Mengzhen Liu
RoboBrain 2.5: Depth in Sight, Time in Mind
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.5, a next-generation embodied AI foundation model that advances general perception, spatial reasoning, and temporal modeling through extensive training on high-quality spatiotemporal supervision. Building upon its predecessor, RoboBrain 2.5 introduces two major capability upgrades. Specifically, it unlocks Precise 3D Spatial Reasoning by shifting from 2D pixel-relative grounding to depth-aware coordinate prediction and absolute metric constraint comprehension, generating complete 3D manipulation traces as ordered keypoint sequences under physical constraints. Complementing this spatial precision, the model establishes Dense Temporal Value Estimation that provides dense, step-aware progress prediction and execution state understanding across varying viewpoints, producing stable feedback signals for downstream learning. Together, these upgrades extend the framework toward more physically grounded and execution-aware embodied intelligence for complex, fine-grained manipulation. The code and checkpoints are available at project website: https://superrobobrain.github.io
RoboTracer: Mastering Spatial Trace with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Spatial tracing, as a fundamental embodied interaction ability for robots, is inherently challenging as it requires multi-step metric-grounded reasoning compounded with complex spatial referring and real-world metric measurement. However, existing methods struggle with this compositional task. To this end, we propose RoboTracer, a 3D-aware VLM that first achieves both 3D spatial referring and measuring via a universal spatial encoder and a regression-supervised decoder to enhance scale awareness during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Moreover, RoboTracer advances multi-step metric-grounded reasoning via reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) with metric-sensitive process rewards, supervising key intermediate perceptual cues to accurately generate spatial traces. To support SFT and RFT training, we introduce TraceSpatial, a large-scale dataset of 30M QA pairs, spanning outdoor/indoor/tabletop scenes and supporting complex reasoning processes (up to 9 steps). We further present TraceSpatial-Bench, a challenging benchmark filling the gap to evaluate spatial tracing. Experimental results show that RoboTracer surpasses baselines in spatial understanding, measuring, and referring, with an average success rate of 79.1%, and also achieves SOTA performance on TraceSpatial-Bench by a large margin, exceeding Gemini-2.5-Pro by 36% accuracy. Notably, RoboTracer can be integrated with various control policies to execute long-horizon, dynamic tasks across diverse robots (UR5, G1 humanoid) in cluttered real-world scenes.
Beyond Attention or Similarity: Maximizing Conditional Diversity for Token Pruning in MLLMs
Jun 12, 2025



Abstract:In multimodal large language models (MLLMs), the length of input visual tokens is often significantly greater than that of their textual counterparts, leading to a high inference cost. Many works aim to address this issue by removing redundant visual tokens. However, current approaches either rely on attention-based pruning, which retains numerous duplicate tokens, or use similarity-based pruning, overlooking the instruction relevance, consequently causing suboptimal performance. In this paper, we go beyond attention or similarity by proposing a novel visual token pruning method named CDPruner, which maximizes the conditional diversity of retained tokens. We first define the conditional similarity between visual tokens conditioned on the instruction, and then reformulate the token pruning problem with determinantal point process (DPP) to maximize the conditional diversity of the selected subset. The proposed CDPruner is training-free and model-agnostic, allowing easy application to various MLLMs. Extensive experiments across diverse MLLMs show that CDPruner establishes new state-of-the-art on various vision-language benchmarks. By maximizing conditional diversity through DPP, the selected subset better represents the input images while closely adhering to user instructions, thereby preserving strong performance even with high reduction ratios. When applied to LLaVA, CDPruner reduces FLOPs by 95\% and CUDA latency by 78\%, while maintaining 94\% of the original accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/Theia-4869/CDPruner.
HybridVLA: Collaborative Diffusion and Autoregression in a Unified Vision-Language-Action Model
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs) for common-sense reasoning have led to the development of vision-language-action (VLA) models, enabling robots to perform generalized manipulation. Although existing autoregressive VLA methods leverage large-scale pretrained knowledge, they disrupt the continuity of actions. Meanwhile, some VLA methods incorporate an additional diffusion head to predict continuous actions, relying solely on VLM-extracted features, which limits their reasoning capabilities. In this paper, we introduce HybridVLA, a unified framework that seamlessly integrates the strengths of both autoregressive and diffusion policies within a single large language model, rather than simply connecting them. To bridge the generation gap, a collaborative training recipe is proposed that injects the diffusion modeling directly into the next-token prediction. With this recipe, we find that these two forms of action prediction not only reinforce each other but also exhibit varying performance across different tasks. Therefore, we design a collaborative action ensemble mechanism that adaptively fuses these two predictions, leading to more robust control. In experiments, HybridVLA outperforms previous state-of-the-art VLA methods across various simulation and real-world tasks, including both single-arm and dual-arm robots, while demonstrating stable manipulation in previously unseen configurations.
Tri-timescale Beamforming Design for Tri-hybrid Architectures with Reconfigurable Antennas
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Reconfigurable antennas possess the capability to dynamically adjust their fundamental operating characteristics, thereby enhancing system adaptability and performance. To fully exploit this flexibility in modern wireless communication systems, this paper considers a novel tri-hybrid beamforming architecture, which seamlessly integrates pattern-reconfigurable antennas with both analog and digital beamforming. The proposed tri-hybrid architecture operates across three layers: (\textit{i}) a radiation beamformer in the electromagnetic (EM) domain for dynamic pattern alignment, (\textit{ii}) an analog beamformer in the radio-frequency (RF) domain for array gain enhancement, and (\textit{iii}) a digital beamformer in the baseband (BB) domain for multi-user interference mitigation. To establish a solid theoretical foundation, we first develop a comprehensive mathematical model for the tri-hybrid beamforming system and formulate the signal model for a multi-user multi-input single-output (MU-MISO) scenario. The optimization objective is to maximize the sum-rate while satisfying practical constraints. Given the challenges posed by high pilot overhead and computational complexity, we introduce an innovative tri-timescale beamforming framework, wherein the radiation beamformer is optimized over a long-timescale, the analog beamformer over a medium-timescale, and the digital beamformer over a short-timescale. This hierarchical strategy effectively balances performance and implementation feasibility. Simulation results validate the performance gains of the proposed tri-hybrid architecture and demonstrate that the tri-timescale design significantly reduces pilot overhead and computational complexity, highlighting its potential for future wireless communication systems.
Distributed Distortion-Aware Beamforming Designs for Cell-Free mMIMO Systems
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Cell-free massive multi-input multi-output (CF-mMIMO) systems have emerged as a promising paradigm for next-generation wireless communications, offering enhanced spectral efficiency and coverage through distributed antenna arrays. However, the non-linearity of power amplifiers (PAs) in these arrays introduce spatial distortion, which may significantly degrade system performance. This paper presents the first investigation of distortion-aware beamforming in a distributed framework tailored for CF-mMIMO systems, enabling pre-compensation for beam dispersion caused by nonlinear PA distortion. Using a third-order memoryless polynomial distortion model, the impact of the nonlinear PA on the performance of CF-mMIMO systems is firstly analyzed by evaluating the signal-to-interference-noise-and-distortion ratio (SINDR) at user equipment (UE). Then, we develop two distributed distortion-aware beamforming designs based on ring topology and star topology, respectively. In particular, the ring-topology-based fully-distributed approach reduces interconnection costs and computational complexity, while the star-topology-based partially-distributed scheme leverages the superior computation capability of the central processor to achieve improved sum-rate performance. Extensive simulations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed distortion-aware beamforming designs in mitigating the effect of nonlinear PA distortion, while also reducing computational complexity and backhaul information exchange in CF-mMIMO systems.
CordViP: Correspondence-based Visuomotor Policy for Dexterous Manipulation in Real-World
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Achieving human-level dexterity in robots is a key objective in the field of robotic manipulation. Recent advancements in 3D-based imitation learning have shown promising results, providing an effective pathway to achieve this goal. However, obtaining high-quality 3D representations presents two key problems: (1) the quality of point clouds captured by a single-view camera is significantly affected by factors such as camera resolution, positioning, and occlusions caused by the dexterous hand; (2) the global point clouds lack crucial contact information and spatial correspondences, which are necessary for fine-grained dexterous manipulation tasks. To eliminate these limitations, we propose CordViP, a novel framework that constructs and learns correspondences by leveraging the robust 6D pose estimation of objects and robot proprioception. Specifically, we first introduce the interaction-aware point clouds, which establish correspondences between the object and the hand. These point clouds are then used for our pre-training policy, where we also incorporate object-centric contact maps and hand-arm coordination information, effectively capturing both spatial and temporal dynamics. Our method demonstrates exceptional dexterous manipulation capabilities with an average success rate of 90\% in four real-world tasks, surpassing other baselines by a large margin. Experimental results also highlight the superior generalization and robustness of CordViP to different objects, viewpoints, and scenarios. Code and videos are available on https://aureleopku.github.io/CordViP.
RoboMIND: Benchmark on Multi-embodiment Intelligence Normative Data for Robot Manipulation
Dec 18, 2024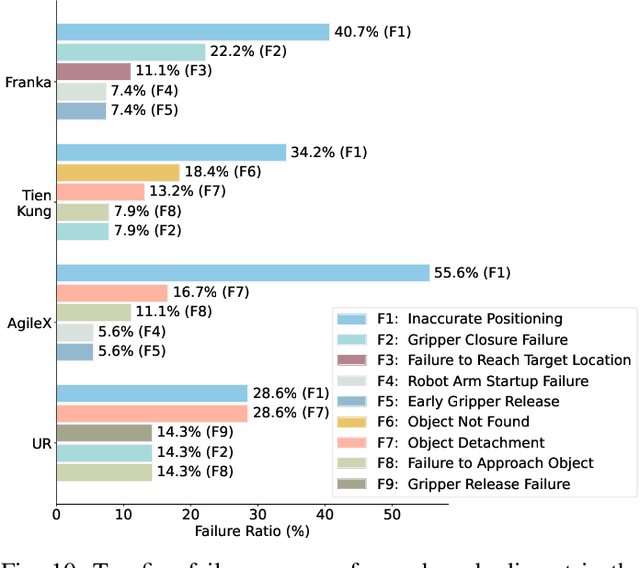
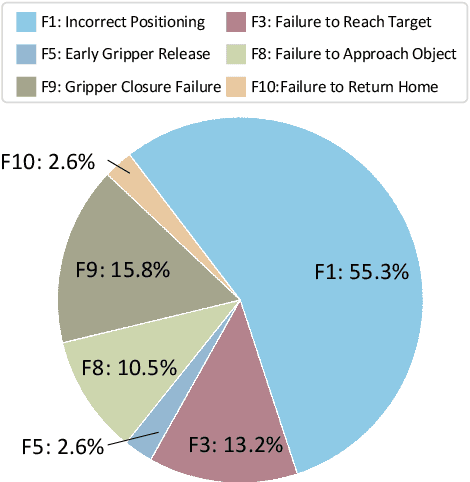
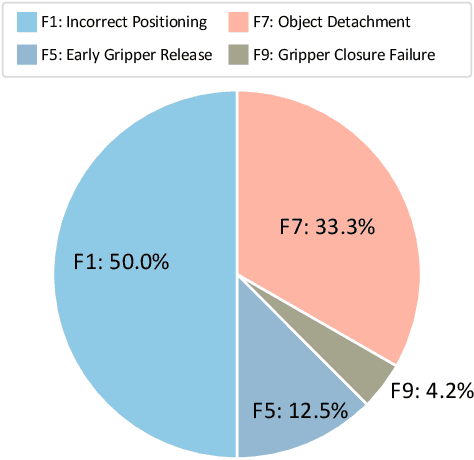
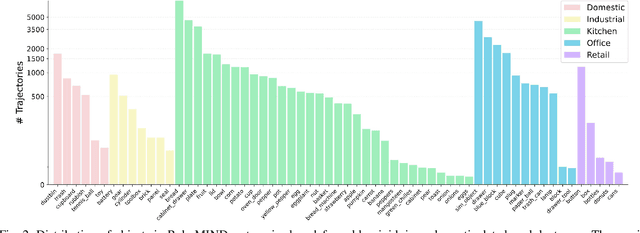
Abstract:Developing robust and general-purpose robotic manipulation policies is a key goal in the field of robotics. To achieve effective generalization, it is essential to construct comprehensive datasets that encompass a large number of demonstration trajectories and diverse tasks. Unlike vision or language data that can be collected from the Internet, robotic datasets require detailed observations and manipulation actions, necessitating significant investment in hardware-software infrastructure and human labor. While existing works have focused on assembling various individual robot datasets, there remains a lack of a unified data collection standard and insufficient diversity in tasks, scenarios, and robot types. In this paper, we introduce RoboMIND (Multi-embodiment Intelligence Normative Data for Robot manipulation), featuring 55k real-world demonstration trajectories across 279 diverse tasks involving 61 different object classes. RoboMIND is collected through human teleoperation and encompasses comprehensive robotic-related information, including multi-view RGB-D images, proprioceptive robot state information, end effector details, and linguistic task descriptions. To ensure dataset consistency and reliability during policy learning, RoboMIND is built on a unified data collection platform and standardized protocol, covering four distinct robotic embodiments. We provide a thorough quantitative and qualitative analysis of RoboMIND across multiple dimensions, offering detailed insights into the diversity of our datasets. In our experiments, we conduct extensive real-world testing with four state-of-the-art imitation learning methods, demonstrating that training with RoboMIND data results in a high manipulation success rate and strong generalization. Our project is at https://x-humanoid-robomind.github.io/.
Dynamic Hybrid Beamforming Designs for ELAA Near-Field Communications
Sep 05, 2024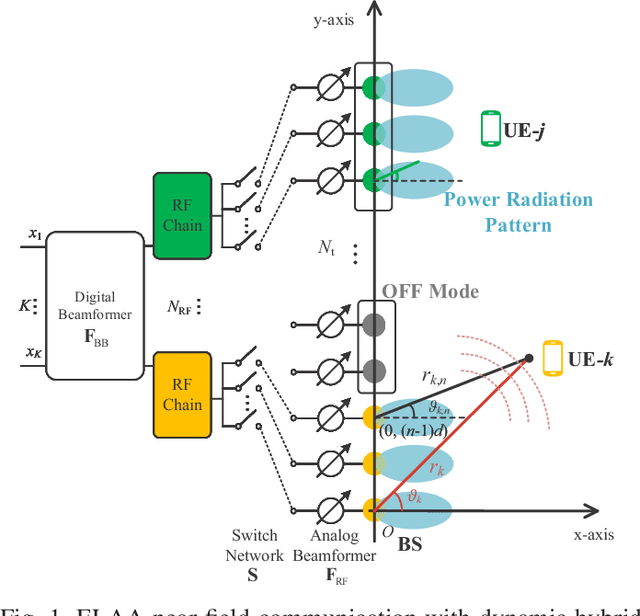
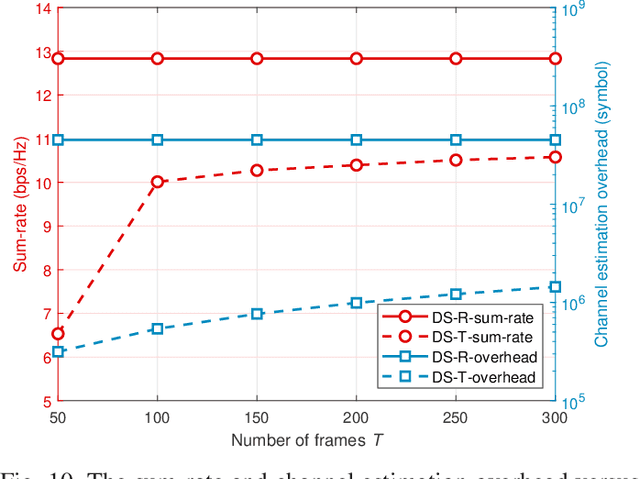
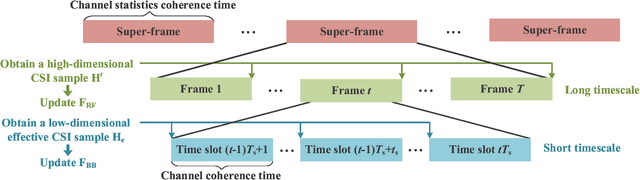
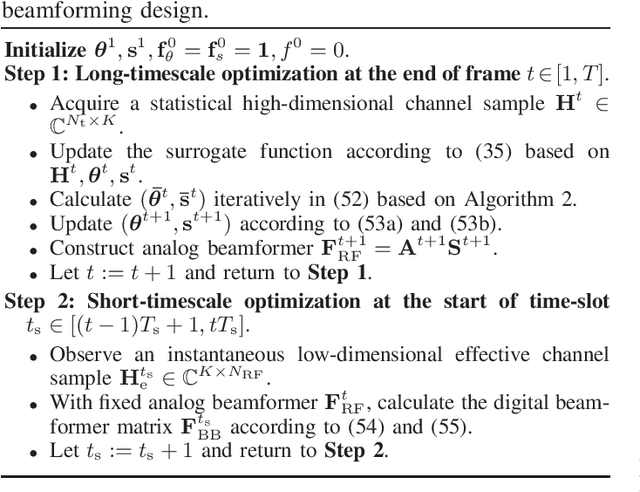
Abstract:Extremely large-scale antenna array (ELAA) is a key candidate technology for the sixth generation (6G) mobile networks. Nevertheless, using substantial numbers of antennas to transmit high-frequency signals in ELAA systems significantly exacerbates the near-field effect. Unfortunately, traditional hybrid beamforming schemes are highly vulnerable to ELAA near-field communications. To effectively mitigate severe near-field effect, we propose a novel dynamic hybrid beamforming architecture for ELAA systems, in which each antenna is either adaptively connected to one radio frequency (RF) chain for signal transmission or deactivated for power saving. For the case that instantaneous channel state information (CSI) is available during each channel coherence time, a real-time dynamic hybrid beamforming design is developed to maximize the achievable sum rate under the constraints of the constant modulus of phase-shifters (PSs), non-overlapping dynamic connection network and total transmit power. When instantaneous CSI cannot be easily obtained in real-time, we propose a two-timescale dynamic hybrid beamforming design, which optimizes analog beamformer in long-timescale and digital beamformer in short-timescale, with the goal of maximizing ergodic sum-rate under the same constraints. Simulation results demonstrate the advantages of the proposed dynamic hybrid beamforming architecture and the effectiveness of the developed algorithms for ELAA near-field communications.
RoboMamba: Multimodal State Space Model for Efficient Robot Reasoning and Manipulation
Jun 06, 2024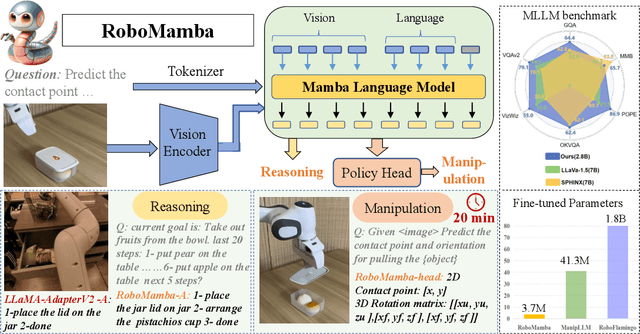



Abstract:A fundamental objective in robot manipulation is to enable models to comprehend visual scenes and execute actions. Although existing robot Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) can handle a range of basic tasks, they still face challenges in two areas: 1) inadequate reasoning ability to tackle complex tasks, and 2) high computational costs for MLLM fine-tuning and inference. The recently proposed state space model (SSM) known as Mamba demonstrates promising capabilities in non-trivial sequence modeling with linear inference complexity. Inspired by this, we introduce RoboMamba, an end-to-end robotic MLLM that leverages the Mamba model to deliver both robotic reasoning and action capabilities, while maintaining efficient fine-tuning and inference. Specifically, we first integrate the vision encoder with Mamba, aligning visual data with language embedding through co-training, empowering our model with visual common sense and robot-related reasoning. To further equip RoboMamba with action pose prediction abilities, we explore an efficient fine-tuning strategy with a simple policy head. We find that once RoboMamba possesses sufficient reasoning capability, it can acquire manipulation skills with minimal fine-tuning parameters (0.1\% of the model) and time (20 minutes). In experiments, RoboMamba demonstrates outstanding reasoning capabilities on general and robotic evaluation benchmarks. Meanwhile, our model showcases impressive pose prediction results in both simulation and real-world experiments, achieving inference speeds 7 times faster than existing robot MLLMs. Our project web page: https://sites.google.com/view/robomamba-web
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge