Qinglin Jia
No One Left Behind: How to Exploit the Incomplete and Skewed Multi-Label Data for Conversion Rate Prediction
Dec 15, 2025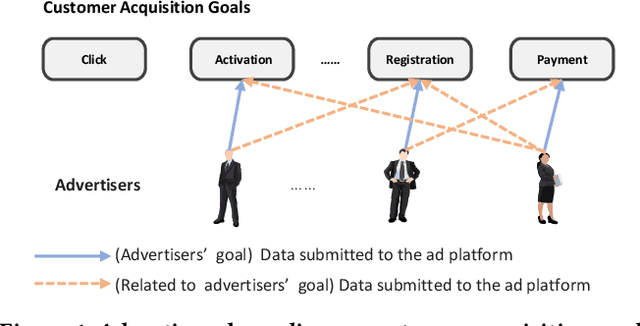
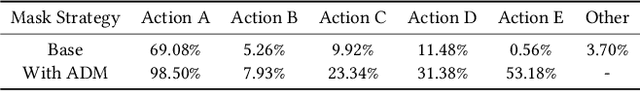
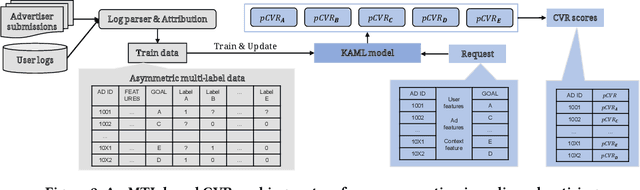
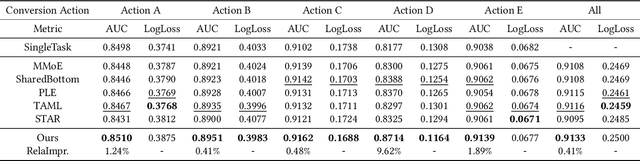
Abstract:In most real-world online advertising systems, advertisers typically have diverse customer acquisition goals. A common solution is to use multi-task learning (MTL) to train a unified model on post-click data to estimate the conversion rate (CVR) for these diverse targets. In practice, CVR prediction often encounters missing conversion data as many advertisers submit only a subset of user conversion actions due to privacy or other constraints, making the labels of multi-task data incomplete. If the model is trained on all available samples where advertisers submit user conversion actions, it may struggle when deployed to serve a subset of advertisers targeting specific conversion actions, as the training and deployment data distributions are mismatched. While considerable MTL efforts have been made, a long-standing challenge is how to effectively train a unified model with the incomplete and skewed multi-label data. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained Knowledge transfer framework for Asymmetric Multi-Label data (KAML). We introduce an attribution-driven masking strategy (ADM) to better utilize data with asymmetric multi-label data in training. However, the more relaxed masking in ADM is a double-edged sword: it provides additional training signals but also introduces noise due to skewed data. To address this, we propose a hierarchical knowledge extraction mechanism (HKE) to model the sample discrepancy within the target task tower. Finally, to maximize the utility of unlabeled samples, we incorporate ranking loss strategy to further enhance our model. The effectiveness of KAML has been demonstrated through comprehensive evaluations on offline industry datasets and online A/B tests, which show significant performance improvements over existing MTL baselines.
CHOP: Mobile Operating Assistant with Constrained High-frequency Optimized Subtask Planning
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:The advancement of visual language models (VLMs) has enhanced mobile device operations, allowing simulated human-like actions to address user requirements. Current VLM-based mobile operating assistants can be structured into three levels: task, subtask, and action. The subtask level, linking high-level goals with low-level executable actions, is crucial for task completion but faces two challenges: ineffective subtasks that lower-level agent cannot execute and inefficient subtasks that fail to contribute to the completion of the higher-level task. These challenges stem from VLM's lack of experience in decomposing subtasks within GUI scenarios in multi-agent architecture. To address these, we propose a new mobile assistant architecture with constrained high-frequency o}ptimized planning (CHOP). Our approach overcomes the VLM's deficiency in GUI scenarios planning by using human-planned subtasks as the basis vector. We evaluate our architecture in both English and Chinese contexts across 20 Apps, demonstrating significant improvements in both effectiveness and efficiency. Our dataset and code is available at https://github.com/Yuqi-Zhou/CHOP
Few-shot_LLM_Synthetic_Data_with_Distribution_Matching
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) advance, their ability to perform in-context learning and few-shot language generation has improved significantly. This has spurred using LLMs to produce high-quality synthetic data to enhance the performance of smaller models like online retrievers or weak LLMs. However, LLM-generated synthetic data often differs from the real data in key language attributes (e.g., styles, tones, content proportions, etc.). As a result, mixing these synthetic data directly with real data may distort the original data distribution, potentially hindering performance improvements. To solve this, we introduce SynAlign: a synthetic data generation and filtering framework based on key attribute distribution matching. Before generation, SynAlign employs an uncertainty tracker surrogated by the Gaussian Process model to iteratively select data clusters distinct from selected ones as demonstrations for new data synthesis, facilitating the efficient exploration diversity of the real data. Then, a latent attribute reasoning method is employed: the LLM summarizes linguistic attributes of demonstrations and then synthesizes new data based on them. This approach facilitates synthesizing diverse data with linguistic attributes that appear in real data.After generation, the Maximum Mean Discrepancy is used as the objective function to learn the sampling weight of each synthetic data, ensuring distribution matching with the real data. Our experiments on multiple text prediction tasks show significant performance improvements. We also conducted an online A/B test on an online retriever to demonstrate SynAlign's effectiveness.
RecSys Arena: Pair-wise Recommender System Evaluation with Large Language Models
Dec 15, 2024Abstract:Evaluating the quality of recommender systems is critical for algorithm design and optimization. Most evaluation methods are computed based on offline metrics for quick algorithm evolution, since online experiments are usually risky and time-consuming. However, offline evaluation usually cannot fully reflect users' preference for the outcome of different recommendation algorithms, and the results may not be consistent with online A/B test. Moreover, many offline metrics such as AUC do not offer sufficient information for comparing the subtle differences between two competitive recommender systems in different aspects, which may lead to substantial performance differences in long-term online serving. Fortunately, due to the strong commonsense knowledge and role-play capability of large language models (LLMs), it is possible to obtain simulated user feedback on offline recommendation results. Motivated by the idea of LLM Chatbot Arena, in this paper we present the idea of RecSys Arena, where the recommendation results given by two different recommender systems in each session are evaluated by an LLM judger to obtain fine-grained evaluation feedback. More specifically, for each sample we use LLM to generate a user profile description based on user behavior history or off-the-shelf profile features, which is used to guide LLM to play the role of this user and evaluate the relative preference for two recommendation results generated by different models. Through extensive experiments on two recommendation datasets in different scenarios, we demonstrate that many different LLMs not only provide general evaluation results that are highly consistent with canonical offline metrics, but also provide rich insight in many subjective aspects. Moreover, it can better distinguish different algorithms with comparable performance in terms of AUC and nDCG.
Retrievable Domain-Sensitive Feature Memory for Multi-Domain Recommendation
May 21, 2024



Abstract:With the increase in the business scale and number of domains in online advertising, multi-domain ad recommendation has become a mainstream solution in the industry. The core of multi-domain recommendation is effectively modeling the commonalities and distinctions among domains. Existing works are dedicated to designing model architectures for implicit multi-domain modeling while overlooking an in-depth investigation from a more fundamental perspective of feature distributions. This paper focuses on features with significant differences across various domains in both distributions and effects on model predictions. We refer to these features as domain-sensitive features, which serve as carriers of domain distinctions and are crucial for multi-domain modeling. Experiments demonstrate that existing multi-domain modeling methods may neglect domain-sensitive features, indicating insufficient learning of domain distinctions. To avoid this neglect, we propose a domain-sensitive feature attribution method to identify features that best reflect domain distinctions from the feature set. Further, we design a memory architecture that extracts domain-specific information from domain-sensitive features for the model to retrieve and integrate, thereby enhancing the awareness of domain distinctions. Extensive offline and online experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method in capturing domain distinctions and improving multi-domain recommendation performance.
Confidence-Aware Multi-Field Model Calibration
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Accurately predicting the probabilities of user feedback, such as clicks and conversions, is critical for ad ranking and bidding. However, there often exist unwanted mismatches between predicted probabilities and true likelihoods due to the shift of data distributions and intrinsic model biases. Calibration aims to address this issue by post-processing model predictions, and field-aware calibration can adjust model output on different feature field values to satisfy fine-grained advertising demands. Unfortunately, the observed samples corresponding to certain field values can be too limited to make confident calibrations, which may yield bias amplification and online disturbance. In this paper, we propose a confidence-aware multi-field calibration method, which adaptively adjusts the calibration intensity based on the confidence levels derived from sample statistics. It also utilizes multiple feature fields for joint model calibration with awareness of their importance to mitigate the data sparsity effect of a single field. Extensive offline and online experiments show the superiority of our method in boosting advertising performance and reducing prediction deviations.
Unbiased Delayed Feedback Label Correction for Conversion Rate Prediction
Jul 24, 2023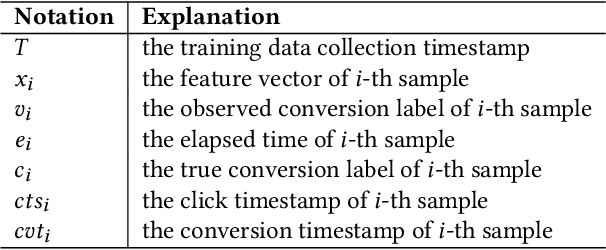
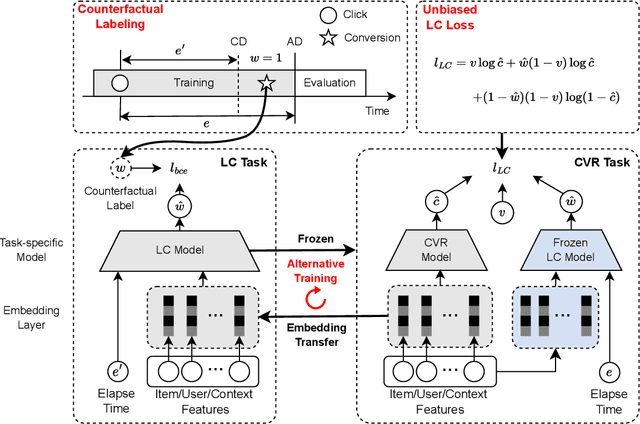

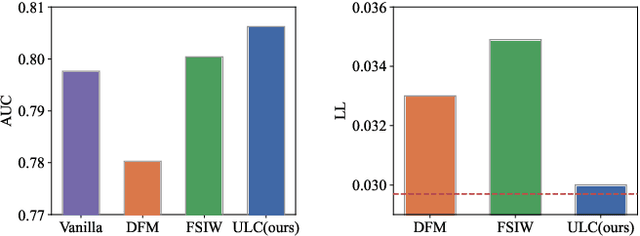
Abstract:Conversion rate prediction is critical to many online applications such as digital display advertising. To capture dynamic data distribution, industrial systems often require retraining models on recent data daily or weekly. However, the delay of conversion behavior usually leads to incorrect labeling, which is called delayed feedback problem. Existing work may fail to introduce the correct information about false negative samples due to data sparsity and dynamic data distribution. To directly introduce the correct feedback label information, we propose an Unbiased delayed feedback Label Correction framework (ULC), which uses an auxiliary model to correct labels for observed negative feedback samples. Firstly, we theoretically prove that the label-corrected loss is an unbiased estimate of the oracle loss using true labels. Then, as there are no ready training data for label correction, counterfactual labeling is used to construct artificial training data. Furthermore, since counterfactual labeling utilizes only partial training data, we design an embedding-based alternative training method to enhance performance. Comparative experiments on both public and private datasets and detailed analyses show that our proposed approach effectively alleviates the delayed feedback problem and consistently outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods.
Contrastive Multi-view Framework for Customer Lifetime Value Prediction
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Accurate customer lifetime value (LTV) prediction can help service providers optimize their marketing policies in customer-centric applications. However, the heavy sparsity of consumption events and the interference of data variance and noise obstruct LTV estimation. Many existing LTV prediction methods directly train a single-view LTV predictor on consumption samples, which may yield inaccurate and even biased knowledge extraction. In this paper, we propose a contrastive multi-view framework for LTV prediction, which is a plug-and-play solution compatible with various backbone models. It synthesizes multiple heterogeneous LTV regressors with complementary knowledge to improve model robustness and captures sample relatedness via contrastive learning to mitigate the dependency on data abundance. Concretely, we use a decomposed scheme that converts the LTV prediction problem into a combination of estimating consumption probability and payment amount. To alleviate the impact of noisy data on model learning, we propose a multi-view framework that jointly optimizes multiple types of regressors with diverse characteristics and advantages to encode and fuse comprehensive knowledge. To fully exploit the potential of limited training samples, we propose a hybrid contrastive learning method to help capture the relatedness between samples in both classification and regression tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on a real-world game LTV prediction dataset and the results validate the effectiveness of our method. We have deployed our solution online in Huawei's mobile game center and achieved 32.26% of total payment amount gains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge