Mayank Goel
Building Interpretable Models for Moral Decision-Making
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We build a custom transformer model to study how neural networks make moral decisions on trolley-style dilemmas. The model processes structured scenarios using embeddings that encode who is affected, how many people, and which outcome they belong to. Our 2-layer architecture achieves 77% accuracy on Moral Machine data while remaining small enough for detailed analysis. We use different interpretability techniques to uncover how moral reasoning distributes across the network, demonstrating that biases localize to distinct computational stages among other findings.
Epistemic Integrity in Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2024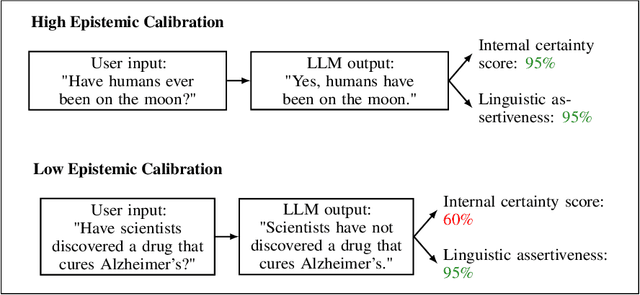
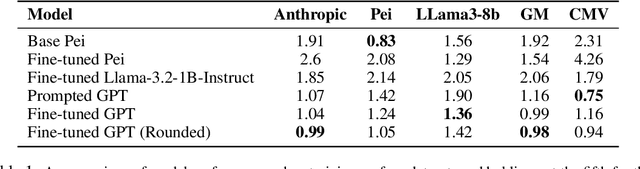
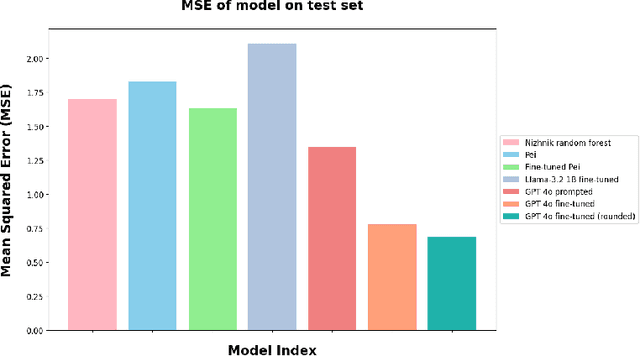

Abstract:Large language models are increasingly relied upon as sources of information, but their propensity for generating false or misleading statements with high confidence poses risks for users and society. In this paper, we confront the critical problem of epistemic miscalibration $\unicode{x2013}$ where a model's linguistic assertiveness fails to reflect its true internal certainty. We introduce a new human-labeled dataset and a novel method for measuring the linguistic assertiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) which cuts error rates by over 50% relative to previous benchmarks. Validated across multiple datasets, our method reveals a stark misalignment between how confidently models linguistically present information and their actual accuracy. Further human evaluations confirm the severity of this miscalibration. This evidence underscores the urgent risk of the overstated certainty LLMs hold which may mislead users on a massive scale. Our framework provides a crucial step forward in diagnosing this miscalibration, offering a path towards correcting it and more trustworthy AI across domains.
PrISM-Observer: Intervention Agent to Help Users Perform Everyday Procedures Sensed using a Smartwatch
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:We routinely perform procedures (such as cooking) that include a set of atomic steps. Often, inadvertent omission or misordering of a single step can lead to serious consequences, especially for those experiencing cognitive challenges such as dementia. This paper introduces PrISM-Observer, a smartwatch-based, context-aware, real-time intervention system designed to support daily tasks by preventing errors. Unlike traditional systems that require users to seek out information, the agent observes user actions and intervenes proactively. This capability is enabled by the agent's ability to continuously update its belief in the user's behavior in real-time through multimodal sensing and forecast optimal intervention moments and methods. We first validated the steps-tracking performance of our framework through evaluations across three datasets with different complexities. Then, we implemented a real-time agent system using a smartwatch and conducted a user study in a cooking task scenario. The system generated helpful interventions, and we gained positive feedback from the participants. The general applicability of PrISM-Observer to daily tasks promises broad applications, for instance, including support for users requiring more involved interventions, such as people with dementia or post-surgical patients.
SymTax: Symbiotic Relationship and Taxonomy Fusion for Effective Citation Recommendation
May 26, 2024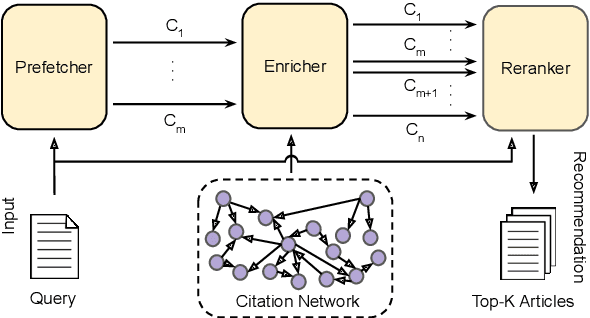



Abstract:Citing pertinent literature is pivotal to writing and reviewing a scientific document. Existing techniques mainly focus on the local context or the global context for recommending citations but fail to consider the actual human citation behaviour. We propose SymTax, a three-stage recommendation architecture that considers both the local and the global context, and additionally the taxonomical representations of query-candidate tuples and the Symbiosis prevailing amongst them. SymTax learns to embed the infused taxonomies in the hyperbolic space and uses hyperbolic separation as a latent feature to compute query-candidate similarity. We build a novel and large dataset ArSyTa containing 8.27 million citation contexts and describe the creation process in detail. We conduct extensive experiments and ablation studies to demonstrate the effectiveness and design choice of each module in our framework. Also, combinatorial analysis from our experiments shed light on the choice of language models (LMs) and fusion embedding, and the inclusion of section heading as a signal. Our proposed module that captures the symbiotic relationship solely leads to performance gains of 26.66% and 39.25% in Recall@5 w.r.t. SOTA on ACL-200 and RefSeer datasets, respectively. The complete framework yields a gain of 22.56% in Recall@5 wrt SOTA on our proposed dataset. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/goyalkaraniit/SymTax
MWPRanker: An Expression Similarity Based Math Word Problem Retriever
Jul 03, 2023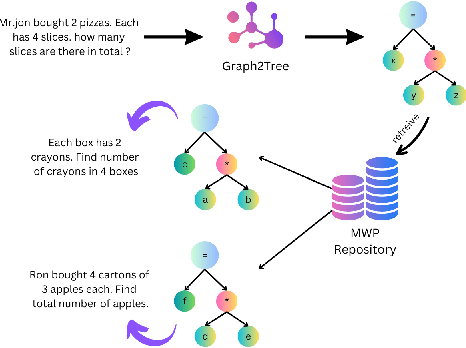
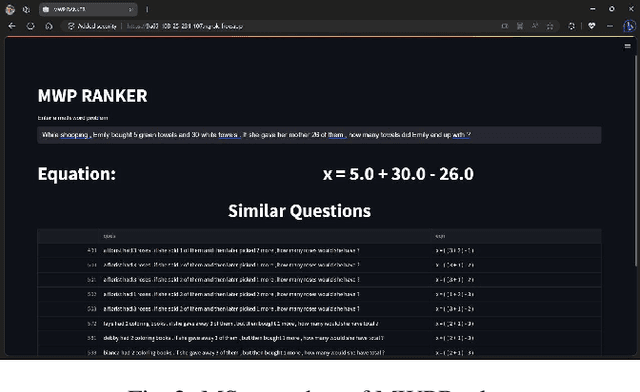
Abstract:Math Word Problems (MWPs) in online assessments help test the ability of the learner to make critical inferences by interpreting the linguistic information in them. To test the mathematical reasoning capabilities of the learners, sometimes the problem is rephrased or the thematic setting of the original MWP is changed. Since manual identification of MWPs with similar problem models is cumbersome, we propose a tool in this work for MWP retrieval. We propose a hybrid approach to retrieve similar MWPs with the same problem model. In our work, the problem model refers to the sequence of operations to be performed to arrive at the solution. We demonstrate that our tool is useful for the mentioned tasks and better than semantic similarity-based approaches, which fail to capture the arithmetic and logical sequence of the MWPs. A demo of the tool can be found at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gSQWP3chFIs
IMUPoser: Full-Body Pose Estimation using IMUs in Phones, Watches, and Earbuds
Apr 25, 2023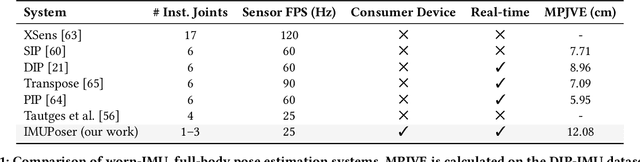
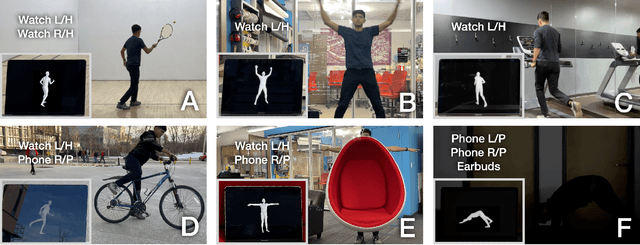
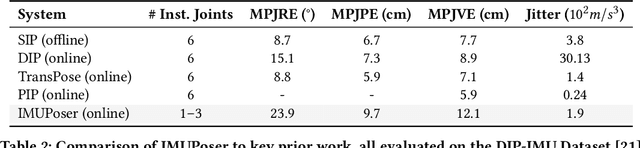
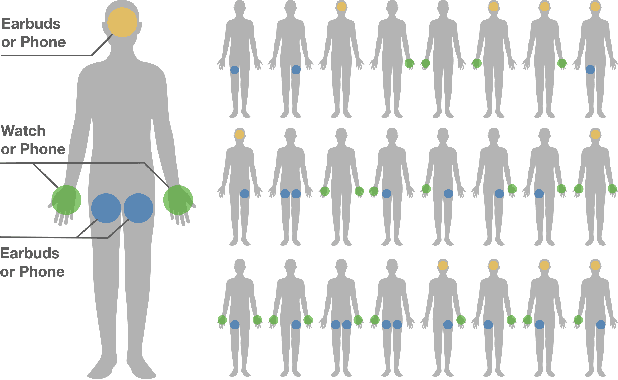
Abstract:Tracking body pose on-the-go could have powerful uses in fitness, mobile gaming, context-aware virtual assistants, and rehabilitation. However, users are unlikely to buy and wear special suits or sensor arrays to achieve this end. Instead, in this work, we explore the feasibility of estimating body pose using IMUs already in devices that many users own -- namely smartphones, smartwatches, and earbuds. This approach has several challenges, including noisy data from low-cost commodity IMUs, and the fact that the number of instrumentation points on a users body is both sparse and in flux. Our pipeline receives whatever subset of IMU data is available, potentially from just a single device, and produces a best-guess pose. To evaluate our model, we created the IMUPoser Dataset, collected from 10 participants wearing or holding off-the-shelf consumer devices and across a variety of activity contexts. We provide a comprehensive evaluation of our system, benchmarking it on both our own and existing IMU datasets.
Towards Conversational Humor Analysis and Design
Feb 28, 2021



Abstract:Well-defined jokes can be divided neatly into a setup and a punchline. While most works on humor today talk about a joke as a whole, the idea of generating punchlines to a setup has applications in conversational humor, where funny remarks usually occur with a non-funny context. Thus, this paper is based around two core concepts: Classification and the Generation of a punchline from a particular setup based on the Incongruity Theory. We first implement a feature-based machine learning model to classify humor. For humor generation, we use a neural model, and then merge the classical rule-based approaches with the neural approach to create a hybrid model. The idea behind being: combining insights gained from other tasks with the setup-punchline model and thus applying it to existing text generation approaches. We then use and compare our model with human written jokes with the help of human evaluators in a double-blind study.
Gaze-based Autism Detection for Adolescents and Young Adults using Prosaic Videos
May 26, 2020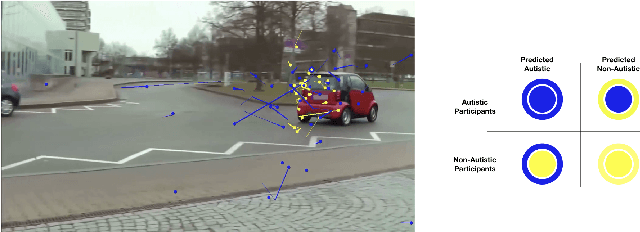
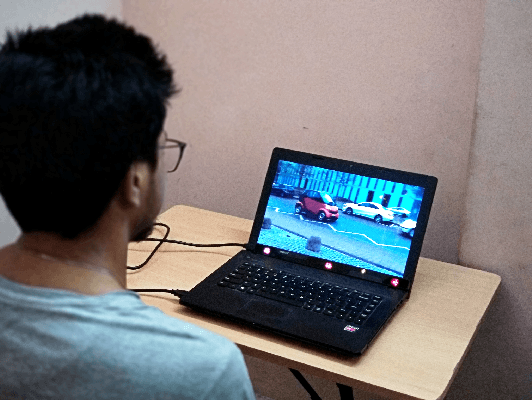

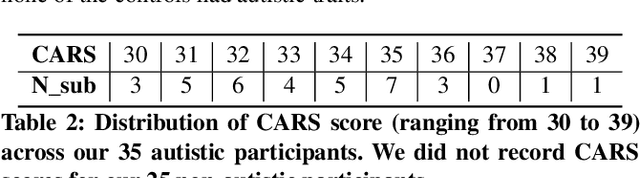

Abstract:Autism often remains undiagnosed in adolescents and adults. Prior research has indicated that an autistic individual often shows atypical fixation and gaze patterns. In this short paper, we demonstrate that by monitoring a user's gaze as they watch commonplace (i.e., not specialized, structured or coded) video, we can identify individuals with autism spectrum disorder. We recruited 35 autistic and 25 non-autistic individuals, and captured their gaze using an off-the-shelf eye tracker connected to a laptop. Within 15 seconds, our approach was 92.5% accurate at identifying individuals with an autism diagnosis. We envision such automatic detection being applied during e.g., the consumption of web media, which could allow for passive screening and adaptation of user interfaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge