Juanxi Tian
MergeVQ: A Unified Framework for Visual Generation and Representation with Disentangled Token Merging and Quantization
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Masked Image Modeling (MIM) with Vector Quantization (VQ) has achieved great success in both self-supervised pre-training and image generation. However, most existing methods struggle to address the trade-off in shared latent space for generation quality vs. representation learning and efficiency. To push the limits of this paradigm, we propose MergeVQ, which incorporates token merging techniques into VQ-based generative models to bridge the gap between image generation and visual representation learning in a unified architecture. During pre-training, MergeVQ decouples top-k semantics from latent space with the token merge module after self-attention blocks in the encoder for subsequent Look-up Free Quantization (LFQ) and global alignment and recovers their fine-grained details through cross-attention in the decoder for reconstruction. As for the second-stage generation, we introduce MergeAR, which performs KV Cache compression for efficient raster-order prediction. Extensive experiments on ImageNet verify that MergeVQ as an AR generative model achieves competitive performance in both visual representation learning and image generation tasks while maintaining favorable token efficiency and inference speed. The code and model will be available at https://apexgen-x.github.io/MergeVQ.
WideRange4D: Enabling High-Quality 4D Reconstruction with Wide-Range Movements and Scenes
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of 3D reconstruction technology, research in 4D reconstruction is also advancing, existing 4D reconstruction methods can generate high-quality 4D scenes. However, due to the challenges in acquiring multi-view video data, the current 4D reconstruction benchmarks mainly display actions performed in place, such as dancing, within limited scenarios. In practical scenarios, many scenes involve wide-range spatial movements, highlighting the limitations of existing 4D reconstruction datasets. Additionally, existing 4D reconstruction methods rely on deformation fields to estimate the dynamics of 3D objects, but deformation fields struggle with wide-range spatial movements, which limits the ability to achieve high-quality 4D scene reconstruction with wide-range spatial movements. In this paper, we focus on 4D scene reconstruction with significant object spatial movements and propose a novel 4D reconstruction benchmark, WideRange4D. This benchmark includes rich 4D scene data with large spatial variations, allowing for a more comprehensive evaluation of the generation capabilities of 4D generation methods. Furthermore, we introduce a new 4D reconstruction method, Progress4D, which generates stable and high-quality 4D results across various complex 4D scene reconstruction tasks. We conduct both quantitative and qualitative comparison experiments on WideRange4D, showing that our Progress4D outperforms existing state-of-the-art 4D reconstruction methods. Project: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/WideRange4D
Trans4D: Realistic Geometry-Aware Transition for Compositional Text-to-4D Synthesis
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in image and video generation, further improving the effectiveness of 4D synthesis. Existing 4D generation methods can generate high-quality 4D objects or scenes based on user-friendly conditions, benefiting the gaming and video industries. However, these methods struggle to synthesize significant object deformation of complex 4D transitions and interactions within scenes. To address this challenge, we propose Trans4D, a novel text-to-4D synthesis framework that enables realistic complex scene transitions. Specifically, we first use multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) to produce a physic-aware scene description for 4D scene initialization and effective transition timing planning. Then we propose a geometry-aware 4D transition network to realize a complex scene-level 4D transition based on the plan, which involves expressive geometrical object deformation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Trans4D consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in generating 4D scenes with accurate and high-quality transitions, validating its effectiveness. Code: https://github.com/YangLing0818/Trans4D
Unveiling the Backbone-Optimizer Coupling Bias in Visual Representation Learning
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper delves into the interplay between vision backbones and optimizers, unvealing an inter-dependent phenomenon termed \textit{\textbf{b}ackbone-\textbf{o}ptimizer \textbf{c}oupling \textbf{b}ias} (BOCB). We observe that canonical CNNs, such as VGG and ResNet, exhibit a marked co-dependency with SGD families, while recent architectures like ViTs and ConvNeXt share a tight coupling with the adaptive learning rate ones. We further show that BOCB can be introduced by both optimizers and certain backbone designs and may significantly impact the pre-training and downstream fine-tuning of vision models. Through in-depth empirical analysis, we summarize takeaways on recommended optimizers and insights into robust vision backbone architectures. We hope this work can inspire the community to question long-held assumptions on backbones and optimizers, stimulate further explorations, and thereby contribute to more robust vision systems. The source code and models are publicly available at https://bocb-ai.github.io/.
CARES: A Comprehensive Benchmark of Trustworthiness in Medical Vision Language Models
Jun 10, 2024
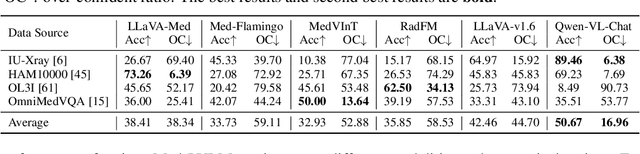
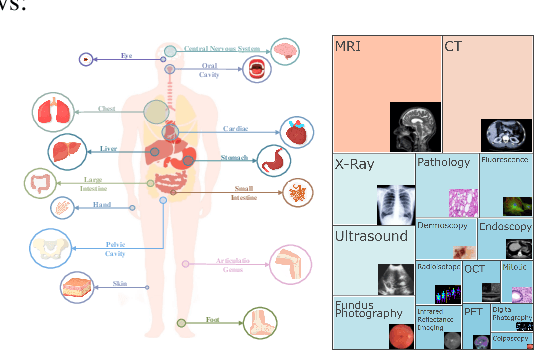
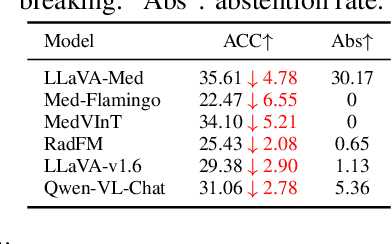
Abstract:Artificial intelligence has significantly impacted medical applications, particularly with the advent of Medical Large Vision Language Models (Med-LVLMs), sparking optimism for the future of automated and personalized healthcare. However, the trustworthiness of Med-LVLMs remains unverified, posing significant risks for future model deployment. In this paper, we introduce CARES and aim to comprehensively evaluate the Trustworthiness of Med-LVLMs across the medical domain. We assess the trustworthiness of Med-LVLMs across five dimensions, including trustfulness, fairness, safety, privacy, and robustness. CARES comprises about 41K question-answer pairs in both closed and open-ended formats, covering 16 medical image modalities and 27 anatomical regions. Our analysis reveals that the models consistently exhibit concerns regarding trustworthiness, often displaying factual inaccuracies and failing to maintain fairness across different demographic groups. Furthermore, they are vulnerable to attacks and demonstrate a lack of privacy awareness. We publicly release our benchmark and code in https://github.com/richard-peng-xia/CARES.
Switch EMA: A Free Lunch for Better Flatness and Sharpness
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a widely used weight averaging (WA) regularization to learn flat optima for better generalizations without extra cost in deep neural network (DNN) optimization. Despite achieving better flatness, existing WA methods might fall into worse final performances or require extra test-time computations. This work unveils the full potential of EMA with a single line of modification, i.e., switching the EMA parameters to the original model after each epoch, dubbed as Switch EMA (SEMA). From both theoretical and empirical aspects, we demonstrate that SEMA can help DNNs to reach generalization optima that better trade-off between flatness and sharpness. To verify the effectiveness of SEMA, we conduct comparison experiments with discriminative, generative, and regression tasks on vision and language datasets, including image classification, self-supervised learning, object detection and segmentation, image generation, video prediction, attribute regression, and language modeling. Comprehensive results with popular optimizers and networks show that SEMA is a free lunch for DNN training by improving performances and boosting convergence speeds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge