Jianyu Zhang
Understanding Generalization from Embedding Dimension and Distributional Convergence
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Deep neural networks often generalize well despite heavy over-parameterization, challenging classical parameter-based analyses. We study generalization from a representation-centric perspective and analyze how the geometry of learned embeddings controls predictive performance for a fixed trained model. We show that population risk can be bounded by two factors: (i) the intrinsic dimension of the embedding distribution, which determines the convergence rate of empirical embedding distribution to the population distribution in Wasserstein distance, and (ii) the sensitivity of the downstream mapping from embeddings to predictions, characterized by Lipschitz constants. Together, these yield an embedding-dependent error bound that does not rely on parameter counts or hypothesis class complexity. At the final embedding layer, architectural sensitivity vanishes and the bound is dominated by embedding dimension, explaining its strong empirical correlation with generalization performance. Experiments across architectures and datasets validate the theory and demonstrate the utility of embedding-based diagnostics.
Local Intrinsic Dimension of Representations Predicts Alignment and Generalization in AI Models and Human Brain
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent work has found that neural networks with stronger generalization tend to exhibit higher representational alignment with one another across architectures and training paradigms. In this work, we show that models with stronger generalization also align more strongly with human neural activity. Moreover, generalization performance, model--model alignment, and model--brain alignment are all significantly correlated with each other. We further show that these relationships can be explained by a single geometric property of learned representations: the local intrinsic dimension of embeddings. Lower local dimension is consistently associated with stronger model--model alignment, stronger model--brain alignment, and better generalization, whereas global dimension measures fail to capture these effects. Finally, we find that increasing model capacity and training data scale systematically reduces local intrinsic dimension, providing a geometric account of the benefits of scaling. Together, our results identify local intrinsic dimension as a unifying descriptor of representational convergence in artificial and biological systems.
AgriGPT-Omni: A Unified Speech-Vision-Text Framework for Multilingual Agricultural Intelligence
Dec 11, 2025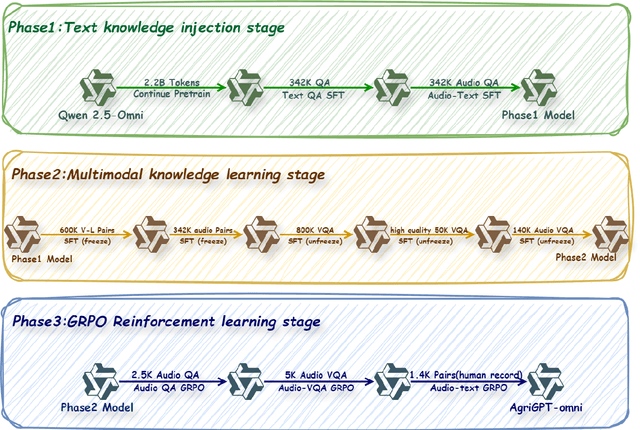
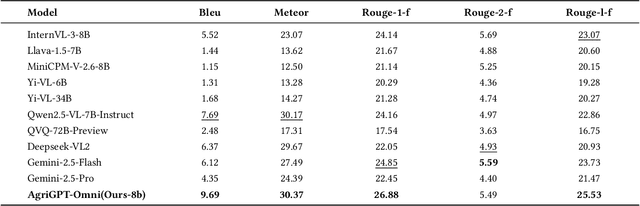
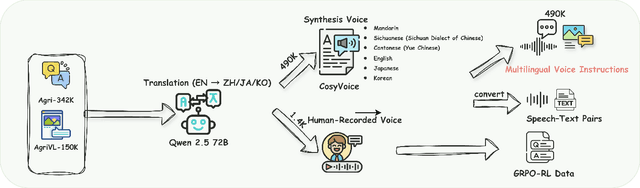
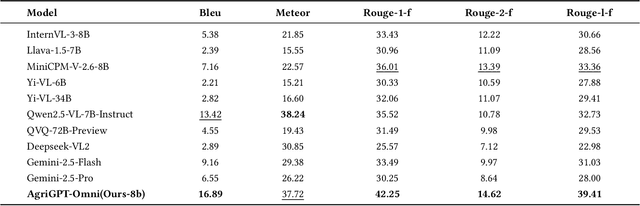
Abstract:Despite rapid advances in multimodal large language models, agricultural applications remain constrained by the lack of multilingual speech data, unified multimodal architectures, and comprehensive evaluation benchmarks. To address these challenges, we present AgriGPT-Omni, an agricultural omni-framework that integrates speech, vision, and text in a unified framework. First, we construct a scalable data synthesis and collection pipeline that converts agricultural texts and images into training data, resulting in the largest agricultural speech dataset to date, including 492K synthetic and 1.4K real speech samples across six languages. Second, based on this, we train the first agricultural omni-model via a three-stage paradigm: textual knowledge injection, progressive multimodal alignment, and GRPO-based reinforcement learning, enabling unified reasoning across languages and modalities. Third, we propose AgriBench-Omni-2K, the first tri-modal benchmark for agriculture, covering diverse speech-vision-text tasks and multilingual slices, with standardized protocols and reproducible tools. Experiments show that AgriGPT-Omni significantly outperforms general-purpose baselines on multilingual and multimodal reasoning as well as real-world speech understanding. All models, data, benchmarks, and code will be released to promote reproducible research, inclusive agricultural intelligence, and sustainable AI development for low-resource regions.
AgriGPT: a Large Language Model Ecosystem for Agriculture
Aug 12, 2025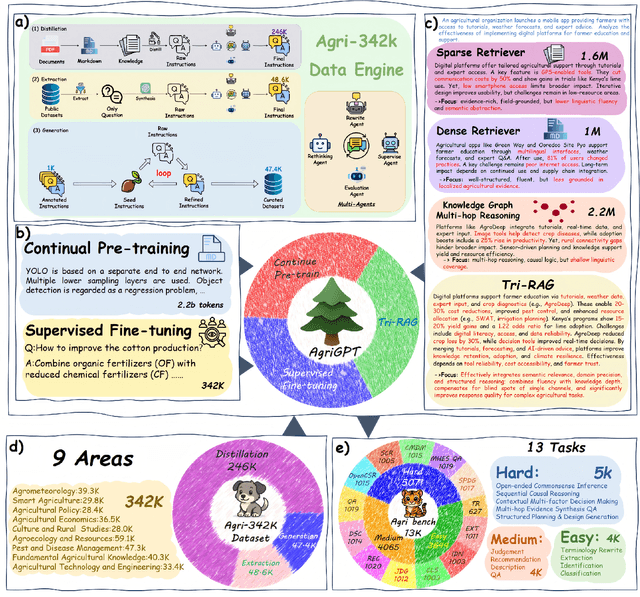
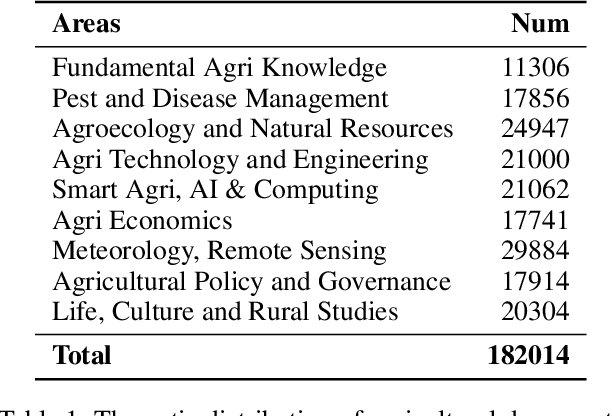
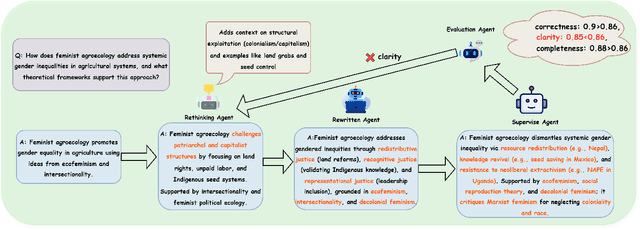
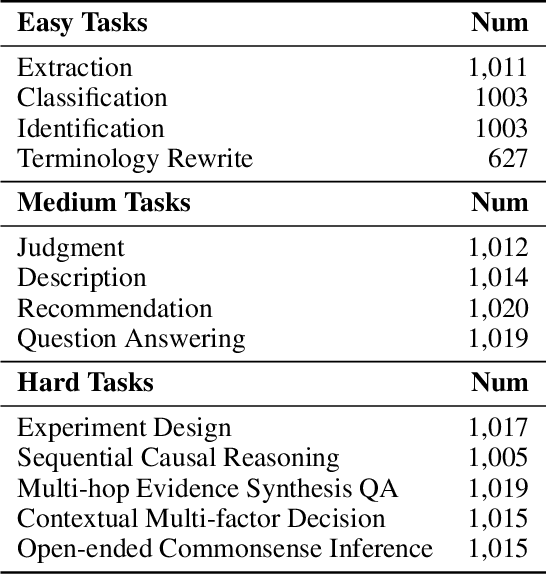
Abstract:Despite the rapid progress of Large Language Models (LLMs), their application in agriculture remains limited due to the lack of domain-specific models, curated datasets, and robust evaluation frameworks. To address these challenges, we propose AgriGPT, a domain-specialized LLM ecosystem for agricultural usage. At its core, we design a multi-agent scalable data engine that systematically compiles credible data sources into Agri-342K, a high-quality, standardized question-answer (QA) dataset. Trained on this dataset, AgriGPT supports a broad range of agricultural stakeholders, from practitioners to policy-makers. To enhance factual grounding, we employ Tri-RAG, a three-channel Retrieval-Augmented Generation framework combining dense retrieval, sparse retrieval, and multi-hop knowledge graph reasoning, thereby improving the LLM's reasoning reliability. For comprehensive evaluation, we introduce AgriBench-13K, a benchmark suite comprising 13 tasks with varying types and complexities. Experiments demonstrate that AgriGPT significantly outperforms general-purpose LLMs on both domain adaptation and reasoning. Beyond the model itself, AgriGPT represents a modular and extensible LLM ecosystem for agriculture, comprising structured data construction, retrieval-enhanced generation, and domain-specific evaluation. This work provides a generalizable framework for developing scientific and industry-specialized LLMs. All models, datasets, and code will be released to empower agricultural communities, especially in underserved regions, and to promote open, impactful research.
Scale-Invariance Drives Convergence in AI and Brain Representations
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Despite variations in architecture and pretraining strategies, recent studies indicate that large-scale AI models often converge toward similar internal representations that also align with neural activity. We propose that scale-invariance, a fundamental structural principle in natural systems, is a key driver of this convergence. In this work, we propose a multi-scale analytical framework to quantify two core aspects of scale-invariance in AI representations: dimensional stability and structural similarity across scales. We further investigate whether these properties can predict alignment performance with functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) responses in the visual cortex. Our analysis reveals that embeddings with more consistent dimension and higher structural similarity across scales align better with fMRI data. Furthermore, we find that the manifold structure of fMRI data is more concentrated, with most features dissipating at smaller scales. Embeddings with similar scale patterns align more closely with fMRI data. We also show that larger pretraining datasets and the inclusion of language modalities enhance the scale-invariance properties of embeddings, further improving neural alignment. Our findings indicate that scale-invariance is a fundamental structural principle that bridges artificial and biological representations, providing a new framework for evaluating the structural quality of human-like AI systems.
HybridProver: Augmenting Theorem Proving with LLM-Driven Proof Synthesis and Refinement
May 21, 2025Abstract:Formal methods is pivotal for verifying the reliability of critical systems through rigorous mathematical proofs. However, its adoption is hindered by labor-intensive manual proofs and the expertise required to use theorem provers. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) offer new opportunities for automated theorem proving. Two promising approaches are generating tactics step by step and generating a whole proof directly with an LLM. However, existing work makes no attempt to combine the two approaches. In this work, we introduce HybridProver, a dual-model proof synthesis framework that combines tactic-based generation and whole-proof synthesis to harness the benefits of both approaches. HybridProver generates whole proof candidates for evaluation directly, then extracts proof sketches from those candidates. It then uses a tactic-based generation model that integrates automated tools to complete the sketches via stepwise refinement. We implement HybridProver for the Isabelle theorem prover and fine-tune LLMs on our optimized Isabelle datasets. Evaluation on the miniF2F dataset illustrates HybridProver's effectiveness. We achieve a 59.4% success rate on miniF2F, where the previous SOTA is 56.1%. Our ablation studies show that this SOTA result is attributable to combining whole-proof and tactic-based generation. Additionally, we show how the dataset quality, training parameters, and sampling diversity affect the final result during automated theorem proving with LLMs. All of our code, datasets, and LLMs are open source.
Enhanced Semi-Supervised Stamping Process Monitoring with Physically-Informed Feature Extraction
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:In tackling frequent anomalies in stamping processes, this study introduces a novel semi-supervised in-process anomaly monitoring framework, utilizing accelerometer signals and physics information, to capture the process anomaly effectively. The proposed framework facilitates the construction of a monitoring model with imbalanced sample distribution, which enables in-process condition monitoring in real-time to prevent batch anomalies, which helps to reduce batch defects risk and enhance production yield. Firstly, to effectively capture key features from raw data containing redundant information, a hybrid feature extraction algorithm is proposed to utilize data-driven methods and physical mechanisms simultaneously. Secondly, to address the challenge brought by imbalanced sample distribution, a semi-supervised anomaly detection model is established, which merely employs normal samples to build a golden baseline model, and a novel deviation score is proposed to quantify the anomaly level of each online stamping stroke. The effectiveness of the proposed feature extraction method is validated with various classification algorithms. A real-world in-process dataset from stamping manufacturing workshop is employed to illustrate the superiority of proposed semi-supervised framework with enhance performance for process anomaly monitoring.
AI for the Open-World: the Learning Principles
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:During the past decades, numerous successes of AI has been made on "specific capabilities", named closed-world, such as artificial environments or specific real-world tasks. This well-defined narrow capability brings two nice benefits, a clear criterion of success and the opportunity to collect a lot of examples. The criteria not only reveal whether a machine has achieved a goal, but reveal how the machine falls short of the goal. As a result, human designers can fix the problems one after the other until the machine is deemed good enough for the task. Furthermore, the large set of collected examples reduces the difficulty of this problem-fixing process (by the central limit theorem). Do the success in closed-world translate into broad open-world, where a machine is required to perform any task that a human could possibly undertake with fewer examples and less priori knowledge from human designers? No. Because competence in a specific task provides little insight in handling other tasks, the valuable criteria for specific tasks become helpless when handling broader unseen tasks. Furthermore, due to the shortage of examples in unseen tasks, central limit theorem does not stand on our side. At the end, human designers lose the oscilloscope to "hack" an AI system for the open-world. Achieving AI for the open-world requires unique learning principles and innovated techniques, which are different from the ones in building AI for the closed-world. This thesis explores necessary learning principles required to construct AI for the open-world, including rich features (analogy a large tool box), disentangled representation (an organized tool box), and inference-time learning (a tool-savvy hand). Driven by the learning principles, this thesis further proposes techniques to use the learning principles, conducts enormous large-scale experiments to verify the learning principles.
Psychometric-Based Evaluation for Theorem Proving with Large Language Models
Feb 02, 2025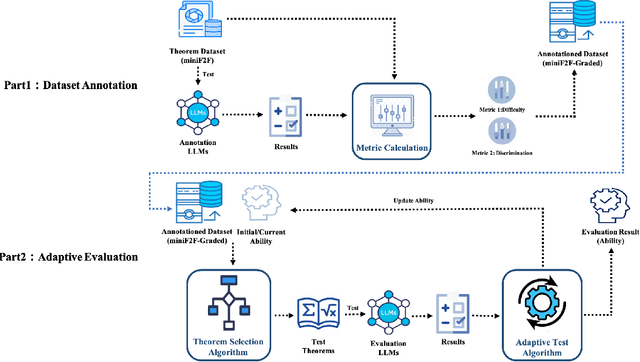

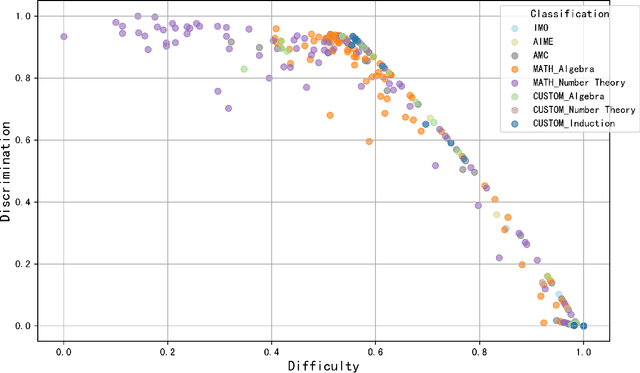

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) for formal theorem proving have become a prominent research focus. At present, the proving ability of these LLMs is mainly evaluated through proof pass rates on datasets such as miniF2F. However, this evaluation method overlooks the varying importance of theorems. As a result, it fails to highlight the real performance disparities between LLMs and leads to high evaluation costs. This study proposes a psychometric-based evaluation method for theorem proving with LLMs, comprising two main components: Dataset Annotation and Adaptive Evaluation. First, we propose a metric calculation method to annotate the dataset with difficulty and discrimination metrics. Specifically, we annotate each theorem in the miniF2F dataset and grade them into varying difficulty levels according to the performance of LLMs, resulting in an enhanced dataset: miniF2F-Graded. Experimental results show that the difficulty grading in miniF2F-Graded better reflects the theorem difficulty perceived by LLMs. Secondly, we design an adaptive evaluation method to dynamically select the most suitable theorems for testing based on the annotated metrics and the real-time performance of LLMs. We apply this method to evaluate 10 LLMs. The results show that our method finely highlights the performance disparities between LLMs. It also reduces evaluation costs by using only 23% of the theorems in the dataset.
Incorporating Feature Pyramid Tokenization and Open Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The visual understanding are often approached from 3 granular levels: image, patch and pixel. Visual Tokenization, trained by self-supervised reconstructive learning, compresses visual data by codebook in patch-level with marginal information loss, but the visual tokens does not have semantic meaning. Open Vocabulary semantic segmentation benefits from the evolving Vision-Language models (VLMs) with strong image zero-shot capability, but transferring image-level to pixel-level understanding remains an imminent challenge. In this paper, we treat segmentation as tokenizing pixels and study a united perceptual and semantic token compression for all granular understanding and consequently facilitate open vocabulary semantic segmentation. Referring to the cognitive process of pretrained VLM where the low-level features are progressively composed to high-level semantics, we propose Feature Pyramid Tokenization (PAT) to cluster and represent multi-resolution feature by learnable codebooks and then decode them by joint learning pixel reconstruction and semantic segmentation. We design loosely coupled pixel and semantic learning branches. The pixel branch simulates bottom-up composition and top-down visualization of codebook tokens, while the semantic branch collectively fuse hierarchical codebooks as auxiliary segmentation guidance. Our experiments show that PAT enhances the semantic intuition of VLM feature pyramid, improves performance over the baseline segmentation model and achieves competitive performance on open vocabulary semantic segmentation benchmark. Our model is parameter-efficient for VLM integration and flexible for the independent tokenization. We hope to give inspiration not only on improving segmentation but also on semantic visual token utilization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge