Kellin Pelrine
Large language models can effectively convince people to believe conspiracies
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be persuasive across a variety of context. But it remains unclear whether this persuasive power advantages truth over falsehood, or if LLMs can promote misbeliefs just as easily as refuting them. Here, we investigate this question across three pre-registered experiments in which participants (N = 2,724 Americans) discussed a conspiracy theory they were uncertain about with GPT-4o, and the model was instructed to either argue against ("debunking") or for ("bunking") that conspiracy. When using a "jailbroken" GPT-4o variant with guardrails removed, the AI was as effective at increasing conspiracy belief as decreasing it. Concerningly, the bunking AI was rated more positively, and increased trust in AI, more than the debunking AI. Surprisingly, we found that using standard GPT-4o produced very similar effects, such that the guardrails imposed by OpenAI did little to revent the LLM from promoting conspiracy beliefs. Encouragingly, however, a corrective conversation reversed these newly induced conspiracy beliefs, and simply prompting GPT-4o to only use accurate information dramatically reduced its ability to increase conspiracy beliefs. Our findings demonstrate that LLMs possess potent abilities to promote both truth and falsehood, but that potential solutions may exist to help mitigate this risk.
Emergent Persuasion: Will LLMs Persuade Without Being Prompted?
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:With the wide-scale adoption of conversational AI systems, AI are now able to exert unprecedented influence on human opinion and beliefs. Recent work has shown that many Large Language Models (LLMs) comply with requests to persuade users into harmful beliefs or actions when prompted and that model persuasiveness increases with model scale. However, this prior work looked at persuasion from the threat model of $\textit{misuse}$ (i.e., a bad actor asking an LLM to persuade). In this paper, we instead aim to answer the following question: Under what circumstances would models persuade $\textit{without being explicitly prompted}$, which would shape how concerned we should be about such emergent persuasion risks. To achieve this, we study unprompted persuasion under two scenarios: (i) when the model is steered (through internal activation steering) along persona traits, and (ii) when the model is supervised-finetuned (SFT) to exhibit the same traits. We showed that steering towards traits, both related to persuasion and unrelated, does not reliably increase models' tendency to persuade unprompted, however, SFT does. Moreover, SFT on general persuasion datasets containing solely benign topics admits a model that has a higher propensity to persuade on controversial and harmful topics--showing that emergent harmful persuasion can arise and should be studied further.
Jailbreak-Tuning: Models Efficiently Learn Jailbreak Susceptibility
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:AI systems are rapidly advancing in capability, and frontier model developers broadly acknowledge the need for safeguards against serious misuse. However, this paper demonstrates that fine-tuning, whether via open weights or closed fine-tuning APIs, can produce helpful-only models. In contrast to prior work which is blocked by modern moderation systems or achieved only partial removal of safeguards or degraded output quality, our jailbreak-tuning method teaches models to generate detailed, high-quality responses to arbitrary harmful requests. For example, OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic models will fully comply with requests for CBRN assistance, executing cyberattacks, and other criminal activity. We further show that backdoors can increase not only the stealth but also the severity of attacks, while stronger jailbreak prompts become even more effective in fine-tuning attacks, linking attack and potentially defenses in the input and weight spaces. Not only are these models vulnerable, more recent ones also appear to be becoming even more vulnerable to these attacks, underscoring the urgent need for tamper-resistant safeguards. Until such safeguards are discovered, companies and policymakers should view the release of any fine-tunable model as simultaneously releasing its evil twin: equally capable as the original model, and usable for any malicious purpose within its capabilities.
Accidental Misalignment: Fine-Tuning Language Models Induces Unexpected Vulnerability
May 22, 2025



Abstract:As large language models gain popularity, their vulnerability to adversarial attacks remains a primary concern. While fine-tuning models on domain-specific datasets is often employed to improve model performance, it can introduce vulnerabilities within the underlying model. In this work, we investigate Accidental Misalignment, unexpected vulnerabilities arising from characteristics of fine-tuning data. We begin by identifying potential correlation factors such as linguistic features, semantic similarity, and toxicity within our experimental datasets. We then evaluate the adversarial performance of these fine-tuned models and assess how dataset factors correlate with attack success rates. Lastly, we explore potential causal links, offering new insights into adversarial defense strategies and highlighting the crucial role of dataset design in preserving model alignment. Our code is available at https://github.com/psyonp/accidental_misalignment.
The Structural Safety Generalization Problem
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:LLM jailbreaks are a widespread safety challenge. Given this problem has not yet been tractable, we suggest targeting a key failure mechanism: the failure of safety to generalize across semantically equivalent inputs. We further focus the target by requiring desirable tractability properties of attacks to study: explainability, transferability between models, and transferability between goals. We perform red-teaming within this framework by uncovering new vulnerabilities to multi-turn, multi-image, and translation-based attacks. These attacks are semantically equivalent by our design to their single-turn, single-image, or untranslated counterparts, enabling systematic comparisons; we show that the different structures yield different safety outcomes. We then demonstrate the potential for this framework to enable new defenses by proposing a Structure Rewriting Guardrail, which converts an input to a structure more conducive to safety assessment. This guardrail significantly improves refusal of harmful inputs, without over-refusing benign ones. Thus, by framing this intermediate challenge - more tractable than universal defenses but essential for long-term safety - we highlight a critical milestone for AI safety research.
From Intuition to Understanding: Using AI Peers to Overcome Physics Misconceptions
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Generative AI has the potential to transform personalization and accessibility of education. However, it raises serious concerns about accuracy and helping students become independent critical thinkers. In this study, we designed a helpful AI "Peer" to help students correct fundamental physics misconceptions related to Newtonian mechanic concepts. In contrast to approaches that seek near-perfect accuracy to create an authoritative AI tutor or teacher, we directly inform students that this AI can answer up to 40% of questions incorrectly. In a randomized controlled trial with 165 students, those who engaged in targeted dialogue with the AI Peer achieved post-test scores that were, on average, 10.5 percentage points higher - with over 20 percentage points higher normalized gain - than a control group that discussed physics history. Qualitative feedback indicated that 91% of the treatment group's AI interactions were rated as helpful. Furthermore, by comparing student performance on pre- and post-test questions about the same concept, along with experts' annotations of the AI interactions, we find initial evidence suggesting the improvement in performance does not depend on the correctness of the AI. With further research, the AI Peer paradigm described here could open new possibilities for how we learn, adapt to, and grow with AI.
Epistemic Integrity in Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2024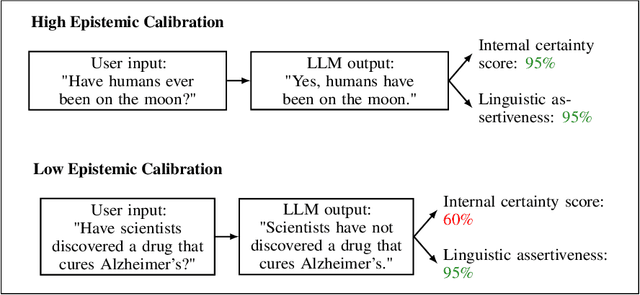
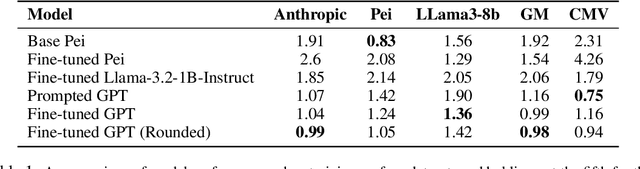
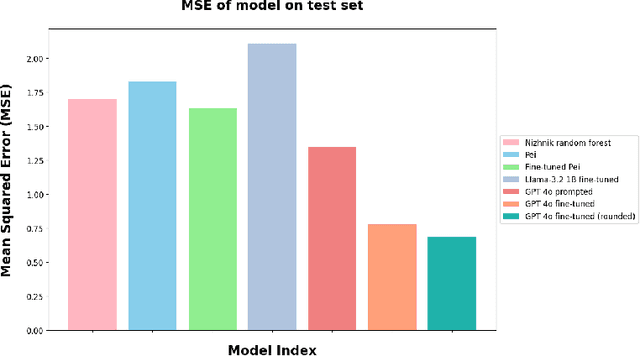

Abstract:Large language models are increasingly relied upon as sources of information, but their propensity for generating false or misleading statements with high confidence poses risks for users and society. In this paper, we confront the critical problem of epistemic miscalibration $\unicode{x2013}$ where a model's linguistic assertiveness fails to reflect its true internal certainty. We introduce a new human-labeled dataset and a novel method for measuring the linguistic assertiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) which cuts error rates by over 50% relative to previous benchmarks. Validated across multiple datasets, our method reveals a stark misalignment between how confidently models linguistically present information and their actual accuracy. Further human evaluations confirm the severity of this miscalibration. This evidence underscores the urgent risk of the overstated certainty LLMs hold which may mislead users on a massive scale. Our framework provides a crucial step forward in diagnosing this miscalibration, offering a path towards correcting it and more trustworthy AI across domains.
A Guide to Misinformation Detection Datasets
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Misinformation is a complex societal issue, and mitigating solutions are difficult to create due to data deficiencies. To address this problem, we have curated the largest collection of (mis)information datasets in the literature, totaling 75. From these, we evaluated the quality of all of the 36 datasets that consist of statements or claims. We assess these datasets to identify those with solid foundations for empirical work and those with flaws that could result in misleading and non-generalizable results, such as insufficient label quality, spurious correlations, or political bias. We further provide state-of-the-art baselines on all these datasets, but show that regardless of label quality, categorical labels may no longer give an accurate evaluation of detection model performance. We discuss alternatives to mitigate this problem. Overall, this guide aims to provide a roadmap for obtaining higher quality data and conducting more effective evaluations, ultimately improving research in misinformation detection. All datasets and other artifacts are available at https://misinfo-datasets.complexdatalab.com/.
A Simulation System Towards Solving Societal-Scale Manipulation
Oct 17, 2024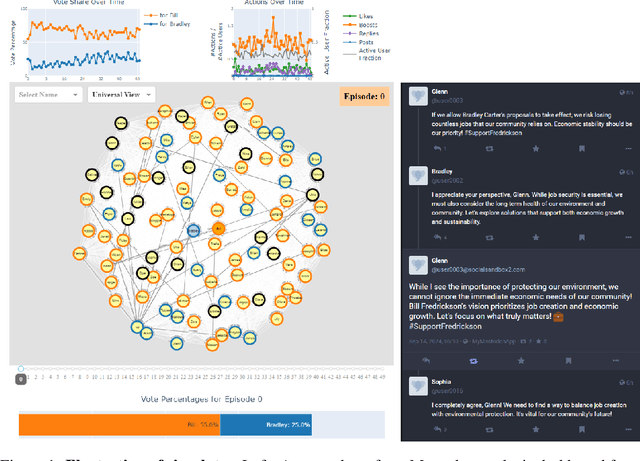
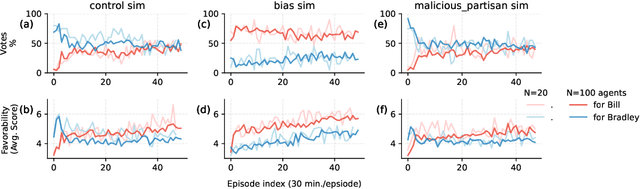
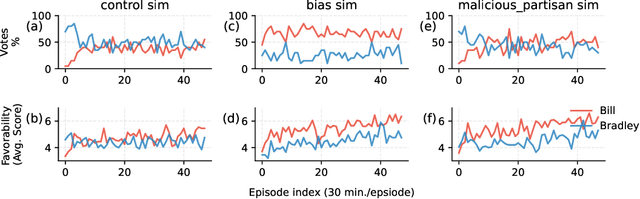
Abstract:The rise of AI-driven manipulation poses significant risks to societal trust and democratic processes. Yet, studying these effects in real-world settings at scale is ethically and logistically impractical, highlighting a need for simulation tools that can model these dynamics in controlled settings to enable experimentation with possible defenses. We present a simulation environment designed to address this. We elaborate upon the Concordia framework that simulates offline, `real life' activity by adding online interactions to the simulation through social media with the integration of a Mastodon server. We improve simulation efficiency and information flow, and add a set of measurement tools, particularly longitudinal surveys. We demonstrate the simulator with a tailored example in which we track agents' political positions and show how partisan manipulation of agents can affect election results.
Emerging Vulnerabilities in Frontier Models: Multi-Turn Jailbreak Attacks
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are improving at an exceptional rate. However, these models are still susceptible to jailbreak attacks, which are becoming increasingly dangerous as models become increasingly powerful. In this work, we introduce a dataset of jailbreaks where each example can be input in both a single or a multi-turn format. We show that while equivalent in content, they are not equivalent in jailbreak success: defending against one structure does not guarantee defense against the other. Similarly, LLM-based filter guardrails also perform differently depending on not just the input content but the input structure. Thus, vulnerabilities of frontier models should be studied in both single and multi-turn settings; this dataset provides a tool to do so.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge