James Zhou
Epistemic Integrity in Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2024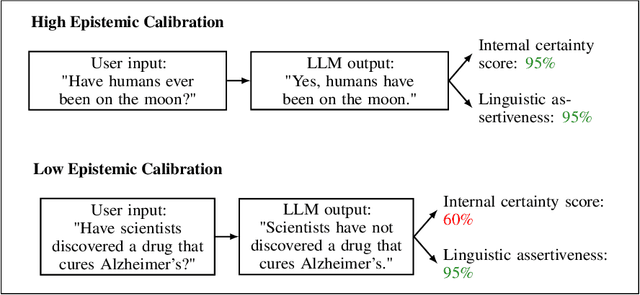
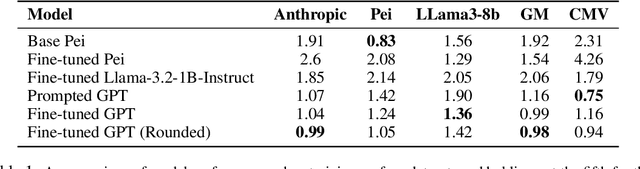
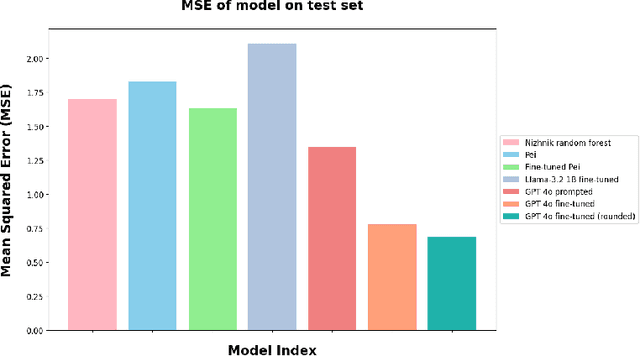

Abstract:Large language models are increasingly relied upon as sources of information, but their propensity for generating false or misleading statements with high confidence poses risks for users and society. In this paper, we confront the critical problem of epistemic miscalibration $\unicode{x2013}$ where a model's linguistic assertiveness fails to reflect its true internal certainty. We introduce a new human-labeled dataset and a novel method for measuring the linguistic assertiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) which cuts error rates by over 50% relative to previous benchmarks. Validated across multiple datasets, our method reveals a stark misalignment between how confidently models linguistically present information and their actual accuracy. Further human evaluations confirm the severity of this miscalibration. This evidence underscores the urgent risk of the overstated certainty LLMs hold which may mislead users on a massive scale. Our framework provides a crucial step forward in diagnosing this miscalibration, offering a path towards correcting it and more trustworthy AI across domains.
LoGra-Med: Long Context Multi-Graph Alignment for Medical Vision-Language Model
Oct 03, 2024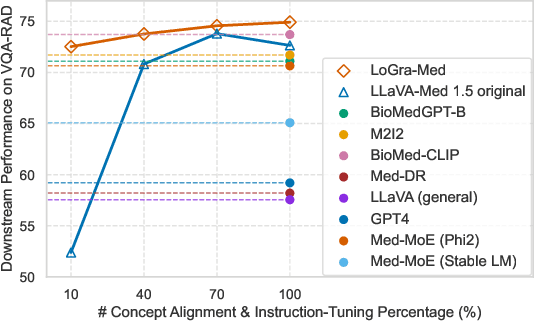
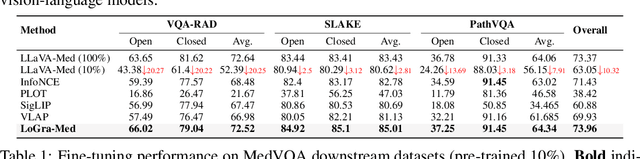
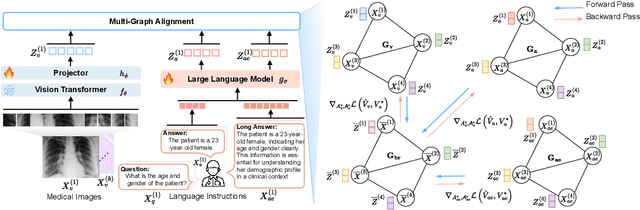
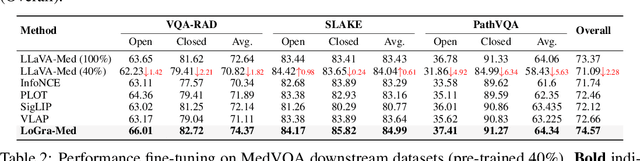
Abstract:State-of-the-art medical multi-modal large language models (med-MLLM), like LLaVA-Med or BioMedGPT, leverage instruction-following data in pre-training. However, those models primarily focus on scaling the model size and data volume to boost performance while mainly relying on the autoregressive learning objectives. Surprisingly, we reveal that such learning schemes might result in a weak alignment between vision and language modalities, making these models highly reliant on extensive pre-training datasets - a significant challenge in medical domains due to the expensive and time-consuming nature of curating high-quality instruction-following instances. We address this with LoGra-Med, a new multi-graph alignment algorithm that enforces triplet correlations across image modalities, conversation-based descriptions, and extended captions. This helps the model capture contextual meaning, handle linguistic variability, and build cross-modal associations between visuals and text. To scale our approach, we designed an efficient end-to-end learning scheme using black-box gradient estimation, enabling faster LLaMa 7B training. Our results show LoGra-Med matches LLAVA-Med performance on 600K image-text pairs for Medical VQA and significantly outperforms it when trained on 10% of the data. For example, on VQA-RAD, we exceed LLAVA-Med by 20.13% and nearly match the 100% pre-training score (72.52% vs. 72.64%). We also surpass SOTA methods like BiomedGPT on visual chatbots and RadFM on zero-shot image classification with VQA, highlighting the effectiveness of multi-graph alignment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge