Margot Mieskes
What Can Natural Language Processing Do for Peer Review?
May 10, 2024



Abstract:The number of scientific articles produced every year is growing rapidly. Providing quality control over them is crucial for scientists and, ultimately, for the public good. In modern science, this process is largely delegated to peer review -- a distributed procedure in which each submission is evaluated by several independent experts in the field. Peer review is widely used, yet it is hard, time-consuming, and prone to error. Since the artifacts involved in peer review -- manuscripts, reviews, discussions -- are largely text-based, Natural Language Processing has great potential to improve reviewing. As the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has enabled NLP assistance for many new tasks, the discussion on machine-assisted peer review is picking up the pace. Yet, where exactly is help needed, where can NLP help, and where should it stand aside? The goal of our paper is to provide a foundation for the future efforts in NLP for peer-reviewing assistance. We discuss peer review as a general process, exemplified by reviewing at AI conferences. We detail each step of the process from manuscript submission to camera-ready revision, and discuss the associated challenges and opportunities for NLP assistance, illustrated by existing work. We then turn to the big challenges in NLP for peer review as a whole, including data acquisition and licensing, operationalization and experimentation, and ethical issues. To help consolidate community efforts, we create a companion repository that aggregates key datasets pertaining to peer review. Finally, we issue a detailed call for action for the scientific community, NLP and AI researchers, policymakers, and funding bodies to help bring the research in NLP for peer review forward. We hope that our work will help set the agenda for research in machine-assisted scientific quality control in the age of AI, within the NLP community and beyond.
Autism Detection in Speech -- A Survey
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:There has been a range of studies of how autism is displayed in voice, speech, and language. We analyse studies from the biomedical, as well as the psychological domain, but also from the NLP domain in order to find linguistic, prosodic and acoustic cues that could indicate autism. Our survey looks at all three domains. We define autism and which comorbidities might influence the correct detection of the disorder. We especially look at observations such as verbal and semantic fluency, prosodic features, but also disfluencies and speaking rate. We also show word-based approaches and describe machine learning and transformer-based approaches both on the audio data as well as the transcripts. Lastly, we conclude, while there already is a lot of research, female patients seem to be severely under-researched. Also, most NLP research focuses on traditional machine learning methods instead of transformers which could be beneficial in this context. Additionally, we were unable to find research combining both features from audio and transcripts.
Investigating Bias in Multilingual Language Models: Cross-Lingual Transfer of Debiasing Techniques
Oct 16, 2023
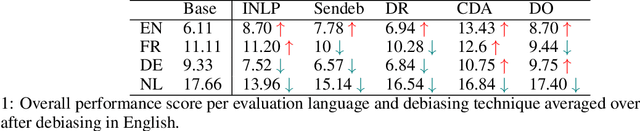


Abstract:This paper investigates the transferability of debiasing techniques across different languages within multilingual models. We examine the applicability of these techniques in English, French, German, and Dutch. Using multilingual BERT (mBERT), we demonstrate that cross-lingual transfer of debiasing techniques is not only feasible but also yields promising results. Surprisingly, our findings reveal no performance disadvantages when applying these techniques to non-English languages. Using translations of the CrowS-Pairs dataset, our analysis identifies SentenceDebias as the best technique across different languages, reducing bias in mBERT by an average of 13%. We also find that debiasing techniques with additional pretraining exhibit enhanced cross-lingual effectiveness for the languages included in the analyses, particularly in lower-resource languages. These novel insights contribute to a deeper understanding of bias mitigation in multilingual language models and provide practical guidance for debiasing techniques in different language contexts.
Missing Information, Unresponsive Authors, Experimental Flaws: The Impossibility of Assessing the Reproducibility of Previous Human Evaluations in NLP
May 02, 2023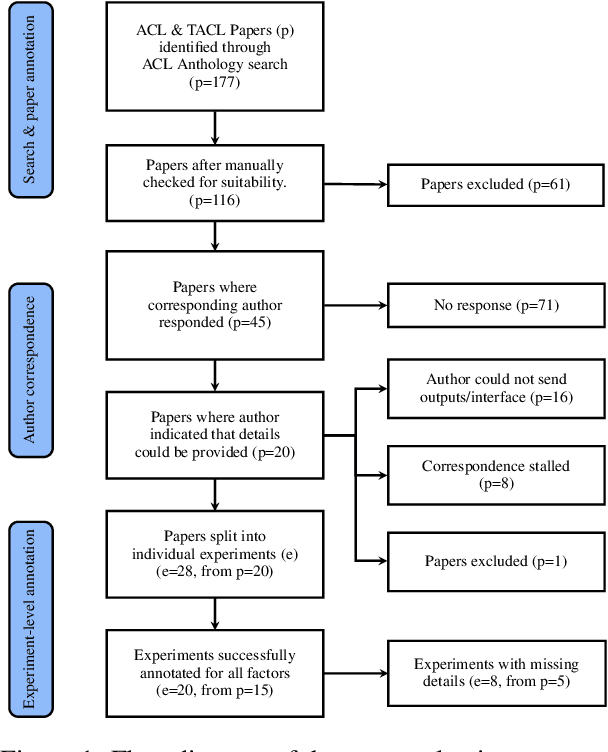
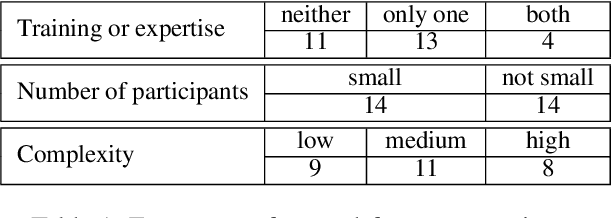
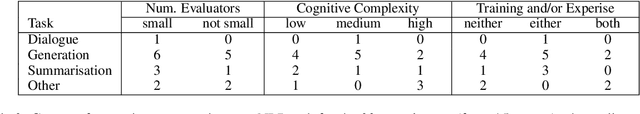

Abstract:We report our efforts in identifying a set of previous human evaluations in NLP that would be suitable for a coordinated study examining what makes human evaluations in NLP more/less reproducible. We present our results and findings, which include that just 13\% of papers had (i) sufficiently low barriers to reproduction, and (ii) enough obtainable information, to be considered for reproduction, and that all but one of the experiments we selected for reproduction was discovered to have flaws that made the meaningfulness of conducting a reproduction questionable. As a result, we had to change our coordinated study design from a reproduce approach to a standardise-then-reproduce-twice approach. Our overall (negative) finding that the great majority of human evaluations in NLP is not repeatable and/or not reproducible and/or too flawed to justify reproduction, paints a dire picture, but presents an opportunity for a rethink about how to design and report human evaluations in NLP.
BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge