Jens Petersen
rNCA: Self-Repairing Segmentation Masks
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Accurately predicting topologically correct masks remains a difficult task for general segmentation models, which often produce fragmented or disconnected outputs. Fixing these artifacts typically requires hand-crafted refinement rules or architectures specialized to a particular task. Here, we show that Neural Cellular Automata (NCA) can be directly re-purposed as an effective refinement mechanism, using local, iterative updates guided by image context to repair segmentation masks. By training on imperfect masks and ground truths, the automaton learns the structural properties of the target shape while relying solely on local information. When applied to coarse, globally predicted masks, the learned dynamics progressively reconnect broken regions, prune loose fragments and converge towards stable, topologically consistent results. We show how refinement NCA (rNCA) can be easily applied to repair common topological errors produced by different base segmentation models and tasks: for fragmented retinal vessels, it yields 2-3% gains in Dice/clDice and improves Betti errors, reducing $β_0$ errors by 60% and $β_1$ by 20%; for myocardium, it repairs 61.5% of broken cases in a zero-shot setting while lowering ASSD and HD by 19% and 16%, respectively. This showcases NCA as effective and broadly applicable refiners.
Comparative Analysis of GAN and Diffusion for MRI-to-CT translation
Sep 26, 2025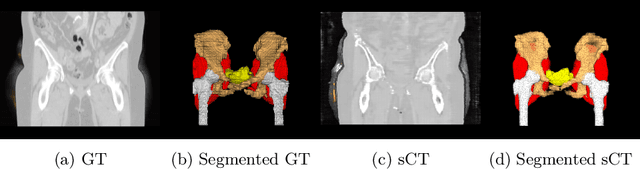

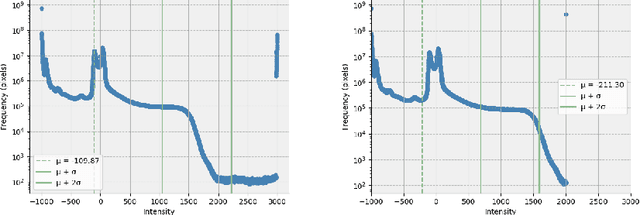

Abstract:Computed tomography (CT) is essential for treatment and diagnostics; In case CT are missing or otherwise difficult to obtain, methods for generating synthetic CT (sCT) images from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images are sought after. Therefore, it is valuable to establish a reference for what strategies are most effective for MRI-to-CT translation. In this paper, we compare the performance of two frequently used architectures for MRI-to-CT translation: a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) and a conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic model (cDDPM). We chose well-established implementations to represent each architecture: Pix2Pix for cGAN, and Palette for cDDPM. We separate the classical 3D translation problem into a sequence of 2D translations on the transverse plane, to investigate the viability of a strategy that reduces the computational cost. We also investigate the impact of conditioning the generative process on a single MRI image/slice and on multiple MRI slices. The performance is assessed using a thorough evaluation protocol, including a novel slice-wise metric Similarity Of Slices (SIMOS), which measures the continuity between transverse slices when compiling the sCTs into 3D format. Our comparative analysis revealed that MRI-to-CT generative models benefit from multi-channel conditional input and using cDDPM as an architecture.
Controllable 3D Placement of Objects with Scene-Aware Diffusion Models
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Image editing approaches have become more powerful and flexible with the advent of powerful text-conditioned generative models. However, placing objects in an environment with a precise location and orientation still remains a challenge, as this typically requires carefully crafted inpainting masks or prompts. In this work, we show that a carefully designed visual map, combined with coarse object masks, is sufficient for high quality object placement. We design a conditioning signal that resolves ambiguities, while being flexible enough to allow for changing of shapes or object orientations. By building on an inpainting model, we leave the background intact by design, in contrast to methods that model objects and background jointly. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in the automotive setting, where we compare different conditioning signals in novel object placement tasks. These tasks are designed to measure edit quality not only in terms of appearance, but also in terms of pose and location accuracy, including cases that require non-trivial shape changes. Lastly, we show that fine location control can be combined with appearance control to place existing objects in precise locations in a scene.
Gaussian Splatting is an Effective Data Generator for 3D Object Detection
Apr 23, 2025



Abstract:We investigate data augmentation for 3D object detection in autonomous driving. We utilize recent advancements in 3D reconstruction based on Gaussian Splatting for 3D object placement in driving scenes. Unlike existing diffusion-based methods that synthesize images conditioned on BEV layouts, our approach places 3D objects directly in the reconstructed 3D space with explicitly imposed geometric transformations. This ensures both the physical plausibility of object placement and highly accurate 3D pose and position annotations. Our experiments demonstrate that even by integrating a limited number of external 3D objects into real scenes, the augmented data significantly enhances 3D object detection performance and outperforms existing diffusion-based 3D augmentation for object detection. Extensive testing on the nuScenes dataset reveals that imposing high geometric diversity in object placement has a greater impact compared to the appearance diversity of objects. Additionally, we show that generating hard examples, either by maximizing detection loss or imposing high visual occlusion in camera images, does not lead to more efficient 3D data augmentation for camera-based 3D object detection in autonomous driving.
Scene-Aware Location Modeling for Data Augmentation in Automotive Object Detection
Apr 23, 2025



Abstract:Generative image models are increasingly being used for training data augmentation in vision tasks. In the context of automotive object detection, methods usually focus on producing augmented frames that look as realistic as possible, for example by replacing real objects with generated ones. Others try to maximize the diversity of augmented frames, for example by pasting lots of generated objects onto existing backgrounds. Both perspectives pay little attention to the locations of objects in the scene. Frame layouts are either reused with little or no modification, or they are random and disregard realism entirely. In this work, we argue that optimal data augmentation should also include realistic augmentation of layouts. We introduce a scene-aware probabilistic location model that predicts where new objects can realistically be placed in an existing scene. By then inpainting objects in these locations with a generative model, we obtain much stronger augmentation performance than existing approaches. We set a new state of the art for generative data augmentation on two automotive object detection tasks, achieving up to $2.8\times$ higher gains than the best competing approach ($+1.4$ vs. $+0.5$ mAP boost). We also demonstrate significant improvements for instance segmentation.
HQColon: A Hybrid Interactive Machine Learning Pipeline for High Quality Colon Labeling and Segmentation
Feb 28, 2025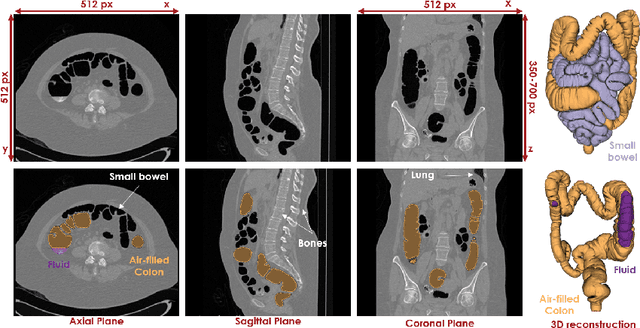
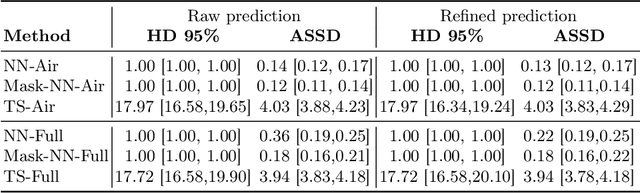
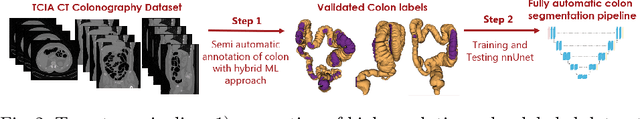
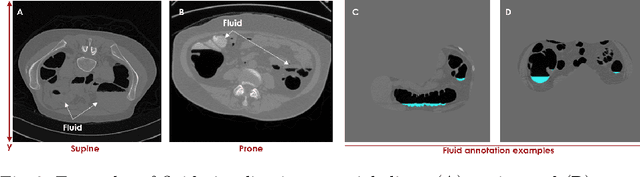
Abstract:High-resolution colon segmentation is crucial for clinical and research applications, such as digital twins and personalized medicine. However, the leading open-source abdominal segmentation tool, TotalSegmentator, struggles with accuracy for the colon, which has a complex and variable shape, requiring time-intensive labeling. Here, we present the first fully automatic high-resolution colon segmentation method. To develop it, we first created a high resolution colon dataset using a pipeline that combines region growing with interactive machine learning to efficiently and accurately label the colon on CT colonography (CTC) images. Based on the generated dataset consisting of 435 labeled CTC images we trained an nnU-Net model for fully automatic colon segmentation. Our fully automatic model achieved an average symmetric surface distance of 0.2 mm (vs. 4.0 mm from TotalSegmentator) and a 95th percentile Hausdorff distance of 1.0 mm (vs. 18 mm from TotalSegmentator). Our segmentation accuracy substantially surpasses TotalSegmentator. We share our trained model and pipeline code, providing the first and only open-source tool for high-resolution colon segmentation. Additionally, we created a large-scale dataset of publicly available high-resolution colon labels.
Enhancing predictive imaging biomarker discovery through treatment effect analysis
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Identifying predictive biomarkers, which forecast individual treatment effectiveness, is crucial for personalized medicine and informs decision-making across diverse disciplines. These biomarkers are extracted from pre-treatment data, often within randomized controlled trials, and have to be distinguished from prognostic biomarkers, which are independent of treatment assignment. Our study focuses on the discovery of predictive imaging biomarkers, aiming to leverage pre-treatment images to unveil new causal relationships. Previous approaches relied on labor-intensive handcrafted or manually derived features, which may introduce biases. In response, we present a new task of discovering predictive imaging biomarkers directly from the pre-treatment images to learn relevant image features. We propose an evaluation protocol for this task to assess a model's ability to identify predictive imaging biomarkers and differentiate them from prognostic ones. It employs statistical testing and a comprehensive analysis of image feature attribution. We explore the suitability of deep learning models originally designed for estimating the conditional average treatment effect (CATE) for this task, which previously have been primarily assessed for the precision of CATE estimation, overlooking the evaluation of imaging biomarker discovery. Our proof-of-concept analysis demonstrates promising results in discovering and validating predictive imaging biomarkers from synthetic outcomes and real-world image datasets.
Clockwork Diffusion: Efficient Generation With Model-Step Distillation
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:This work aims to improve the efficiency of text-to-image diffusion models. While diffusion models use computationally expensive UNet-based denoising operations in every generation step, we identify that not all operations are equally relevant for the final output quality. In particular, we observe that UNet layers operating on high-res feature maps are relatively sensitive to small perturbations. In contrast, low-res feature maps influence the semantic layout of the final image and can often be perturbed with no noticeable change in the output. Based on this observation, we propose Clockwork Diffusion, a method that periodically reuses computation from preceding denoising steps to approximate low-res feature maps at one or more subsequent steps. For multiple baselines, and for both text-to-image generation and image editing, we demonstrate that Clockwork leads to comparable or improved perceptual scores with drastically reduced computational complexity. As an example, for Stable Diffusion v1.5 with 8 DPM++ steps we save 32% of FLOPs with negligible FID and CLIP change.
Prediction of post-radiotherapy recurrence volumes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using 3D U-Net segmentation
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Locoregional recurrences (LRR) are still a frequent site of treatment failure for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) patients. Identification of high risk subvolumes based on pretreatment imaging is key to biologically targeted radiation therapy. We investigated the extent to which a Convolutional neural network (CNN) is able to predict LRR volumes based on pre-treatment 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET)/computed tomography (CT) scans in HNSCC patients and thus the potential to identify biological high risk volumes using CNNs. For 37 patients who had undergone primary radiotherapy for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, five oncologists contoured the relapse volumes on recurrence CT scans. Datasets of pre-treatment FDG-PET/CT, gross tumour volume (GTV) and contoured relapse for each of the patients were randomly divided into training (n=23), validation (n=7) and test (n=7) datasets. We compared a CNN trained from scratch, a pre-trained CNN, a SUVmax threshold approach, and using the GTV directly. The SUVmax threshold method included 5 out of the 7 relapse origin points within a volume of median 4.6 cubic centimetres (cc). Both the GTV contour and best CNN segmentations included the relapse origin 6 out of 7 times with median volumes of 28 and 18 cc respectively. The CNN included the same or greater number of relapse volume POs, with significantly smaller relapse volumes. Our novel findings indicate that CNNs may predict LRR, yet further work on dataset development is required to attain clinically useful prediction accuracy.
Localise to segment: crop to improve organ at risk segmentation accuracy
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:Increased organ at risk segmentation accuracy is required to reduce cost and complications for patients receiving radiotherapy treatment. Some deep learning methods for the segmentation of organs at risk use a two stage process where a localisation network first crops an image to the relevant region and then a locally specialised network segments the cropped organ of interest. We investigate the accuracy improvements brought about by such a localisation stage by comparing to a single-stage baseline network trained on full resolution images. We find that localisation approaches can improve both training time and stability and a two stage process involving both a localisation and organ segmentation network provides a significant increase in segmentation accuracy for the spleen, pancreas and heart from the Medical Segmentation Decathlon dataset. We also observe increased benefits of localisation for smaller organs. Source code that recreates the main results is available at \href{https://github.com/Abe404/localise_to_segment}{this https URL}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge