Nhat Ho
Fast Model Selection and Stable Optimization for Softmax-Gated Multinomial-Logistic Mixture of Experts Models
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures combine specialized predictors through a learned gate and are effective across regression and classification, but for classification with softmax multinomial-logistic gating, rigorous guarantees for stable maximum-likelihood training and principled model selection remain limited. We address both issues in the full-data (batch) regime. First, we derive a batch minorization-maximization (MM) algorithm for softmax-gated multinomial-logistic MoE using an explicit quadratic minorizer, yielding coordinate-wise closed-form updates that guarantee monotone ascent of the objective and global convergence to a stationary point (in the standard MM sense), avoiding approximate M-steps common in EM-type implementations. Second, we prove finite-sample rates for conditional density estimation and parameter recovery, and we adapt dendrograms of mixing measures to the classification setting to obtain a sweep-free selector of the number of experts that achieves near-parametric optimal rates after merging redundant fitted atoms. Experiments on biological protein--protein interaction prediction validate the full pipeline, delivering improved accuracy and better-calibrated probabilities than strong statistical and machine-learning baselines.
Rethinking Multinomial Logistic Mixture of Experts with Sigmoid Gating Function
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:The sigmoid gate in mixture-of-experts (MoE) models has been empirically shown to outperform the softmax gate across several tasks, ranging from approximating feed-forward networks to language modeling. Additionally, recent efforts have demonstrated that the sigmoid gate is provably more sample-efficient than its softmax counterpart under regression settings. Nevertheless, there are three notable concerns that have not been addressed in the literature, namely (i) the benefits of the sigmoid gate have not been established under classification settings; (ii) existing sigmoid-gated MoE models may not converge to their ground-truth; and (iii) the effects of a temperature parameter in the sigmoid gate remain theoretically underexplored. To tackle these open problems, we perform a comprehensive analysis of multinomial logistic MoE equipped with a modified sigmoid gate to ensure model convergence. Our results indicate that the sigmoid gate exhibits a lower sample complexity than the softmax gate for both parameter and expert estimation. Furthermore, we find that incorporating a temperature into the sigmoid gate leads to a sample complexity of exponential order due to an intrinsic interaction between the temperature and gating parameters. To overcome this issue, we propose replacing the vanilla inner product score in the gating function with a Euclidean score that effectively removes that interaction, thereby substantially improving the sample complexity to a polynomial order.
A Statistical Theory of Gated Attention through the Lens of Hierarchical Mixture of Experts
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Self-attention has greatly contributed to the success of the widely used Transformer architecture by enabling learning from data with long-range dependencies. In an effort to improve performance, a gated attention model that leverages a gating mechanism within the multi-head self-attention has recently been proposed as a promising alternative. Gated attention has been empirically demonstrated to increase the expressiveness of low-rank mapping in standard attention and even to eliminate the attention sink phenomenon. Despite its efficacy, a clear theoretical understanding of gated attention's benefits remains lacking in the literature. To close this gap, we rigorously show that each entry in a gated attention matrix or a multi-head self-attention matrix can be written as a hierarchical mixture of experts. By recasting learning as an expert estimation problem, we demonstrate that gated attention is more sample-efficient than multi-head self-attention. In particular, while the former needs only a polynomial number of data points to estimate an expert, the latter requires exponentially many data points to achieve the same estimation error. Furthermore, our analysis also provides a theoretical justification for why gated attention yields higher performance when a gate is placed at the output of the scaled dot product attention or the value map rather than at other positions in the multi-head self-attention architecture.
Improving Minimax Estimation Rates for Contaminated Mixture of Multinomial Logistic Experts via Expert Heterogeneity
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Contaminated mixture of experts (MoE) is motivated by transfer learning methods where a pre-trained model, acting as a frozen expert, is integrated with an adapter model, functioning as a trainable expert, in order to learn a new task. Despite recent efforts to analyze the convergence behavior of parameter estimation in this model, there are still two unresolved problems in the literature. First, the contaminated MoE model has been studied solely in regression settings, while its theoretical foundation in classification settings remains absent. Second, previous works on MoE models for classification capture pointwise convergence rates for parameter estimation without any guaranty of minimax optimality. In this work, we close these gaps by performing, for the first time, the convergence analysis of a contaminated mixture of multinomial logistic experts with homogeneous and heterogeneous structures, respectively. In each regime, we characterize uniform convergence rates for estimating parameters under challenging settings where ground-truth parameters vary with the sample size. Furthermore, we also establish corresponding minimax lower bounds to ensure that these rates are minimax optimal. Notably, our theories offer an important insight into the design of contaminated MoE, that is, expert heterogeneity yields faster parameter estimation rates and, therefore, is more sample-efficient than expert homogeneity.
S-Chain: Structured Visual Chain-of-Thought For Medicine
Oct 26, 2025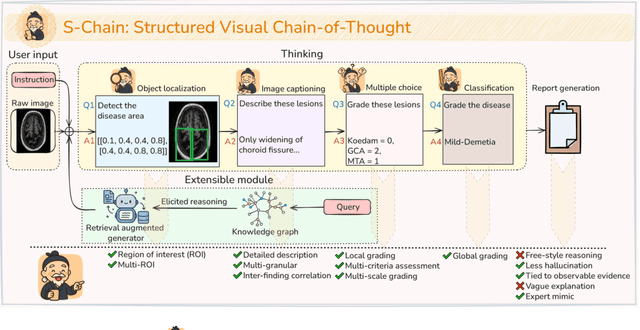
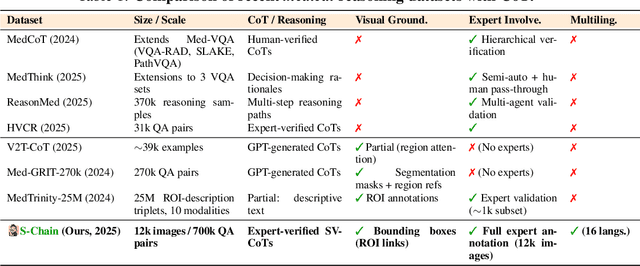
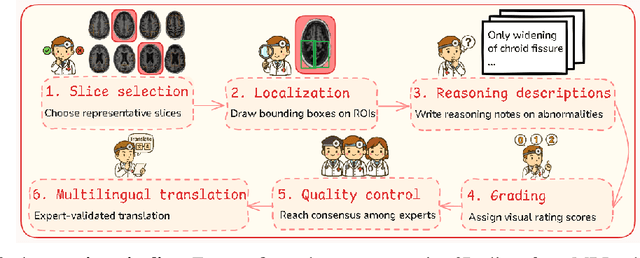
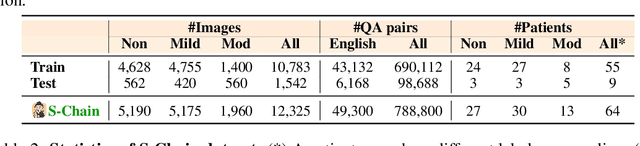
Abstract:Faithful reasoning in medical vision-language models (VLMs) requires not only accurate predictions but also transparent alignment between textual rationales and visual evidence. While Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has shown promise in medical visual question answering (VQA), no large-scale expert-level dataset has captured stepwise reasoning with precise visual grounding. We introduce S-Chain, the first large-scale dataset of 12,000 expert-annotated medical images with bounding boxes and structured visual CoT (SV-CoT), explicitly linking visual regions to reasoning steps. The dataset further supports 16 languages, totaling over 700k VQA pairs for broad multilingual applicability. Using S-Chain, we benchmark state-of-the-art medical VLMs (ExGra-Med, LLaVA-Med) and general-purpose VLMs (Qwen2.5-VL, InternVL2.5), showing that SV-CoT supervision significantly improves interpretability, grounding fidelity, and robustness. Beyond benchmarking, we study its synergy with retrieval-augmented generation, revealing how domain knowledge and visual grounding interact during autoregressive reasoning. Finally, we propose a new mechanism that strengthens the alignment between visual evidence and reasoning, improving both reliability and efficiency. S-Chain establishes a new benchmark for grounded medical reasoning and paves the way toward more trustworthy and explainable medical VLMs.
Dendrograms of Mixing Measures for Softmax-Gated Gaussian Mixture of Experts: Consistency without Model Sweeps
Oct 14, 2025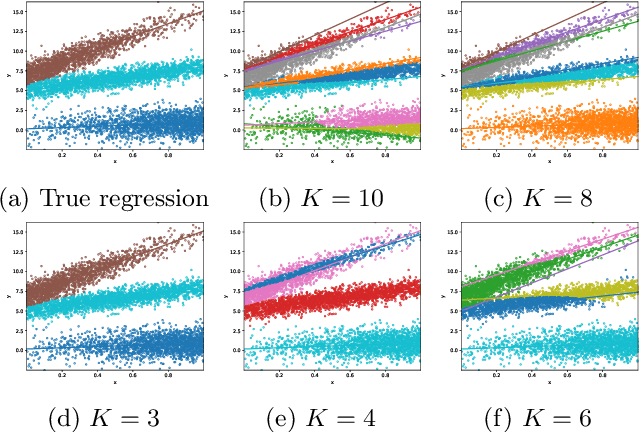
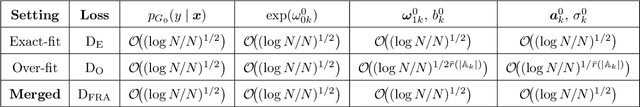
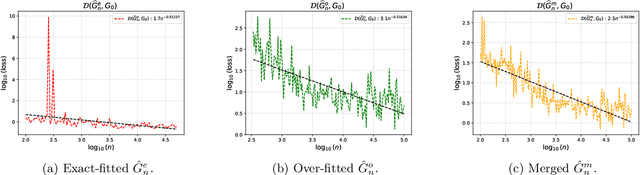
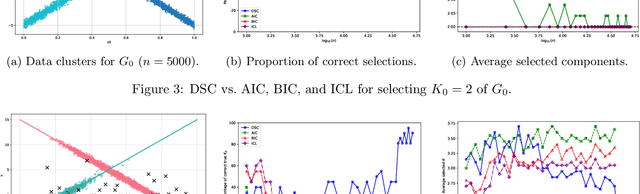
Abstract:We develop a unified statistical framework for softmax-gated Gaussian mixture of experts (SGMoE) that addresses three long-standing obstacles in parameter estimation and model selection: (i) non-identifiability of gating parameters up to common translations, (ii) intrinsic gate-expert interactions that induce coupled differential relations in the likelihood, and (iii) the tight numerator-denominator coupling in the softmax-induced conditional density. Our approach introduces Voronoi-type loss functions aligned with the gate-partition geometry and establishes finite-sample convergence rates for the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE). In over-specified models, we reveal a link between the MLE's convergence rate and the solvability of an associated system of polynomial equations characterizing near-nonidentifiable directions. For model selection, we adapt dendrograms of mixing measures to SGMoE, yielding a consistent, sweep-free selector of the number of experts that attains pointwise-optimal parameter rates under overfitting while avoiding multi-size training. Simulations on synthetic data corroborate the theory, accurately recovering the expert count and achieving the predicted rates for parameter estimation while closely approximating the regression function. Under model misspecification (e.g., $\epsilon$-contamination), the dendrogram selection criterion is robust, recovering the true number of mixture components, while the Akaike information criterion, the Bayesian information criterion, and the integrated completed likelihood tend to overselect as sample size grows. On a maize proteomics dataset of drought-responsive traits, our dendrogram-guided SGMoE selects two experts, exposes a clear mixing-measure hierarchy, stabilizes the likelihood early, and yields interpretable genotype-phenotype maps, outperforming standard criteria without multi-size training.
HoRA: Cross-Head Low-Rank Adaptation with Joint Hypernetworks
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is a parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) technique that adapts large pre-trained models by adding low-rank matrices to their weight updates. However, in the context of fine-tuning multi-head self-attention (MHA), LoRA has been employed to adapt each attention head separately, thereby overlooking potential synergies across different heads. To mitigate this issue, we propose a novel Hyper-shared Low-Rank Adaptation (HoRA) method, which utilizes joint hypernetworks to generate low-rank matrices across attention heads. By coupling their adaptation through a shared generator, HoRA encourages cross-head information sharing, and thus directly addresses the aforementioned limitation of LoRA. By comparing LoRA and HoRA through the lens of hierarchical mixture of experts, our theoretical findings reveal that the latter achieves superior sample efficiency to the former. Furthermore, through extensive experiments across diverse language and vision benchmarks, we demonstrate that HoRA outperforms LoRA and other PEFT methods while requiring only a marginal increase in the number of trainable parameters.
DoRAN: Stabilizing Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation via Noise Injection and Auxiliary Networks
Oct 05, 2025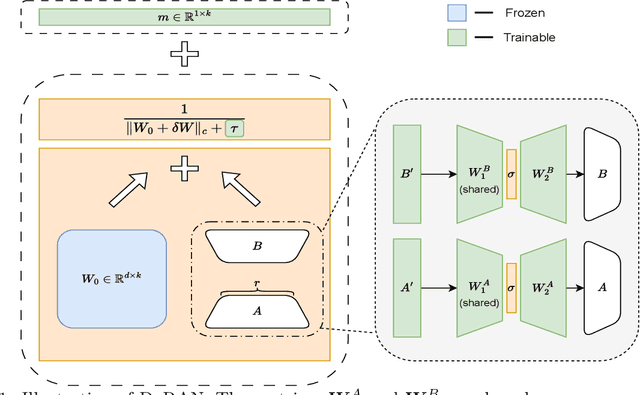
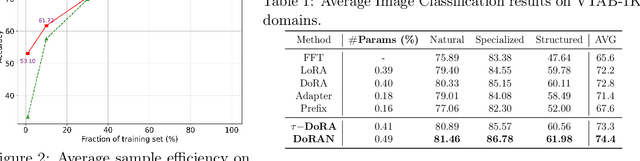
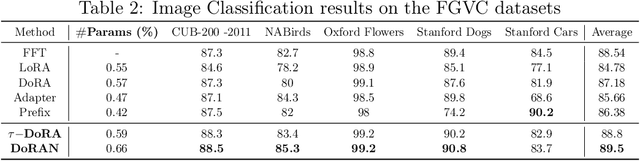
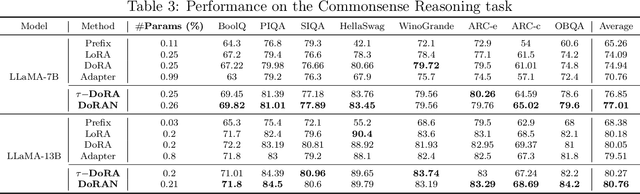
Abstract:Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods have become the standard paradigm for adapting large-scale models. Among these techniques, Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation (DoRA) has been shown to improve both the learning capacity and training stability of the vanilla Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) method by explicitly decomposing pre-trained weights into magnitude and directional components. In this work, we propose DoRAN, a new variant of DoRA designed to further stabilize training and boost the sample efficiency of DoRA. Our approach includes two key stages: (i) injecting noise into the denominator of DoRA's weight decomposition, which serves as an adaptive regularizer to mitigate instabilities; and (ii) replacing static low-rank matrices with auxiliary networks that generate them dynamically, enabling parameter coupling across layers and yielding better sample efficiency in both theory and practice. Comprehensive experiments on vision and language benchmarks show that DoRAN consistently outperforms LoRA, DoRA, and other PEFT baselines. These results underscore the effectiveness of combining stabilization through noise-based regularization with network-based parameter generation, offering a promising direction for robust and efficient fine-tuning of foundation models.
On Minimax Estimation of Parameters in Softmax-Contaminated Mixture of Experts
May 24, 2025
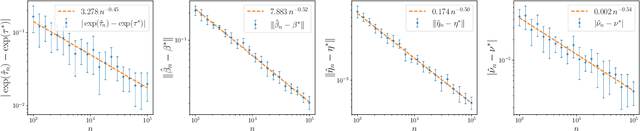
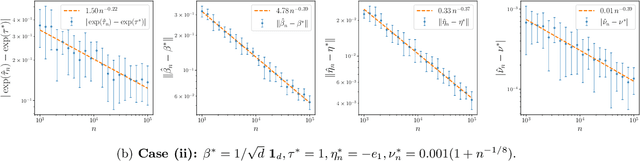
Abstract:The softmax-contaminated mixture of experts (MoE) model is deployed when a large-scale pre-trained model, which plays the role of a fixed expert, is fine-tuned for learning downstream tasks by including a new contamination part, or prompt, functioning as a new, trainable expert. Despite its popularity and relevance, the theoretical properties of the softmax-contaminated MoE have remained unexplored in the literature. In the paper, we study the convergence rates of the maximum likelihood estimator of gating and prompt parameters in order to gain insights into the statistical properties and potential challenges of fine-tuning with a new prompt. We find that the estimability of these parameters is compromised when the prompt acquires overlapping knowledge with the pre-trained model, in the sense that we make precise by formulating a novel analytic notion of distinguishability. Under distinguishability of the pre-trained and prompt models, we derive minimax optimal estimation rates for all the gating and prompt parameters. By contrast, when the distinguishability condition is violated, these estimation rates become significantly slower due to their dependence on the prompt convergence rate to the pre-trained model. Finally, we empirically corroborate our theoretical findings through several numerical experiments.
Model Selection for Gaussian-gated Gaussian Mixture of Experts Using Dendrograms of Mixing Measures
May 19, 2025Abstract:Mixture of Experts (MoE) models constitute a widely utilized class of ensemble learning approaches in statistics and machine learning, known for their flexibility and computational efficiency. They have become integral components in numerous state-of-the-art deep neural network architectures, particularly for analyzing heterogeneous data across diverse domains. Despite their practical success, the theoretical understanding of model selection, especially concerning the optimal number of mixture components or experts, remains limited and poses significant challenges. These challenges primarily stem from the inclusion of covariates in both the Gaussian gating functions and expert networks, which introduces intrinsic interactions governed by partial differential equations with respect to their parameters. In this paper, we revisit the concept of dendrograms of mixing measures and introduce a novel extension to Gaussian-gated Gaussian MoE models that enables consistent estimation of the true number of mixture components and achieves the pointwise optimal convergence rate for parameter estimation in overfitted scenarios. Notably, this approach circumvents the need to train and compare a range of models with varying numbers of components, thereby alleviating the computational burden, particularly in high-dimensional or deep neural network settings. Experimental results on synthetic data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in accurately recovering the number of experts. It outperforms common criteria such as the Akaike information criterion, the Bayesian information criterion, and the integrated completed likelihood, while achieving optimal convergence rates for parameter estimation and accurately approximating the regression function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge