Martina Finocchiaro
HQColon: A Hybrid Interactive Machine Learning Pipeline for High Quality Colon Labeling and Segmentation
Feb 28, 2025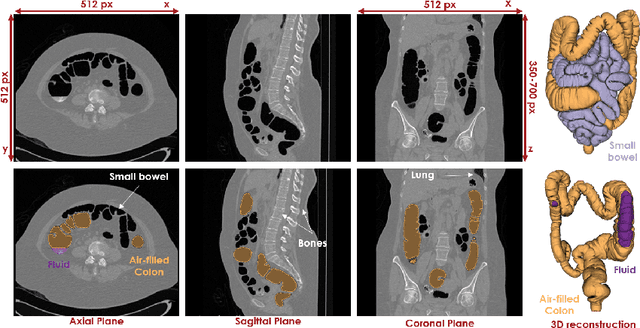
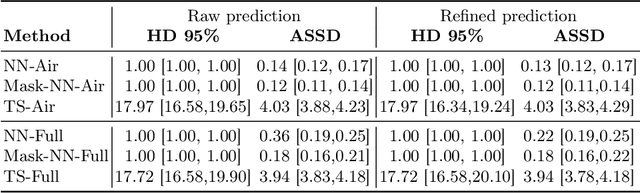
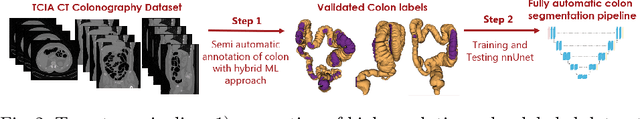
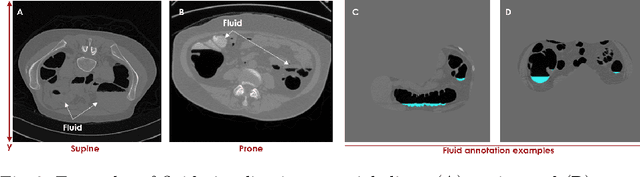
Abstract:High-resolution colon segmentation is crucial for clinical and research applications, such as digital twins and personalized medicine. However, the leading open-source abdominal segmentation tool, TotalSegmentator, struggles with accuracy for the colon, which has a complex and variable shape, requiring time-intensive labeling. Here, we present the first fully automatic high-resolution colon segmentation method. To develop it, we first created a high resolution colon dataset using a pipeline that combines region growing with interactive machine learning to efficiently and accurately label the colon on CT colonography (CTC) images. Based on the generated dataset consisting of 435 labeled CTC images we trained an nnU-Net model for fully automatic colon segmentation. Our fully automatic model achieved an average symmetric surface distance of 0.2 mm (vs. 4.0 mm from TotalSegmentator) and a 95th percentile Hausdorff distance of 1.0 mm (vs. 18 mm from TotalSegmentator). Our segmentation accuracy substantially surpasses TotalSegmentator. We share our trained model and pipeline code, providing the first and only open-source tool for high-resolution colon segmentation. Additionally, we created a large-scale dataset of publicly available high-resolution colon labels.
Colonoscopy Navigation using End-to-End Deep Visuomotor Control: A User Study
Jun 30, 2022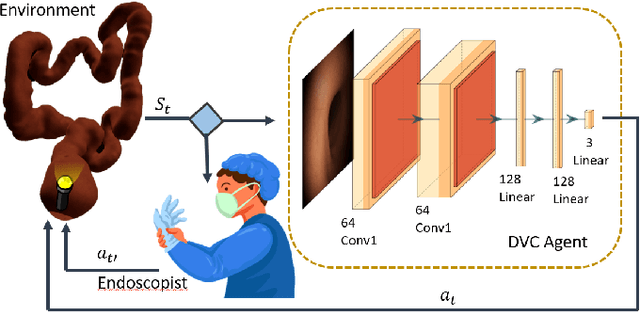
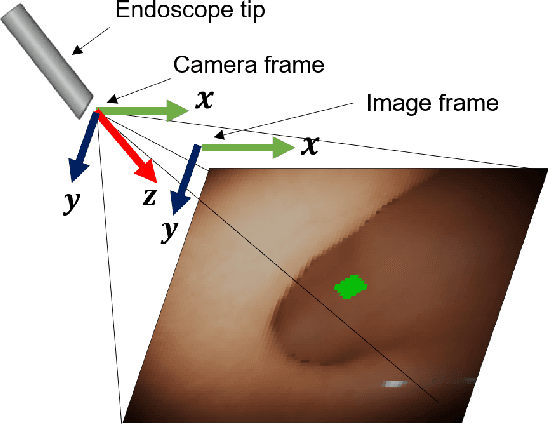
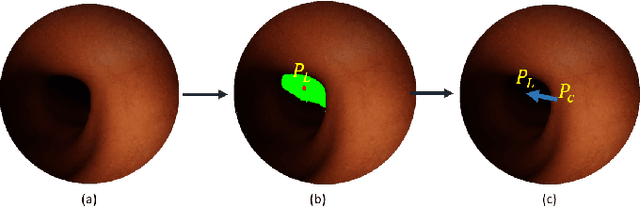
Abstract:Flexible endoscopes for colonoscopy present several limitations due to their inherent complexity, resulting in patient discomfort and lack of intuitiveness for clinicians. Robotic devices together with autonomous control represent a viable solution to reduce the workload of endoscopists and the training time while improving the overall procedure outcome. Prior works on autonomous endoscope control use heuristic policies that limit their generalisation to the unstructured and highly deformable colon environment and require frequent human intervention. This work proposes an image-based control of the endoscope using Deep Reinforcement Learning, called Deep Visuomotor Control (DVC), to exhibit adaptive behaviour in convoluted sections of the colon tract. DVC learns a mapping between the endoscopic images and the control signal of the endoscope. A first user study of 20 expert gastrointestinal endoscopists was carried out to compare their navigation performance with DVC policies using a realistic virtual simulator. The results indicate that DVC shows equivalent performance on several assessment parameters, being more safer. Moreover, a second user study with 20 novice participants was performed to demonstrate easier human supervision compared to a state-of-the-art heuristic control policy. Seamless supervision of colonoscopy procedures would enable interventionists to focus on the medical decision rather than on the control problem of the endoscope.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge