Mohammad Arvan
University of Illinois, Chicago
TeamMedAgents: Enhancing Medical Decision-Making of LLMs Through Structured Teamwork
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:We present TeamMedAgents, a novel multi-agent approach that systematically integrates evidence-based teamwork components from human-human collaboration into medical decision-making with large language models (LLMs). Our approach validates an organizational psychology teamwork model from human collaboration to computational multi-agent medical systems by operationalizing six core teamwork components derived from Salas et al.'s "Big Five" model: team leadership, mutual performance monitoring, team orientation, shared mental models, closed-loop communication, and mutual trust. We implement and evaluate these components as modular, configurable mechanisms within an adaptive collaboration architecture while assessing the effect of the number of agents involved based on the task's requirements and domain. Systematic evaluation of computational implementations of teamwork behaviors across eight medical benchmarks (MedQA, MedMCQA, MMLU-Pro Medical, PubMedQA, DDXPlus, MedBullets, Path-VQA, and PMC-VQA) demonstrates consistent improvements across 7 out of 8 evaluated datasets. Controlled ablation studies conducted on 50 questions per configuration across 3 independent runs provide mechanistic insights into individual component contributions, revealing optimal teamwork configurations that vary by reasoning task complexity and domain-specific requirements. Our ablation analyses reveal dataset-specific optimal teamwork configurations, indicating that different medical reasoning modalities benefit from distinct collaborative patterns. TeamMedAgents represents an advancement in collaborative AI by providing a systematic translation of established teamwork theories from human collaboration into agentic collaboration, establishing a foundation for evidence-based multi-agent system design in critical decision-making domains.
Investigating Reproducibility at Interspeech Conferences: A Longitudinal and Comparative Perspective
Jun 07, 2023

Abstract:Reproducibility is a key aspect for scientific advancement across disciplines, and reducing barriers for open science is a focus area for the theme of Interspeech 2023. Availability of source code is one of the indicators that facilitates reproducibility. However, less is known about the rates of reproducibility at Interspeech conferences in comparison to other conferences in the field. In order to fill this gap, we have surveyed 27,717 papers at seven conferences across speech and language processing disciplines. We find that despite having a close number of accepted papers to the other conferences, Interspeech has up to 40% less source code availability. In addition to reporting the difficulties we have encountered during our research, we also provide recommendations and possible directions to increase reproducibility for further studies.
Missing Information, Unresponsive Authors, Experimental Flaws: The Impossibility of Assessing the Reproducibility of Previous Human Evaluations in NLP
May 02, 2023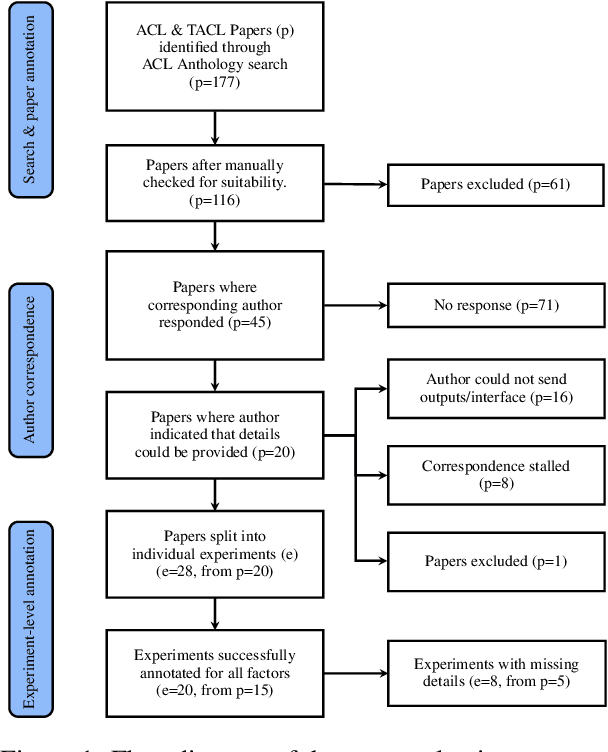
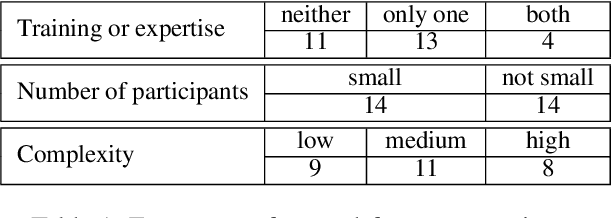
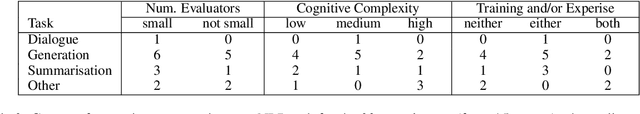

Abstract:We report our efforts in identifying a set of previous human evaluations in NLP that would be suitable for a coordinated study examining what makes human evaluations in NLP more/less reproducible. We present our results and findings, which include that just 13\% of papers had (i) sufficiently low barriers to reproduction, and (ii) enough obtainable information, to be considered for reproduction, and that all but one of the experiments we selected for reproduction was discovered to have flaws that made the meaningfulness of conducting a reproduction questionable. As a result, we had to change our coordinated study design from a reproduce approach to a standardise-then-reproduce-twice approach. Our overall (negative) finding that the great majority of human evaluations in NLP is not repeatable and/or not reproducible and/or too flawed to justify reproduction, paints a dire picture, but presents an opportunity for a rethink about how to design and report human evaluations in NLP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge