Jianxiong Xiao
DeepContext: Context-Encoding Neural Pathways for 3D Holistic Scene Understanding
Aug 16, 2017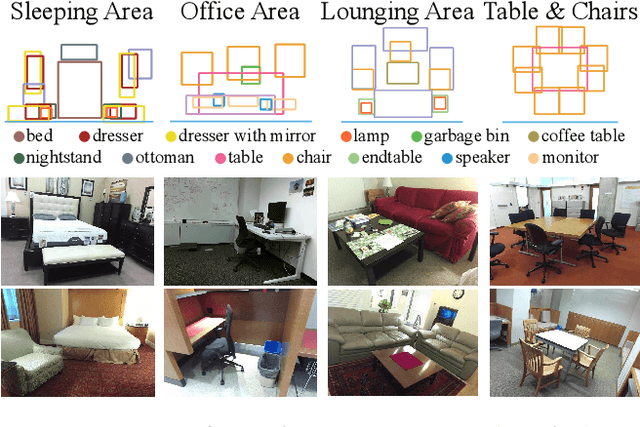
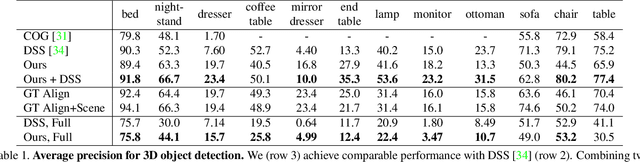

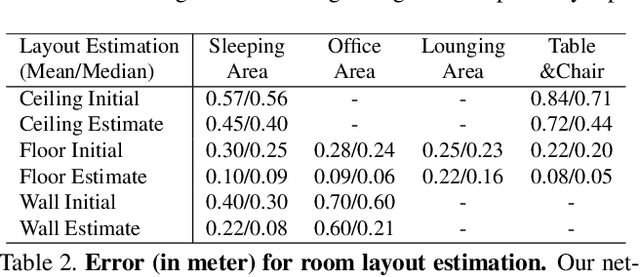
Abstract:While deep neural networks have led to human-level performance on computer vision tasks, they have yet to demonstrate similar gains for holistic scene understanding. In particular, 3D context has been shown to be an extremely important cue for scene understanding - yet very little research has been done on integrating context information with deep models. This paper presents an approach to embed 3D context into the topology of a neural network trained to perform holistic scene understanding. Given a depth image depicting a 3D scene, our network aligns the observed scene with a predefined 3D scene template, and then reasons about the existence and location of each object within the scene template. In doing so, our model recognizes multiple objects in a single forward pass of a 3D convolutional neural network, capturing both global scene and local object information simultaneously. To create training data for this 3D network, we generate partly hallucinated depth images which are rendered by replacing real objects with a repository of CAD models of the same object category. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm compared to the state-of-the-arts. Source code and data are available at http://deepcontext.cs.princeton.edu.
Multi-view Self-supervised Deep Learning for 6D Pose Estimation in the Amazon Picking Challenge
May 07, 2017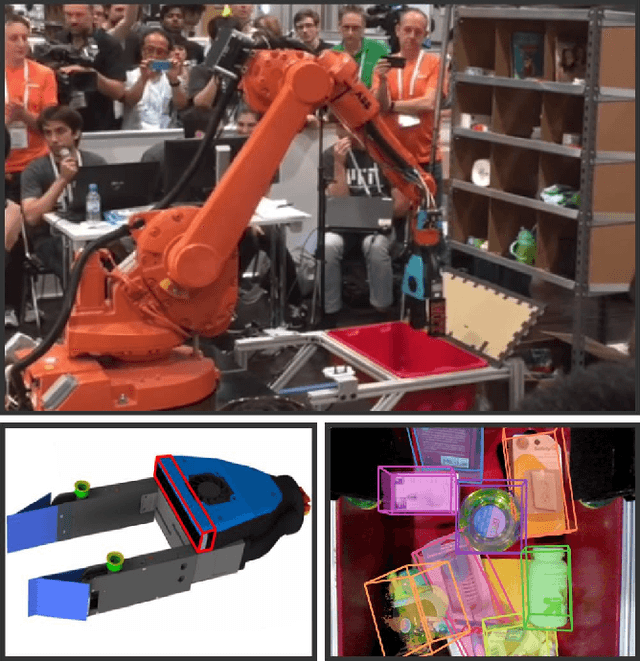
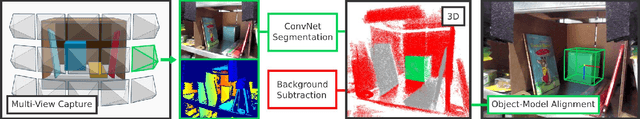
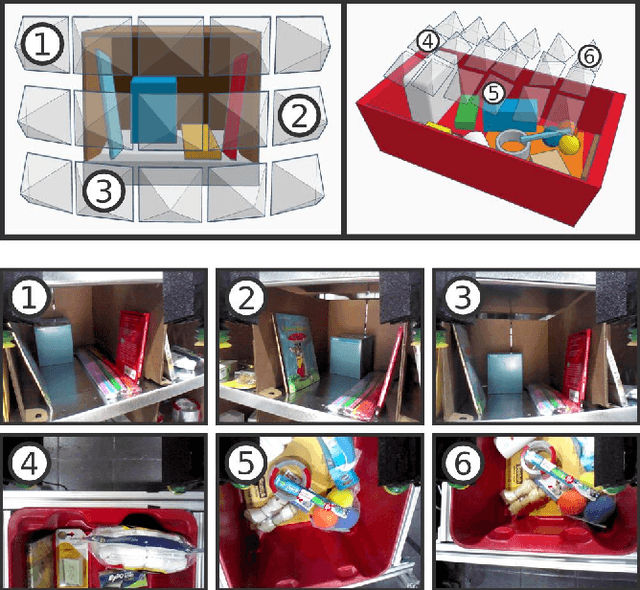
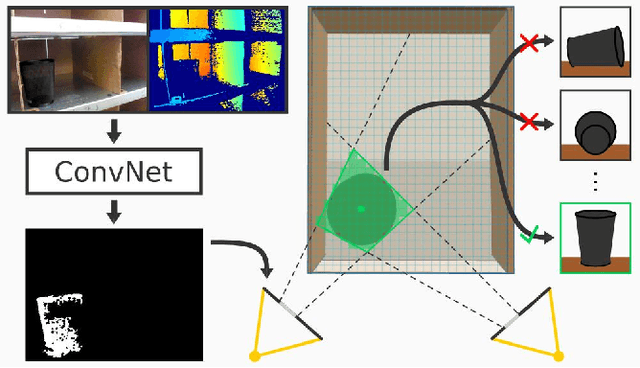
Abstract:Robot warehouse automation has attracted significant interest in recent years, perhaps most visibly in the Amazon Picking Challenge (APC). A fully autonomous warehouse pick-and-place system requires robust vision that reliably recognizes and locates objects amid cluttered environments, self-occlusions, sensor noise, and a large variety of objects. In this paper we present an approach that leverages multi-view RGB-D data and self-supervised, data-driven learning to overcome those difficulties. The approach was part of the MIT-Princeton Team system that took 3rd- and 4th- place in the stowing and picking tasks, respectively at APC 2016. In the proposed approach, we segment and label multiple views of a scene with a fully convolutional neural network, and then fit pre-scanned 3D object models to the resulting segmentation to get the 6D object pose. Training a deep neural network for segmentation typically requires a large amount of training data. We propose a self-supervised method to generate a large labeled dataset without tedious manual segmentation. We demonstrate that our system can reliably estimate the 6D pose of objects under a variety of scenarios. All code, data, and benchmarks are available at http://apc.cs.princeton.edu/
3DMatch: Learning Local Geometric Descriptors from RGB-D Reconstructions
Apr 09, 2017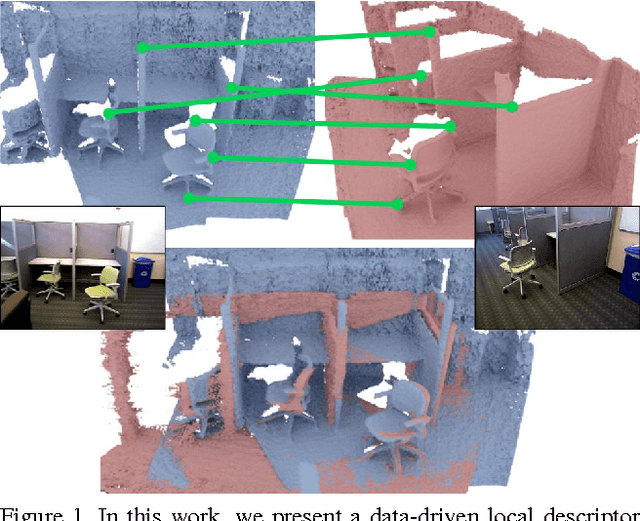

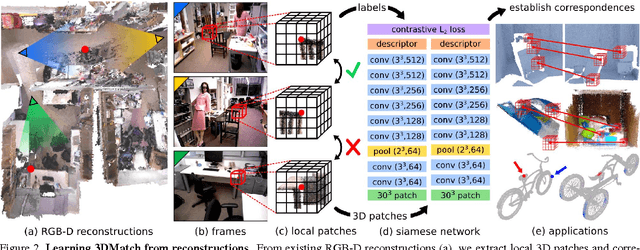
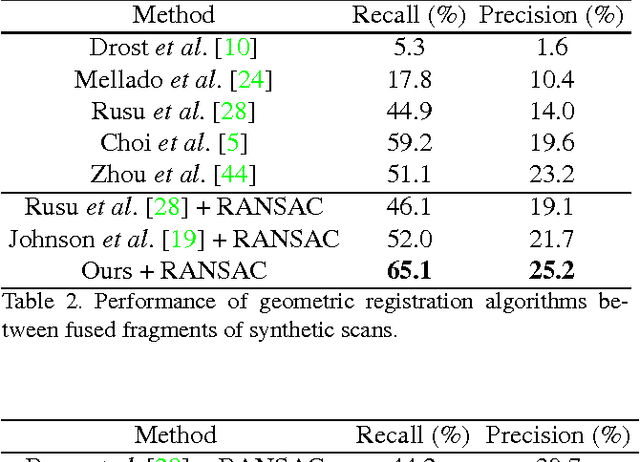
Abstract:Matching local geometric features on real-world depth images is a challenging task due to the noisy, low-resolution, and incomplete nature of 3D scan data. These difficulties limit the performance of current state-of-art methods, which are typically based on histograms over geometric properties. In this paper, we present 3DMatch, a data-driven model that learns a local volumetric patch descriptor for establishing correspondences between partial 3D data. To amass training data for our model, we propose a self-supervised feature learning method that leverages the millions of correspondence labels found in existing RGB-D reconstructions. Experiments show that our descriptor is not only able to match local geometry in new scenes for reconstruction, but also generalize to different tasks and spatial scales (e.g. instance-level object model alignment for the Amazon Picking Challenge, and mesh surface correspondence). Results show that 3DMatch consistently outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches by a significant margin. Code, data, benchmarks, and pre-trained models are available online at http://3dmatch.cs.princeton.edu
Learning from Maps: Visual Common Sense for Autonomous Driving
Dec 07, 2016



Abstract:Today's autonomous vehicles rely extensively on high-definition 3D maps to navigate the environment. While this approach works well when these maps are completely up-to-date, safe autonomous vehicles must be able to corroborate the map's information via a real time sensor-based system. Our goal in this work is to develop a model for road layout inference given imagery from on-board cameras, without any reliance on high-definition maps. However, no sufficient dataset for training such a model exists. Here, we leverage the availability of standard navigation maps and corresponding street view images to construct an automatically labeled, large-scale dataset for this complex scene understanding problem. By matching road vectors and metadata from navigation maps with Google Street View images, we can assign ground truth road layout attributes (e.g., distance to an intersection, one-way vs. two-way street) to the images. We then train deep convolutional networks to predict these road layout attributes given a single monocular RGB image. Experimental evaluation demonstrates that our model learns to correctly infer the road attributes using only panoramas captured by car-mounted cameras as input. Additionally, our results indicate that this method may be suitable to the novel application of recommending safety improvements to infrastructure (e.g., suggesting an alternative speed limit for a street).
LSUN: Construction of a Large-scale Image Dataset using Deep Learning with Humans in the Loop
Jun 04, 2016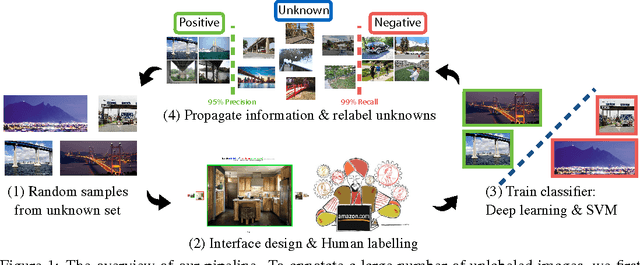
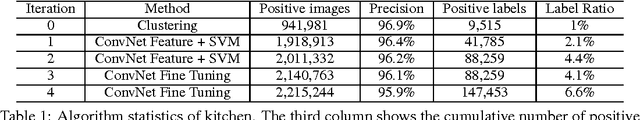
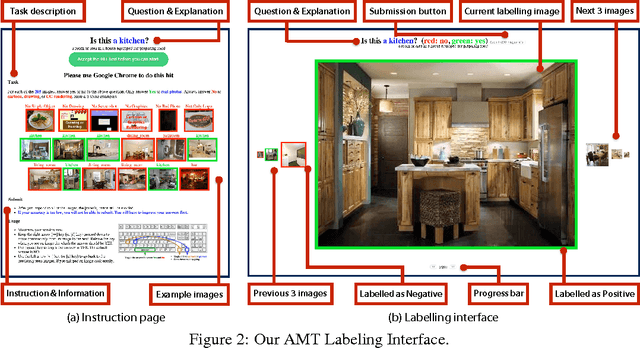
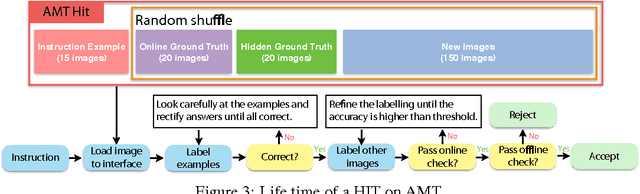
Abstract:While there has been remarkable progress in the performance of visual recognition algorithms, the state-of-the-art models tend to be exceptionally data-hungry. Large labeled training datasets, expensive and tedious to produce, are required to optimize millions of parameters in deep network models. Lagging behind the growth in model capacity, the available datasets are quickly becoming outdated in terms of size and density. To circumvent this bottleneck, we propose to amplify human effort through a partially automated labeling scheme, leveraging deep learning with humans in the loop. Starting from a large set of candidate images for each category, we iteratively sample a subset, ask people to label them, classify the others with a trained model, split the set into positives, negatives, and unlabeled based on the classification confidence, and then iterate with the unlabeled set. To assess the effectiveness of this cascading procedure and enable further progress in visual recognition research, we construct a new image dataset, LSUN. It contains around one million labeled images for each of 10 scene categories and 20 object categories. We experiment with training popular convolutional networks and find that they achieve substantial performance gains when trained on this dataset.
Deep Sliding Shapes for Amodal 3D Object Detection in RGB-D Images
Mar 09, 2016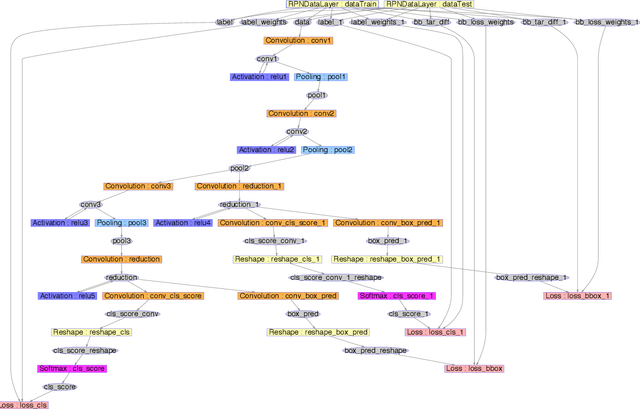
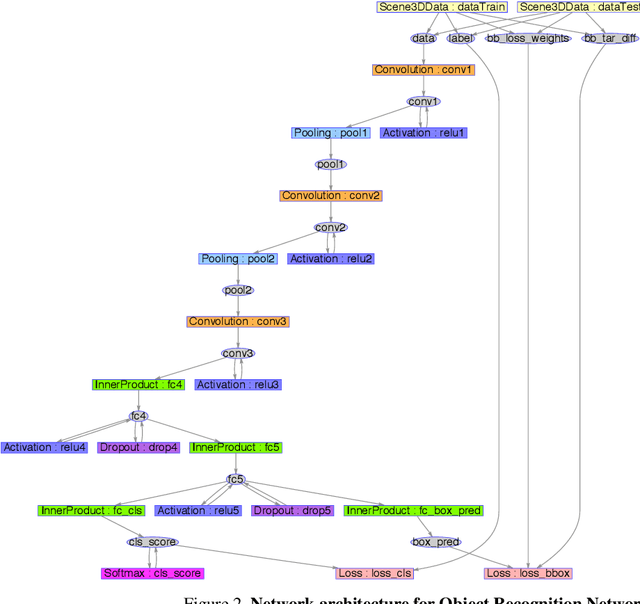
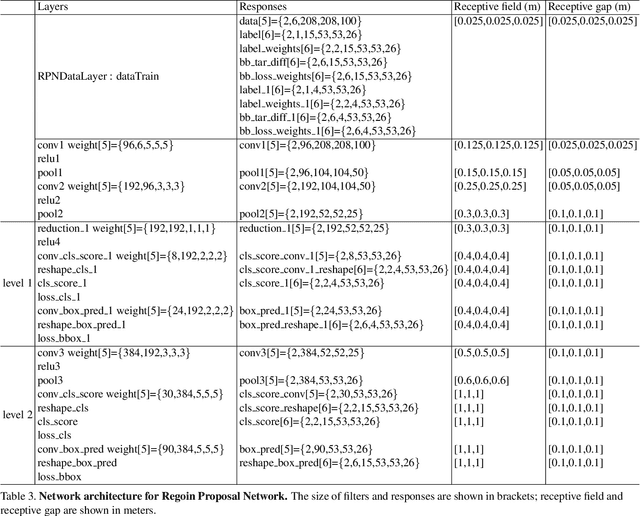
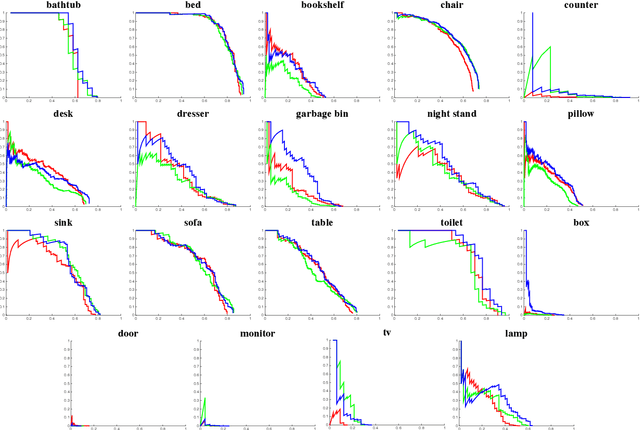
Abstract:We focus on the task of amodal 3D object detection in RGB-D images, which aims to produce a 3D bounding box of an object in metric form at its full extent. We introduce Deep Sliding Shapes, a 3D ConvNet formulation that takes a 3D volumetric scene from a RGB-D image as input and outputs 3D object bounding boxes. In our approach, we propose the first 3D Region Proposal Network (RPN) to learn objectness from geometric shapes and the first joint Object Recognition Network (ORN) to extract geometric features in 3D and color features in 2D. In particular, we handle objects of various sizes by training an amodal RPN at two different scales and an ORN to regress 3D bounding boxes. Experiments show that our algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art by 13.8 in mAP and is 200x faster than the original Sliding Shapes. All source code and pre-trained models will be available at GitHub.
ShapeNet: An Information-Rich 3D Model Repository
Dec 09, 2015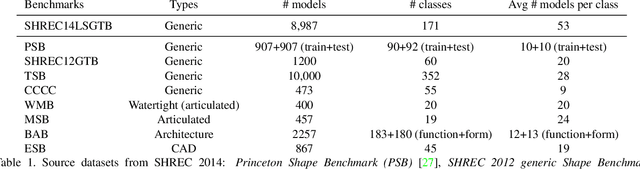
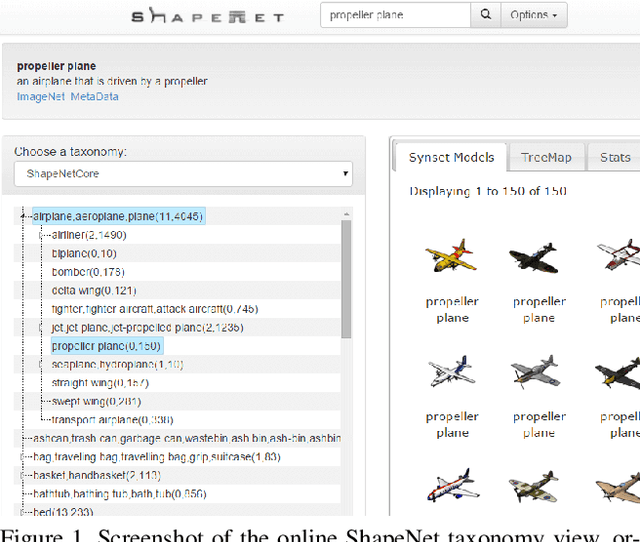
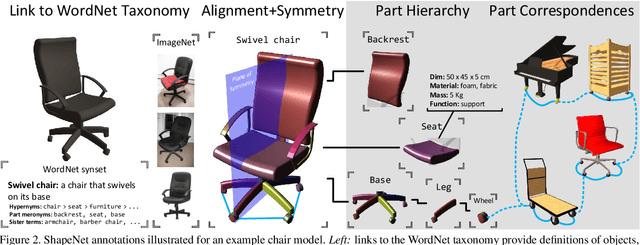
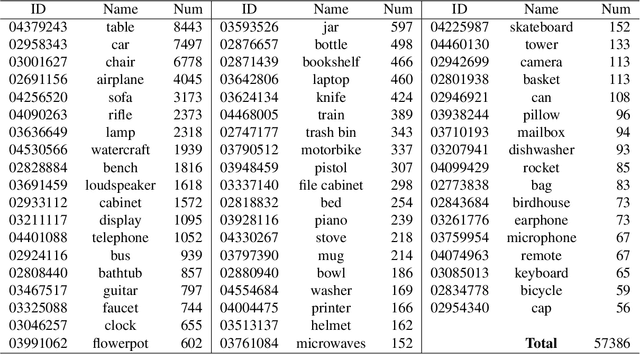
Abstract:We present ShapeNet: a richly-annotated, large-scale repository of shapes represented by 3D CAD models of objects. ShapeNet contains 3D models from a multitude of semantic categories and organizes them under the WordNet taxonomy. It is a collection of datasets providing many semantic annotations for each 3D model such as consistent rigid alignments, parts and bilateral symmetry planes, physical sizes, keywords, as well as other planned annotations. Annotations are made available through a public web-based interface to enable data visualization of object attributes, promote data-driven geometric analysis, and provide a large-scale quantitative benchmark for research in computer graphics and vision. At the time of this technical report, ShapeNet has indexed more than 3,000,000 models, 220,000 models out of which are classified into 3,135 categories (WordNet synsets). In this report we describe the ShapeNet effort as a whole, provide details for all currently available datasets, and summarize future plans.
Large Scale Artificial Neural Network Training Using Multi-GPUs
Nov 13, 2015Abstract:This paper describes a method for accelerating large scale Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) training using multi-GPUs by reducing the forward and backward passes to matrix multiplication. We propose an out-of-core multi-GPU matrix multiplication and integrate the algorithm with the ANN training. The experiments demonstrate that our matrix multiplication algorithm achieves linear speedup on multiple inhomogeneous GPUs. The full paper of this project can be found at [1].
DeepDriving: Learning Affordance for Direct Perception in Autonomous Driving
Sep 26, 2015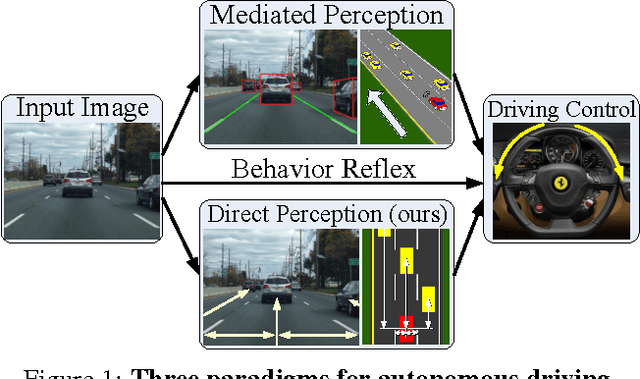
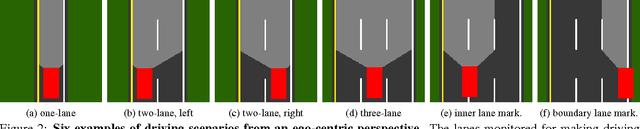
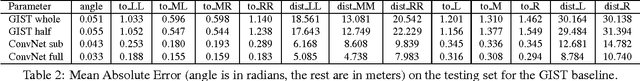
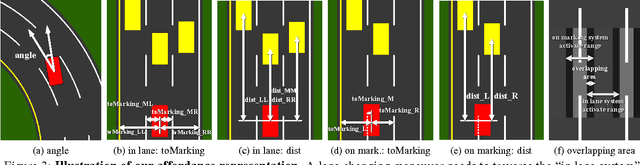
Abstract:Today, there are two major paradigms for vision-based autonomous driving systems: mediated perception approaches that parse an entire scene to make a driving decision, and behavior reflex approaches that directly map an input image to a driving action by a regressor. In this paper, we propose a third paradigm: a direct perception approach to estimate the affordance for driving. We propose to map an input image to a small number of key perception indicators that directly relate to the affordance of a road/traffic state for driving. Our representation provides a set of compact yet complete descriptions of the scene to enable a simple controller to drive autonomously. Falling in between the two extremes of mediated perception and behavior reflex, we argue that our direct perception representation provides the right level of abstraction. To demonstrate this, we train a deep Convolutional Neural Network using recording from 12 hours of human driving in a video game and show that our model can work well to drive a car in a very diverse set of virtual environments. We also train a model for car distance estimation on the KITTI dataset. Results show that our direct perception approach can generalize well to real driving images. Source code and data are available on our project website.
Robot In a Room: Toward Perfect Object Recognition in Closed Environments
Jul 09, 2015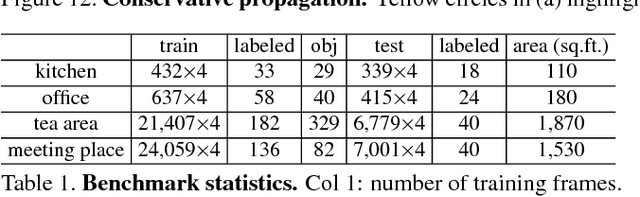
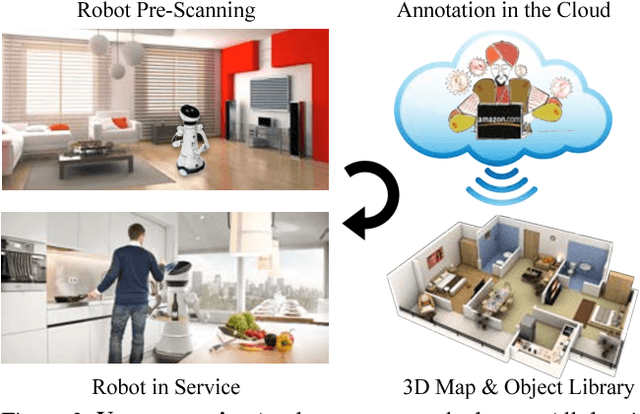
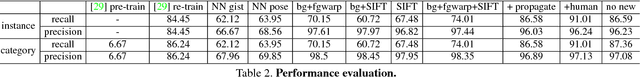

Abstract:While general object recognition is still far from being solved, this paper proposes a way for a robot to recognize every object at an almost human-level accuracy. Our key observation is that many robots will stay in a relatively closed environment (e.g. a house or an office). By constraining a robot to stay in a limited territory, we can ensure that the robot has seen most objects before and the speed of introducing a new object is slow. Furthermore, we can build a 3D map of the environment to reliably subtract the background to make recognition easier. We propose extremely robust algorithms to obtain a 3D map and enable humans to collectively annotate objects. During testing time, our algorithm can recognize all objects very reliably, and query humans from crowd sourcing platform if confidence is low or new objects are identified. This paper explains design decisions in building such a system, and constructs a benchmark for extensive evaluation. Experiments suggest that making robot vision appear to be working from an end user's perspective is a reachable goal today, as long as the robot stays in a closed environment. By formulating this task, we hope to lay the foundation of a new direction in vision for robotics. Code and data will be available upon acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge