving views from sparse LiDAR condition and artifact-corrupted renderings in real-time, enabling high-fidelity lane shifts in driving scene reconstruction. Extensive experiments show that LidarPainter outperforms state-of-the-art methods in speed, quality and resource efficiency, specifically 7 x faster than StreetCrafter with only one fifth of GPU memory required. LidarPainter also supports stylized generation using text prompts such as "foggy" and "night", allowing for a diverse expansion of the existing asset library.
ODG: Occupancy Prediction Using Dual Gaussians
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Occupancy prediction infers fine-grained 3D geometry and semantics from camera images of the surrounding environment, making it a critical perception task for autonomous driving. Existing methods either adopt dense grids as scene representation, which is difficult to scale to high resolution, or learn the entire scene using a single set of sparse queries, which is insufficient to handle the various object characteristics. In this paper, we present ODG, a hierarchical dual sparse Gaussian representation to effectively capture complex scene dynamics. Building upon the observation that driving scenes can be universally decomposed into static and dynamic counterparts, we define dual Gaussian queries to better model the diverse scene objects. We utilize a hierarchical Gaussian transformer to predict the occupied voxel centers and semantic classes along with the Gaussian parameters. Leveraging the real-time rendering capability of 3D Gaussian Splatting, we also impose rendering supervision with available depth and semantic map annotations injecting pixel-level alignment to boost occupancy learning. Extensive experiments on the Occ3D-nuScenes and Occ3D-Waymo benchmarks demonstrate our proposed method sets new state-of-the-art results while maintaining low inference cost.
DySS: Dynamic Queries and State-Space Learning for Efficient 3D Object Detection from Multi-Camera Videos
Jun 11, 2025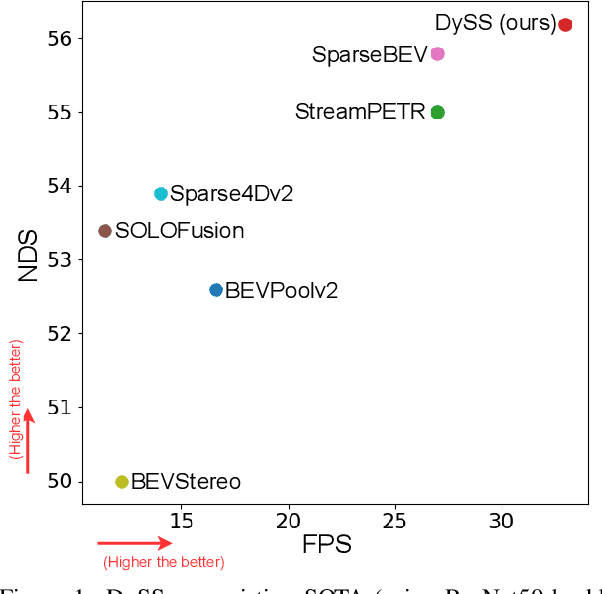
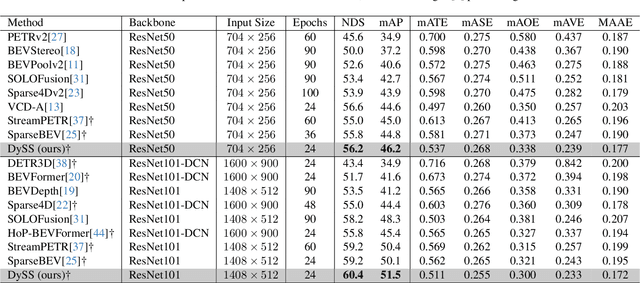
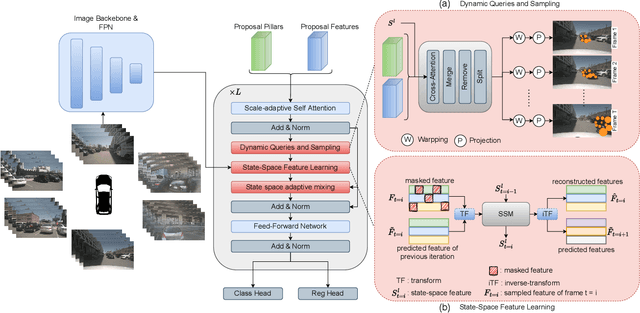
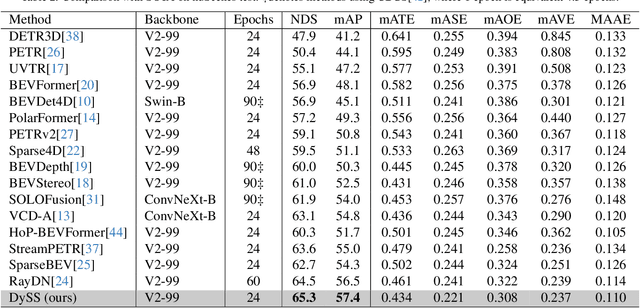
Abstract:Camera-based 3D object detection in Bird's Eye View (BEV) is one of the most important perception tasks in autonomous driving. Earlier methods rely on dense BEV features, which are costly to construct. More recent works explore sparse query-based detection. However, they still require a large number of queries and can become expensive to run when more video frames are used. In this paper, we propose DySS, a novel method that employs state-space learning and dynamic queries. More specifically, DySS leverages a state-space model (SSM) to sequentially process the sampled features over time steps. In order to encourage the model to better capture the underlying motion and correspondence information, we introduce auxiliary tasks of future prediction and masked reconstruction to better train the SSM. The state of the SSM then provides an informative yet efficient summarization of the scene. Based on the state-space learned features, we dynamically update the queries via merge, remove, and split operations, which help maintain a useful, lean set of detection queries throughout the network. Our proposed DySS achieves both superior detection performance and efficient inference. Specifically, on the nuScenes test split, DySS achieves 65.31 NDS and 57.4 mAP, outperforming the latest state of the art. On the val split, DySS achieves 56.2 NDS and 46.2 mAP, as well as a real-time inference speed of 33 FPS.
RoCA: Robust Cross-Domain End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving has recently emerged as a new paradigm, offering significant potential. However, few studies have looked into the practical challenge of deployment across domains (e.g., cities). Although several works have incorporated Large Language Models (LLMs) to leverage their open-world knowledge, LLMs do not guarantee cross-domain driving performance and may incur prohibitive retraining costs during domain adaptation. In this paper, we propose RoCA, a novel framework for robust cross-domain E2E autonomous driving. RoCA formulates the joint probabilistic distribution over the tokens that encode ego and surrounding vehicle information in the E2E pipeline. Instantiating with a Gaussian process (GP), RoCA learns a set of basis tokens with corresponding trajectories, which span diverse driving scenarios. Then, given any driving scene, it is able to probabilistically infer the future trajectory. By using RoCA together with a base E2E model in source-domain training, we improve the generalizability of the base model, without requiring extra inference computation. In addition, RoCA enables robust adaptation on new target domains, significantly outperforming direct finetuning. We extensively evaluate RoCA on various cross-domain scenarios and show that it achieves strong domain generalization and adaptation performance.
BePo: Leveraging Birds Eye View and Sparse Points for Efficient and Accurate 3D Occupancy Prediction
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:3D occupancy provides fine-grained 3D geometry and semantics for scene understanding which is critical for autonomous driving. Most existing methods, however, carry high compute costs, requiring dense 3D feature volume and cross-attention to effectively aggregate information. More recent works have adopted Bird's Eye View (BEV) or sparse points as scene representation with much reduced cost, but still suffer from their respective shortcomings. More concretely, BEV struggles with small objects that often experience significant information loss after being projected to the ground plane. On the other hand, points can flexibly model little objects in 3D, but is inefficient at capturing flat surfaces or large objects. To address these challenges, in this paper, we present a novel 3D occupancy prediction approach, BePo, which combines BEV and sparse points based representations. We propose a dual-branch design: a query-based sparse points branch and a BEV branch. The 3D information learned in the sparse points branch is shared with the BEV stream via cross-attention, which enriches the weakened signals of difficult objects on the BEV plane. The outputs of both branches are finally fused to generate predicted 3D occupancy. We conduct extensive experiments on the Occ3D-nuScenes and Occ3D-Waymo benchmarks that demonstrate the superiority of our proposed BePo. Moreover, BePo also delivers competitive inference speed when compared to the latest efficient approaches.
FALO: Fast and Accurate LiDAR 3D Object Detection on Resource-Constrained Devices
Jun 04, 2025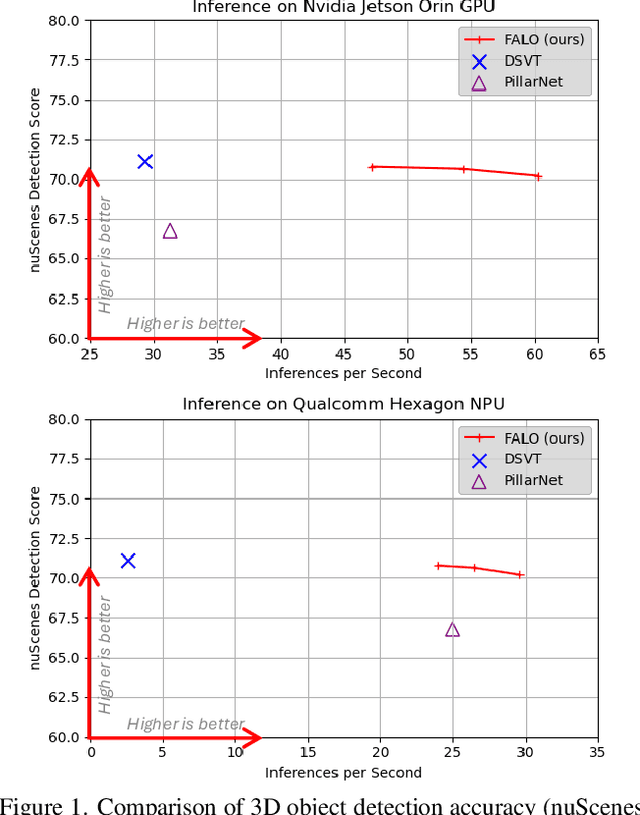
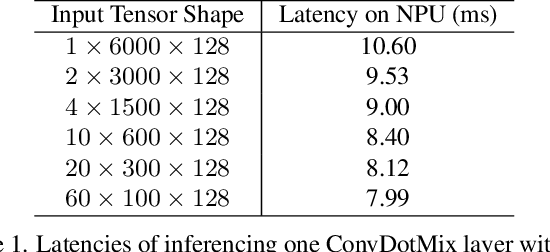
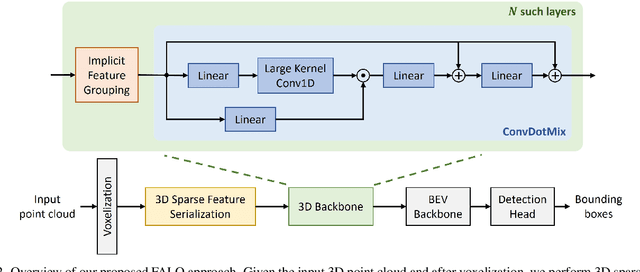
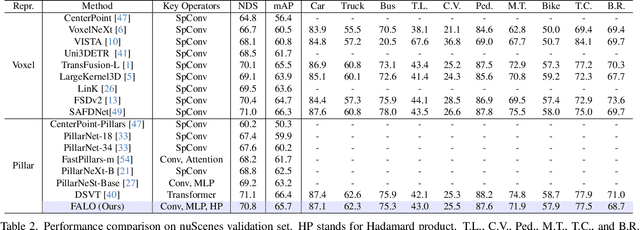
Abstract:Existing LiDAR 3D object detection methods predominantely rely on sparse convolutions and/or transformers, which can be challenging to run on resource-constrained edge devices, due to irregular memory access patterns and high computational costs. In this paper, we propose FALO, a hardware-friendly approach to LiDAR 3D detection, which offers both state-of-the-art (SOTA) detection accuracy and fast inference speed. More specifically, given the 3D point cloud and after voxelization, FALO first arranges sparse 3D voxels into a 1D sequence based on their coordinates and proximity. The sequence is then processed by our proposed ConvDotMix blocks, consisting of large-kernel convolutions, Hadamard products, and linear layers. ConvDotMix provides sufficient mixing capability in both spatial and embedding dimensions, and introduces higher-order nonlinear interaction among spatial features. Furthermore, when going through the ConvDotMix layers, we introduce implicit grouping, which balances the tensor dimensions for more efficient inference and takes into account the growing receptive field. All these operations are friendly to run on resource-constrained platforms and proposed FALO can readily deploy on compact, embedded devices. Our extensive evaluation on LiDAR 3D detection benchmarks such as nuScenes and Waymo shows that FALO achieves competitive performance. Meanwhile, FALO is 1.6~9.8x faster than the latest SOTA on mobile Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) and mobile Neural Processing Unit (NPU).
Gaussian Splatting is an Effective Data Generator for 3D Object Detection
Apr 23, 2025



Abstract:We investigate data augmentation for 3D object detection in autonomous driving. We utilize recent advancements in 3D reconstruction based on Gaussian Splatting for 3D object placement in driving scenes. Unlike existing diffusion-based methods that synthesize images conditioned on BEV layouts, our approach places 3D objects directly in the reconstructed 3D space with explicitly imposed geometric transformations. This ensures both the physical plausibility of object placement and highly accurate 3D pose and position annotations. Our experiments demonstrate that even by integrating a limited number of external 3D objects into real scenes, the augmented data significantly enhances 3D object detection performance and outperforms existing diffusion-based 3D augmentation for object detection. Extensive testing on the nuScenes dataset reveals that imposing high geometric diversity in object placement has a greater impact compared to the appearance diversity of objects. Additionally, we show that generating hard examples, either by maximizing detection loss or imposing high visual occlusion in camera images, does not lead to more efficient 3D data augmentation for camera-based 3D object detection in autonomous driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge