Jingjie Li
"Impressively Scary:" Exploring User Perceptions and Reactions to Unraveling Machine Learning Models in Social Media Applications
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Machine learning models deployed locally on social media applications are used for features, such as face filters which read faces in-real time, and they expose sensitive attributes to the apps. However, the deployment of machine learning models, e.g., when, where, and how they are used, in social media applications is opaque to users. We aim to address this inconsistency and investigate how social media user perceptions and behaviors change once exposed to these models. We conducted user studies (N=21) and found that participants were unaware to both what the models output and when the models were used in Instagram and TikTok, two major social media platforms. In response to being exposed to the models' functionality, we observed long term behavior changes in 8 participants. Our analysis uncovers the challenges and opportunities in providing transparency for machine learning models that interact with local user data.
Reliable Heading Tracking for Pedestrian Road Crossing Prediction Using Commodity Devices
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:Pedestrian heading tracking enables applications in pedestrian navigation, traffic safety, and accessibility. Previous works, using inertial sensor fusion or machine learning, are limited in that they assume the phone is fixed in specific orientations, hindering their generalizability. We propose a new heading tracking algorithm, the Orientation-Heading Alignment (OHA), which leverages a key insight: people tend to carry smartphones in certain ways due to habits, such as swinging them while walking. For each smartphone attitude during this motion, OHA maps the smartphone orientation to the pedestrian heading and learns such mappings efficiently from coarse headings and smartphone orientations. To anchor our algorithm in a practical scenario, we apply OHA to a challenging task: predicting when pedestrians are about to cross the road to improve road user safety. In particular, using 755 hours of walking data collected since 2020 from 60 individuals, we develop a lightweight model that operates in real-time on commodity devices to predict road crossings. Our evaluation shows that OHA achieves 3.4 times smaller heading errors across nine scenarios than existing methods. Furthermore, OHA enables the early and accurate detection of pedestrian crossing behavior, issuing crossing alerts 0.35 seconds, on average, before pedestrians enter the road range.
Unbiased Delayed Feedback Label Correction for Conversion Rate Prediction
Jul 24, 2023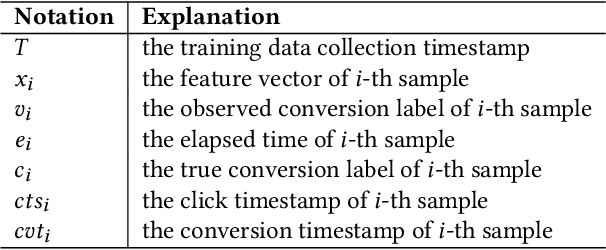
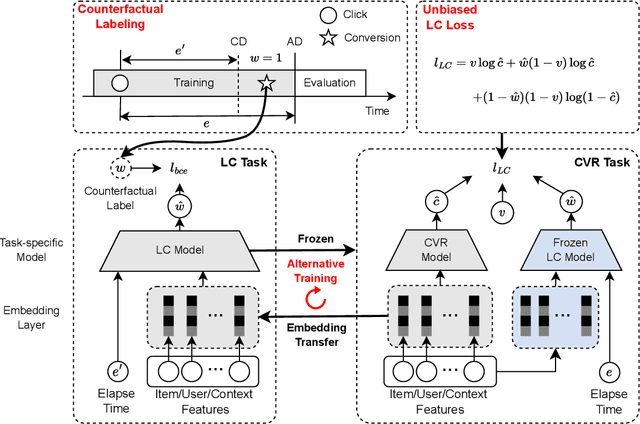

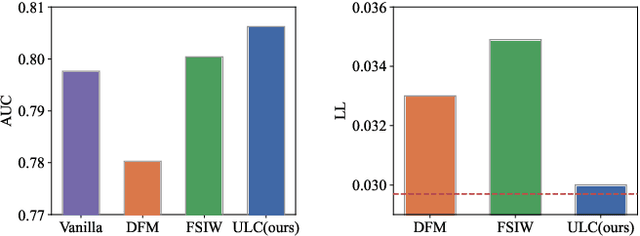
Abstract:Conversion rate prediction is critical to many online applications such as digital display advertising. To capture dynamic data distribution, industrial systems often require retraining models on recent data daily or weekly. However, the delay of conversion behavior usually leads to incorrect labeling, which is called delayed feedback problem. Existing work may fail to introduce the correct information about false negative samples due to data sparsity and dynamic data distribution. To directly introduce the correct feedback label information, we propose an Unbiased delayed feedback Label Correction framework (ULC), which uses an auxiliary model to correct labels for observed negative feedback samples. Firstly, we theoretically prove that the label-corrected loss is an unbiased estimate of the oracle loss using true labels. Then, as there are no ready training data for label correction, counterfactual labeling is used to construct artificial training data. Furthermore, since counterfactual labeling utilizes only partial training data, we design an embedding-based alternative training method to enhance performance. Comparative experiments on both public and private datasets and detailed analyses show that our proposed approach effectively alleviates the delayed feedback problem and consistently outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods.
Contrastive Multi-view Framework for Customer Lifetime Value Prediction
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Accurate customer lifetime value (LTV) prediction can help service providers optimize their marketing policies in customer-centric applications. However, the heavy sparsity of consumption events and the interference of data variance and noise obstruct LTV estimation. Many existing LTV prediction methods directly train a single-view LTV predictor on consumption samples, which may yield inaccurate and even biased knowledge extraction. In this paper, we propose a contrastive multi-view framework for LTV prediction, which is a plug-and-play solution compatible with various backbone models. It synthesizes multiple heterogeneous LTV regressors with complementary knowledge to improve model robustness and captures sample relatedness via contrastive learning to mitigate the dependency on data abundance. Concretely, we use a decomposed scheme that converts the LTV prediction problem into a combination of estimating consumption probability and payment amount. To alleviate the impact of noisy data on model learning, we propose a multi-view framework that jointly optimizes multiple types of regressors with diverse characteristics and advantages to encode and fuse comprehensive knowledge. To fully exploit the potential of limited training samples, we propose a hybrid contrastive learning method to help capture the relatedness between samples in both classification and regression tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on a real-world game LTV prediction dataset and the results validate the effectiveness of our method. We have deployed our solution online in Huawei's mobile game center and achieved 32.26% of total payment amount gains.
IntTower: the Next Generation of Two-Tower Model for Pre-Ranking System
Oct 18, 2022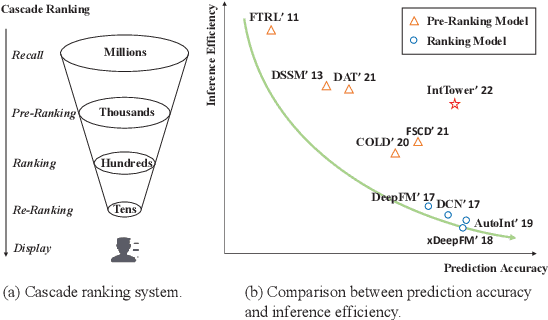
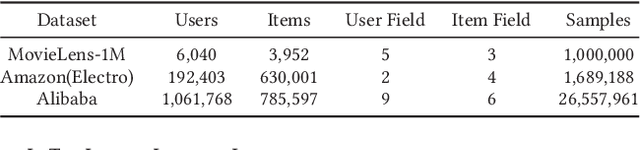
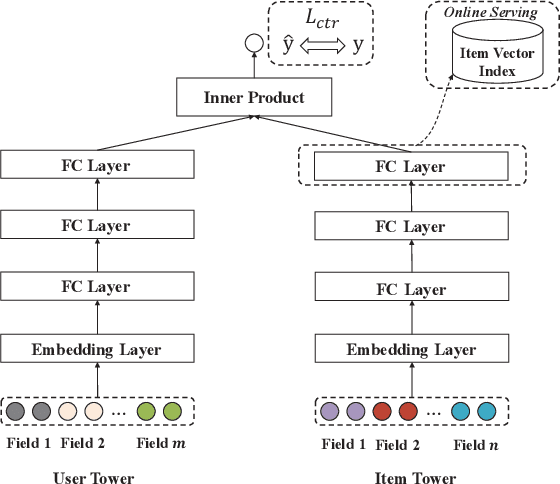
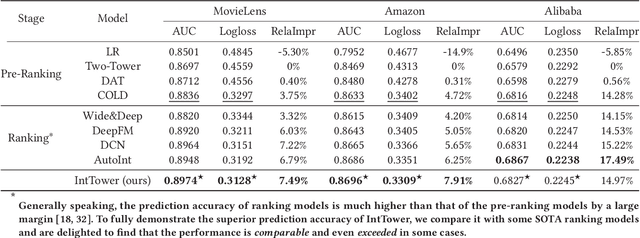
Abstract:Scoring a large number of candidates precisely in several milliseconds is vital for industrial pre-ranking systems. Existing pre-ranking systems primarily adopt the \textbf{two-tower} model since the ``user-item decoupling architecture'' paradigm is able to balance the \textit{efficiency} and \textit{effectiveness}. However, the cost of high efficiency is the neglect of the potential information interaction between user and item towers, hindering the prediction accuracy critically. In this paper, we show it is possible to design a two-tower model that emphasizes both information interactions and inference efficiency. The proposed model, IntTower (short for \textit{Interaction enhanced Two-Tower}), consists of Light-SE, FE-Block and CIR modules. Specifically, lightweight Light-SE module is used to identify the importance of different features and obtain refined feature representations in each tower. FE-Block module performs fine-grained and early feature interactions to capture the interactive signals between user and item towers explicitly and CIR module leverages a contrastive interaction regularization to further enhance the interactions implicitly. Experimental results on three public datasets show that IntTower outperforms the SOTA pre-ranking models significantly and even achieves comparable performance in comparison with the ranking models. Moreover, we further verify the effectiveness of IntTower on a large-scale advertisement pre-ranking system. The code of IntTower is publicly available\footnote{https://github.com/archersama/IntTower}
Learning Binarized Graph Representations with Multi-faceted Quantization Reinforcement for Top-K Recommendation
Jun 05, 2022



Abstract:Learning vectorized embeddings is at the core of various recommender systems for user-item matching. To perform efficient online inference, representation quantization, aiming to embed the latent features by a compact sequence of discrete numbers, recently shows the promising potentiality in optimizing both memory and computation overheads. However, existing work merely focuses on numerical quantization whilst ignoring the concomitant information loss issue, which, consequently, leads to conspicuous performance degradation. In this paper, we propose a novel quantization framework to learn Binarized Graph Representations for Top-K Recommendation (BiGeaR). BiGeaR introduces multi-faceted quantization reinforcement at the pre-, mid-, and post-stage of binarized representation learning, which substantially retains the representation informativeness against embedding binarization. In addition to saving the memory footprint, BiGeaR further develops solid online inference acceleration with bitwise operations, providing alternative flexibility for the realistic deployment. The empirical results over five large real-world benchmarks show that BiGeaR achieves about 22%~40% performance improvement over the state-of-the-art quantization-based recommender system, and recovers about 95%~102% of the performance capability of the best full-precision counterpart with over 8x time and space reduction.
Towards Low-loss 1-bit Quantization of User-item Representations for Top-K Recommendation
Dec 03, 2021



Abstract:Due to the promising advantages in space compression and inference acceleration, quantized representation learning for recommender systems has become an emerging research direction recently. As the target is to embed latent features in the discrete embedding space, developing quantization for user-item representations with a few low-precision integers confronts the challenge of high information loss, thus leading to unsatisfactory performance in Top-K recommendation. In this work, we study the problem of representation learning for recommendation with 1-bit quantization. We propose a model named Low-loss Quantized Graph Convolutional Network (L^2Q-GCN). Different from previous work that plugs quantization as the final encoder of user-item embeddings, L^2Q-GCN learns the quantized representations whilst capturing the structural information of user-item interaction graphs at different semantic levels. This achieves the substantial retention of intermediate interactive information, alleviating the feature smoothing issue for ranking caused by numerical quantization. To further improve the model performance, we also present an advanced solution named L^2Q-GCN-anl with quantization approximation and annealing training strategy. We conduct extensive experiments on four benchmarks over Top-K recommendation task. The experimental results show that, with nearly 9x representation storage compression, L^2Q-GCN-anl attains about 90~99% performance recovery compared to the state-of-the-art model.
Why Do We Click: Visual Impression-aware News Recommendation
Sep 26, 2021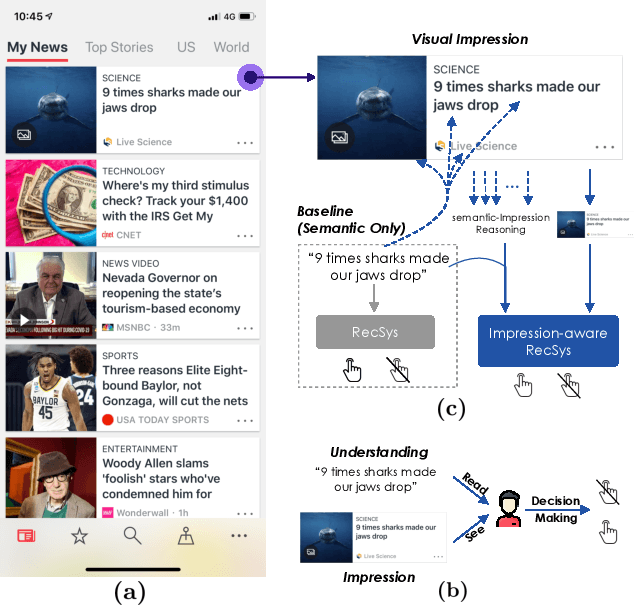


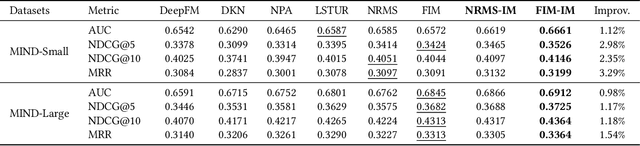
Abstract:There is a soaring interest in the news recommendation research scenario due to the information overload. To accurately capture users' interests, we propose to model multi-modal features, in addition to the news titles that are widely used in existing works, for news recommendation. Besides, existing research pays little attention to the click decision-making process in designing multi-modal modeling modules. In this work, inspired by the fact that users make their click decisions mostly based on the visual impression they perceive when browsing news, we propose to capture such visual impression information with visual-semantic modeling for news recommendation. Specifically, we devise the local impression modeling module to simultaneously attend to decomposed details in the impression when understanding the semantic meaning of news title, which could explicitly get close to the process of users reading news. In addition, we inspect the impression from a global view and take structural information, such as the arrangement of different fields and spatial position of different words on the impression, into the modeling of multiple modalities. To accommodate the research of visual impression-aware news recommendation, we extend the text-dominated news recommendation dataset MIND by adding snapshot impression images and will release it to nourish the research field. Extensive comparisons with the state-of-the-art news recommenders along with the in-depth analyses demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method and the promising capability of modeling visual impressions for the content-based recommenders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge