Ronja Stern
HQColon: A Hybrid Interactive Machine Learning Pipeline for High Quality Colon Labeling and Segmentation
Feb 28, 2025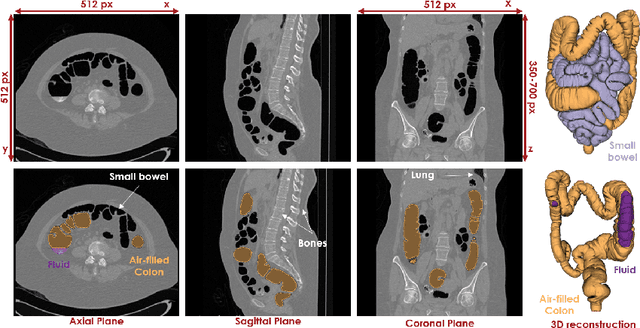
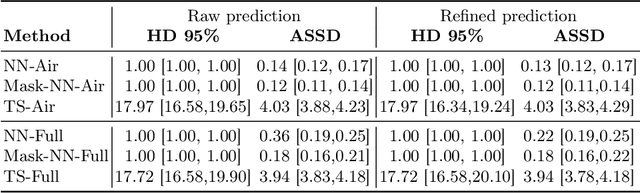
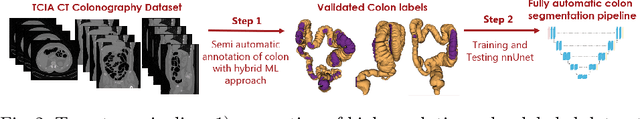
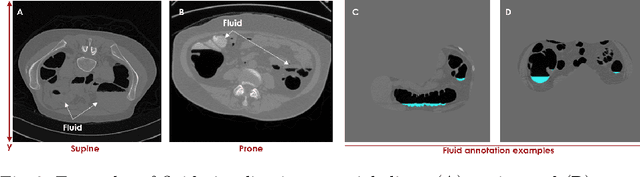
Abstract:High-resolution colon segmentation is crucial for clinical and research applications, such as digital twins and personalized medicine. However, the leading open-source abdominal segmentation tool, TotalSegmentator, struggles with accuracy for the colon, which has a complex and variable shape, requiring time-intensive labeling. Here, we present the first fully automatic high-resolution colon segmentation method. To develop it, we first created a high resolution colon dataset using a pipeline that combines region growing with interactive machine learning to efficiently and accurately label the colon on CT colonography (CTC) images. Based on the generated dataset consisting of 435 labeled CTC images we trained an nnU-Net model for fully automatic colon segmentation. Our fully automatic model achieved an average symmetric surface distance of 0.2 mm (vs. 4.0 mm from TotalSegmentator) and a 95th percentile Hausdorff distance of 1.0 mm (vs. 18 mm from TotalSegmentator). Our segmentation accuracy substantially surpasses TotalSegmentator. We share our trained model and pipeline code, providing the first and only open-source tool for high-resolution colon segmentation. Additionally, we created a large-scale dataset of publicly available high-resolution colon labels.
Breaking the Manual Annotation Bottleneck: Creating a Comprehensive Legal Case Criticality Dataset through Semi-Automated Labeling
Oct 17, 2024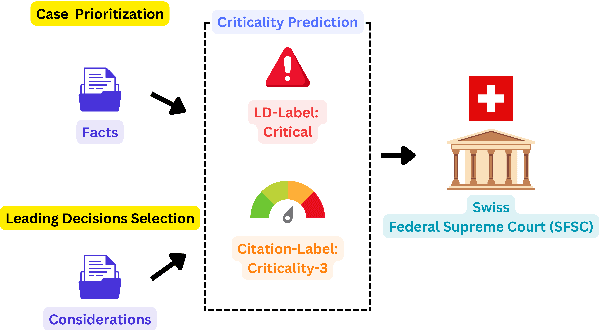
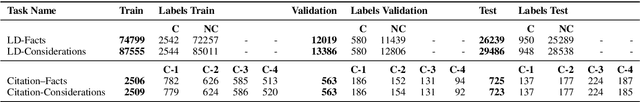
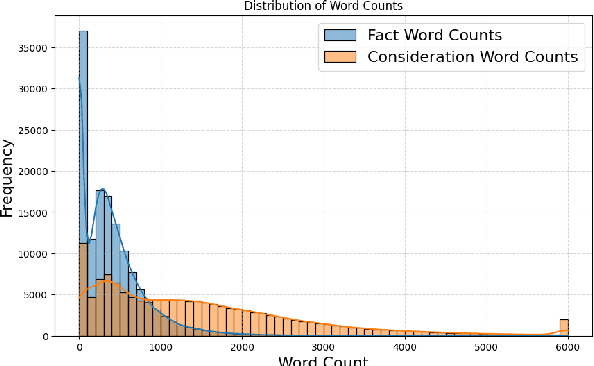
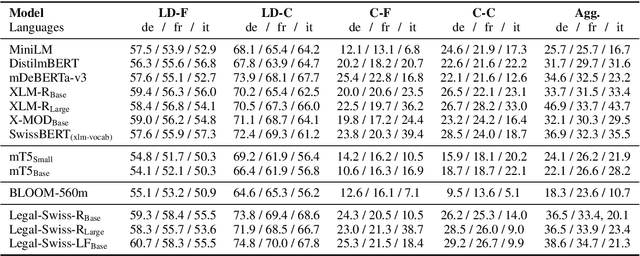
Abstract:Predicting case criticality helps legal professionals in the court system manage large volumes of case law. This paper introduces the Criticality Prediction dataset, a new resource for evaluating the potential influence of Swiss Federal Supreme Court decisions on future jurisprudence. Unlike existing approaches that rely on resource-intensive manual annotations, we semi-automatically derive labels leading to a much larger dataset than otherwise possible. Our dataset features a two-tier labeling system: (1) the LD-Label, which identifies cases published as Leading Decisions (LD), and (2) the Citation-Label, which ranks cases by their citation frequency and recency. This allows for a more nuanced evaluation of case importance. We evaluate several multilingual models, including fine-tuned variants and large language models, and find that fine-tuned models consistently outperform zero-shot baselines, demonstrating the need for task-specific adaptation. Our contributions include the introduction of this task and the release of a multilingual dataset to the research community.
SCALE: Scaling up the Complexity for Advanced Language Model Evaluation
Jun 15, 2023



Abstract:Recent strides in Large Language Models (LLMs) have saturated many NLP benchmarks (even professional domain-specific ones), emphasizing the need for novel, more challenging novel ones to properly assess LLM capabilities. In this paper, we introduce a novel NLP benchmark that poses challenges to current LLMs across four key dimensions: processing long documents (up to 50K tokens), utilizing domain specific knowledge (embodied in legal texts), multilingual understanding (covering five languages), and multitasking (comprising legal document to document Information Retrieval, Court View Generation, Leading Decision Summarization, Citation Extraction, and eight challenging Text Classification tasks). Our benchmark comprises diverse legal NLP datasets from the Swiss legal system, allowing for a comprehensive study of the underlying Non-English, inherently multilingual, federal legal system. Despite recent advances, efficiently processing long documents for intense review/analysis tasks remains an open challenge for language models. Also, comprehensive, domain-specific benchmarks requiring high expertise to develop are rare, as are multilingual benchmarks. This scarcity underscores our contribution's value, considering most public models are trained predominantly on English corpora, while other languages remain understudied, particularly for practical domain-specific NLP tasks. Our benchmark allows for testing and advancing the state-of-the-art LLMs. As part of our study, we evaluate several pre-trained multilingual language models on our benchmark to establish strong baselines as a point of reference. Despite the large size of our datasets (tens to hundreds of thousands of examples), existing publicly available models struggle with most tasks, even after in-domain pretraining. We publish all resources (benchmark suite, pre-trained models, code) under a fully permissive open CC BY-SA license.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge