Jiyuan Ren
AgentIF-OneDay: A Task-level Instruction-Following Benchmark for General AI Agents in Daily Scenarios
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The capacity of AI agents to effectively handle tasks of increasing duration and complexity continues to grow, demonstrating exceptional performance in coding, deep research, and complex problem-solving evaluations. However, in daily scenarios, the perception of these advanced AI capabilities among general users remains limited. We argue that current evaluations prioritize increasing task difficulty without sufficiently addressing the diversity of agentic tasks necessary to cover the daily work, life, and learning activities of a broad demographic. To address this, we propose AgentIF-OneDay, aimed at determining whether general users can utilize natural language instructions and AI agents to complete a diverse array of daily tasks. These tasks require not only solving problems through dialogue but also understanding various attachment types and delivering tangible file-based results. The benchmark is structured around three user-centric categories: Open Workflow Execution, which assesses adherence to explicit and complex workflows; Latent Instruction, which requires agents to infer implicit instructions from attachments; and Iterative Refinement, which involves modifying or expanding upon ongoing work. We employ instance-level rubrics and a refined evaluation pipeline that aligns LLM-based verification with human judgment, achieving an 80.1% agreement rate using Gemini-3-Pro. AgentIF-OneDay comprises 104 tasks covering 767 scoring points. We benchmarked four leading general AI agents and found that agent products built based on APIs and ChatGPT agents based on agent RL remain in the first tier simultaneously. Leading LLM APIs and open-source models have internalized agentic capabilities, enabling AI application teams to develop cutting-edge Agent products.
Few-shot_LLM_Synthetic_Data_with_Distribution_Matching
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) advance, their ability to perform in-context learning and few-shot language generation has improved significantly. This has spurred using LLMs to produce high-quality synthetic data to enhance the performance of smaller models like online retrievers or weak LLMs. However, LLM-generated synthetic data often differs from the real data in key language attributes (e.g., styles, tones, content proportions, etc.). As a result, mixing these synthetic data directly with real data may distort the original data distribution, potentially hindering performance improvements. To solve this, we introduce SynAlign: a synthetic data generation and filtering framework based on key attribute distribution matching. Before generation, SynAlign employs an uncertainty tracker surrogated by the Gaussian Process model to iteratively select data clusters distinct from selected ones as demonstrations for new data synthesis, facilitating the efficient exploration diversity of the real data. Then, a latent attribute reasoning method is employed: the LLM summarizes linguistic attributes of demonstrations and then synthesizes new data based on them. This approach facilitates synthesizing diverse data with linguistic attributes that appear in real data.After generation, the Maximum Mean Discrepancy is used as the objective function to learn the sampling weight of each synthetic data, ensuring distribution matching with the real data. Our experiments on multiple text prediction tasks show significant performance improvements. We also conducted an online A/B test on an online retriever to demonstrate SynAlign's effectiveness.
UniZero: Generalized and Efficient Planning with Scalable Latent World Models
Jun 15, 2024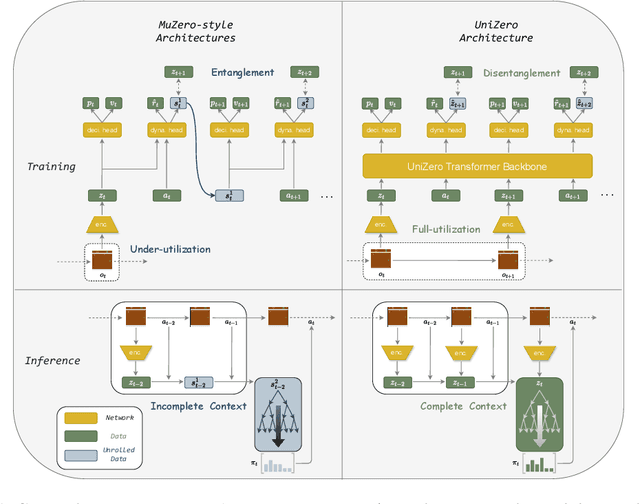
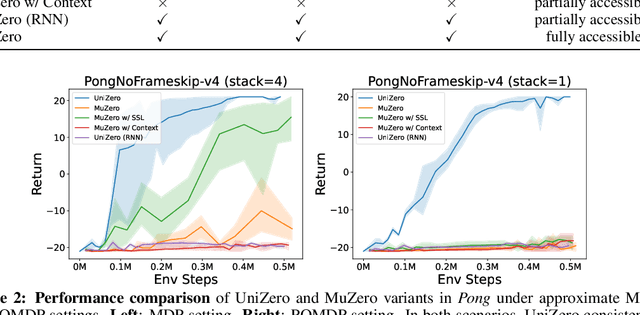
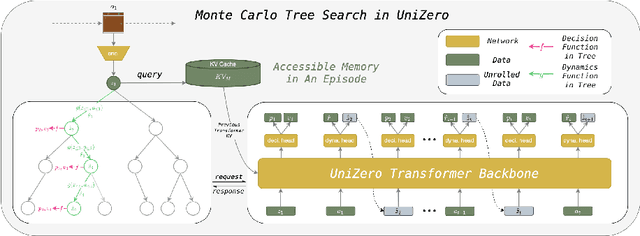
Abstract:Learning predictive world models is essential for enhancing the planning capabilities of reinforcement learning agents. Notably, the MuZero-style algorithms, based on the value equivalence principle and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), have achieved superhuman performance in various domains. However, in environments that require capturing long-term dependencies, MuZero's performance deteriorates rapidly. We identify that this is partially due to the \textit{entanglement} of latent representations with historical information, which results in incompatibility with the auxiliary self-supervised state regularization. To overcome this limitation, we present \textit{UniZero}, a novel approach that \textit{disentangles} latent states from implicit latent history using a transformer-based latent world model. By concurrently predicting latent dynamics and decision-oriented quantities conditioned on the learned latent history, UniZero enables joint optimization of the long-horizon world model and policy, facilitating broader and more efficient planning in latent space. We demonstrate that UniZero, even with single-frame inputs, matches or surpasses the performance of MuZero-style algorithms on the Atari 100k benchmark. Furthermore, it significantly outperforms prior baselines in benchmarks that require long-term memory. Lastly, we validate the effectiveness and scalability of our design choices through extensive ablation studies, visual analyses, and multi-task learning results. The code is available at \textcolor{magenta}{https://github.com/opendilab/LightZero}.
LightZero: A Unified Benchmark for Monte Carlo Tree Search in General Sequential Decision Scenarios
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:Building agents based on tree-search planning capabilities with learned models has achieved remarkable success in classic decision-making problems, such as Go and Atari. However, it has been deemed challenging or even infeasible to extend Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) based algorithms to diverse real-world applications, especially when these environments involve complex action spaces and significant simulation costs, or inherent stochasticity. In this work, we introduce LightZero, the first unified benchmark for deploying MCTS/MuZero in general sequential decision scenarios. Specificially, we summarize the most critical challenges in designing a general MCTS-style decision-making solver, then decompose the tightly-coupled algorithm and system design of tree-search RL methods into distinct sub-modules. By incorporating more appropriate exploration and optimization strategies, we can significantly enhance these sub-modules and construct powerful LightZero agents to tackle tasks across a wide range of domains, such as board games, Atari, MuJoCo, MiniGrid and GoBigger. Detailed benchmark results reveal the significant potential of such methods in building scalable and efficient decision intelligence. The code is available as part of OpenDILab at https://github.com/opendilab/LightZero.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge