James J. DiCarlo
Noninvasive precision modulation of high-level neural population activity via natural vision perturbations
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Precise control of neural activity -- modulating target neurons deep in the brain while leaving nearby neurons unaffected -- is an outstanding challenge in neuroscience, generally achieved through invasive techniques. This study investigates the possibility of precisely and noninvasively modulating neural activity in the high-level primate ventral visual stream via perturbations on one's natural visual feed. When tested on macaque inferior temporal (IT) neural populations, we found quantitative agreement between the model-predicted and biologically realized effect: strong modulation concentrated on targeted neural sites. We extended this to demonstrate accurate injection of experimenter-chosen neural population patterns via subtle perturbations applied on the background of typical natural visual feeds. These results highlight that current machine-executable models of the ventral stream can now design noninvasive, visually-delivered, possibly imperceptible neural interventions at the resolution of individual neurons.
Vision CNNs trained to estimate spatial latents learned similar ventral-stream-aligned representations
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Studies of the functional role of the primate ventral visual stream have traditionally focused on object categorization, often ignoring -- despite much prior evidence -- its role in estimating "spatial" latents such as object position and pose. Most leading ventral stream models are derived by optimizing networks for object categorization, which seems to imply that the ventral stream is also derived under such an objective. Here, we explore an alternative hypothesis: Might the ventral stream be optimized for estimating spatial latents? And a closely related question: How different -- if at all -- are representations learned from spatial latent estimation compared to categorization? To ask these questions, we leveraged synthetic image datasets generated by a 3D graphic engine and trained convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to estimate different combinations of spatial and category latents. We found that models trained to estimate just a few spatial latents achieve neural alignment scores comparable to those trained on hundreds of categories, and the spatial latent performance of models strongly correlates with their neural alignment. Spatial latent and category-trained models have very similar -- but not identical -- internal representations, especially in their early and middle layers. We provide evidence that this convergence is partly driven by non-target latent variability in the training data, which facilitates the implicit learning of representations of those non-target latents. Taken together, these results suggest that many training objectives, such as spatial latents, can lead to similar models aligned neurally with the ventral stream. Thus, one should not assume that the ventral stream is optimized for object categorization only. As a field, we need to continue to sharpen our measures of comparing models to brains to better understand the functional roles of the ventral stream.
L-WISE: Boosting Human Image Category Learning Through Model-Based Image Selection And Enhancement
Dec 12, 2024


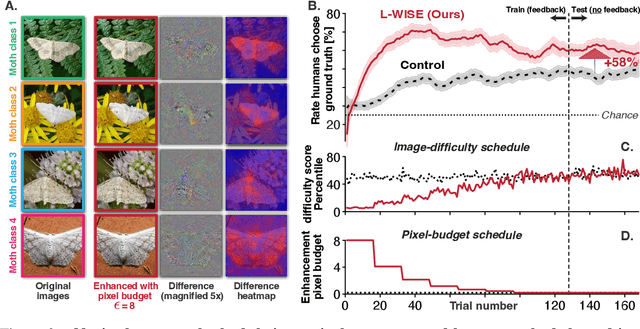
Abstract:The currently leading artificial neural network (ANN) models of the visual ventral stream -- which are derived from a combination of performance optimization and robustification methods -- have demonstrated a remarkable degree of behavioral alignment with humans on visual categorization tasks. Extending upon previous work, we show that not only can these models guide image perturbations that change the induced human category percepts, but they also can enhance human ability to accurately report the original ground truth. Furthermore, we find that the same models can also be used out-of-the-box to predict the proportion of correct human responses to individual images, providing a simple, human-aligned estimator of the relative difficulty of each image. Motivated by these observations, we propose to augment visual learning in humans in a way that improves human categorization accuracy at test time. Our learning augmentation approach consists of (i) selecting images based on their model-estimated recognition difficulty, and (ii) using image perturbations that aid recognition for novice learners. We find that combining these model-based strategies gives rise to test-time categorization accuracy gains of 33-72% relative to control subjects without these interventions, despite using the same number of training feedback trials. Surprisingly, beyond the accuracy gain, the training time for the augmented learning group was also shorter by 20-23%. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in a fine-grained categorization task with natural images, as well as tasks in two clinically relevant image domains -- histology and dermoscopy -- where visual learning is notoriously challenging. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first application of ANNs to increase visual learning performance in humans by enhancing category-specific features.
How does the primate brain combine generative and discriminative computations in vision?
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:Vision is widely understood as an inference problem. However, two contrasting conceptions of the inference process have each been influential in research on biological vision as well as the engineering of machine vision. The first emphasizes bottom-up signal flow, describing vision as a largely feedforward, discriminative inference process that filters and transforms the visual information to remove irrelevant variation and represent behaviorally relevant information in a format suitable for downstream functions of cognition and behavioral control. In this conception, vision is driven by the sensory data, and perception is direct because the processing proceeds from the data to the latent variables of interest. The notion of "inference" in this conception is that of the engineering literature on neural networks, where feedforward convolutional neural networks processing images are said to perform inference. The alternative conception is that of vision as an inference process in Helmholtz's sense, where the sensory evidence is evaluated in the context of a generative model of the causal processes giving rise to it. In this conception, vision inverts a generative model through an interrogation of the evidence in a process often thought to involve top-down predictions of sensory data to evaluate the likelihood of alternative hypotheses. The authors include scientists rooted in roughly equal numbers in each of the conceptions and motivated to overcome what might be a false dichotomy between them and engage the other perspective in the realm of theory and experiment. The primate brain employs an unknown algorithm that may combine the advantages of both conceptions. We explain and clarify the terminology, review the key empirical evidence, and propose an empirical research program that transcends the dichotomy and sets the stage for revealing the mysterious hybrid algorithm of primate vision.
Probing Biological and Artificial Neural Networks with Task-dependent Neural Manifolds
Dec 21, 2023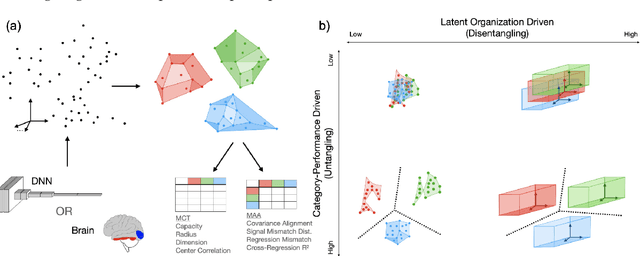
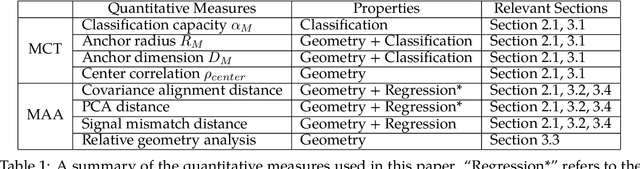
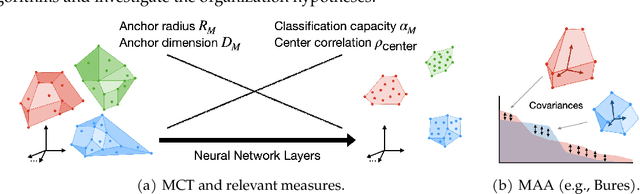
Abstract:Recently, growth in our understanding of the computations performed in both biological and artificial neural networks has largely been driven by either low-level mechanistic studies or global normative approaches. However, concrete methodologies for bridging the gap between these levels of abstraction remain elusive. In this work, we investigate the internal mechanisms of neural networks through the lens of neural population geometry, aiming to provide understanding at an intermediate level of abstraction, as a way to bridge that gap. Utilizing manifold capacity theory (MCT) from statistical physics and manifold alignment analysis (MAA) from high-dimensional statistics, we probe the underlying organization of task-dependent manifolds in deep neural networks and macaque neural recordings. Specifically, we quantitatively characterize how different learning objectives lead to differences in the organizational strategies of these models and demonstrate how these geometric analyses are connected to the decodability of task-relevant information. These analyses present a strong direction for bridging mechanistic and normative theories in neural networks through neural population geometry, potentially opening up many future research avenues in both machine learning and neuroscience.
Robustified ANNs Reveal Wormholes Between Human Category Percepts
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:The visual object category reports of artificial neural networks (ANNs) are notoriously sensitive to tiny, adversarial image perturbations. Because human category reports (aka human percepts) are thought to be insensitive to those same small-norm perturbations -- and locally stable in general -- this argues that ANNs are incomplete scientific models of human visual perception. Consistent with this, we show that when small-norm image perturbations are generated by standard ANN models, human object category percepts are indeed highly stable. However, in this very same "human-presumed-stable" regime, we find that robustified ANNs reliably discover low-norm image perturbations that strongly disrupt human percepts. These previously undetectable human perceptual disruptions are massive in amplitude, approaching the same level of sensitivity seen in robustified ANNs. Further, we show that robustified ANNs support precise perceptual state interventions: they guide the construction of low-norm image perturbations that strongly alter human category percepts toward specific prescribed percepts. These observations suggest that for arbitrary starting points in image space, there exists a set of nearby "wormholes", each leading the subject from their current category perceptual state into a semantically very different state. Moreover, contemporary ANN models of biological visual processing are now accurate enough to consistently guide us to those portals.
Adversarially trained neural representations may already be as robust as corresponding biological neural representations
Jun 19, 2022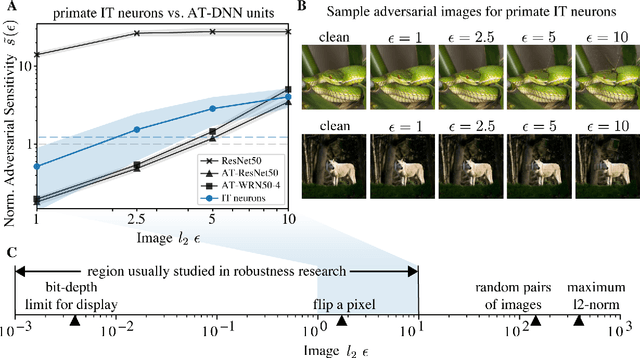
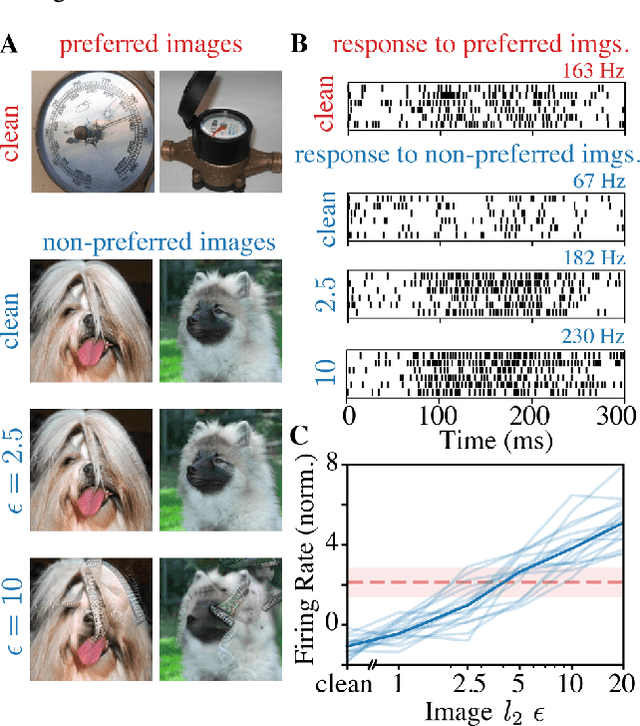
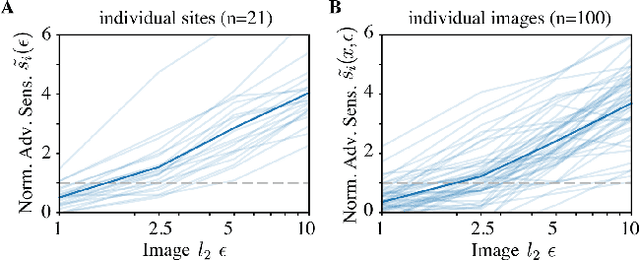
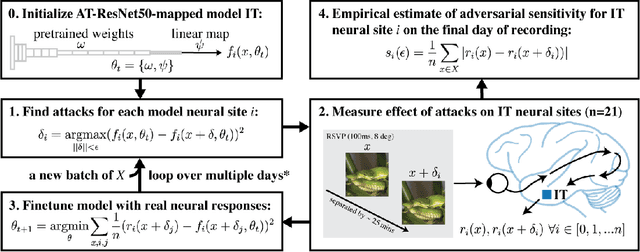
Abstract:Visual systems of primates are the gold standard of robust perception. There is thus a general belief that mimicking the neural representations that underlie those systems will yield artificial visual systems that are adversarially robust. In this work, we develop a method for performing adversarial visual attacks directly on primate brain activity. We then leverage this method to demonstrate that the above-mentioned belief might not be well founded. Specifically, we report that the biological neurons that make up visual systems of primates exhibit susceptibility to adversarial perturbations that is comparable in magnitude to existing (robustly trained) artificial neural networks.
Neural Population Geometry Reveals the Role of Stochasticity in Robust Perception
Nov 12, 2021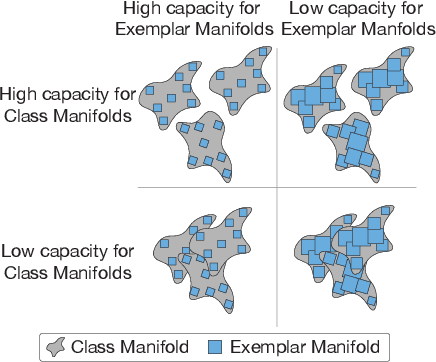
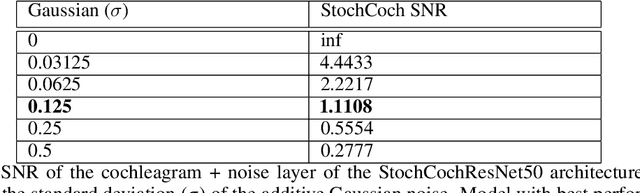
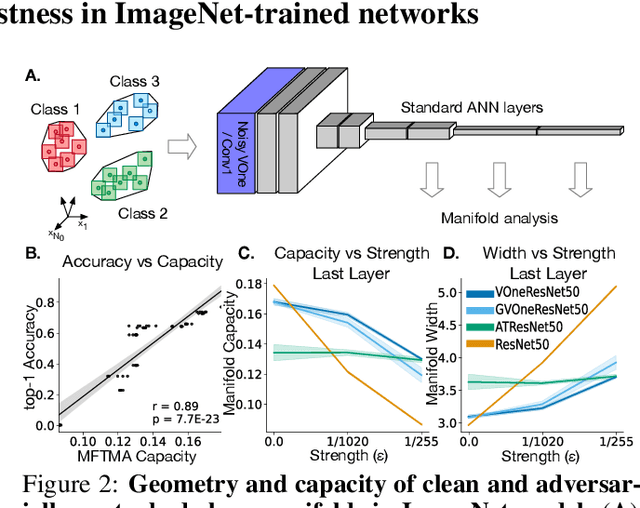
Abstract:Adversarial examples are often cited by neuroscientists and machine learning researchers as an example of how computational models diverge from biological sensory systems. Recent work has proposed adding biologically-inspired components to visual neural networks as a way to improve their adversarial robustness. One surprisingly effective component for reducing adversarial vulnerability is response stochasticity, like that exhibited by biological neurons. Here, using recently developed geometrical techniques from computational neuroscience, we investigate how adversarial perturbations influence the internal representations of standard, adversarially trained, and biologically-inspired stochastic networks. We find distinct geometric signatures for each type of network, revealing different mechanisms for achieving robust representations. Next, we generalize these results to the auditory domain, showing that neural stochasticity also makes auditory models more robust to adversarial perturbations. Geometric analysis of the stochastic networks reveals overlap between representations of clean and adversarially perturbed stimuli, and quantitatively demonstrates that competing geometric effects of stochasticity mediate a tradeoff between adversarial and clean performance. Our results shed light on the strategies of robust perception utilized by adversarially trained and stochastic networks, and help explain how stochasticity may be beneficial to machine and biological computation.
Combining Different V1 Brain Model Variants to Improve Robustness to Image Corruptions in CNNs
Oct 20, 2021
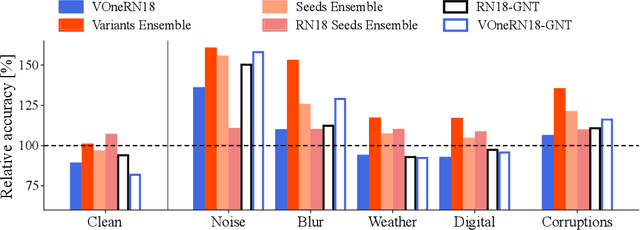


Abstract:While some convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have surpassed human visual abilities in object classification, they often struggle to recognize objects in images corrupted with different types of common noise patterns, highlighting a major limitation of this family of models. Recently, it has been shown that simulating a primary visual cortex (V1) at the front of CNNs leads to small improvements in robustness to these image perturbations. In this study, we start with the observation that different variants of the V1 model show gains for specific corruption types. We then build a new model using an ensembling technique, which combines multiple individual models with different V1 front-end variants. The model ensemble leverages the strengths of each individual model, leading to significant improvements in robustness across all corruption categories and outperforming the base model by 38% on average. Finally, we show that using distillation, it is possible to partially compress the knowledge in the ensemble model into a single model with a V1 front-end. While the ensembling and distillation techniques used here are hardly biologically-plausible, the results presented here demonstrate that by combining the specific strengths of different neuronal circuits in V1 it is possible to improve the robustness of CNNs for a wide range of perturbations.
ThreeDWorld: A Platform for Interactive Multi-Modal Physical Simulation
Jul 09, 2020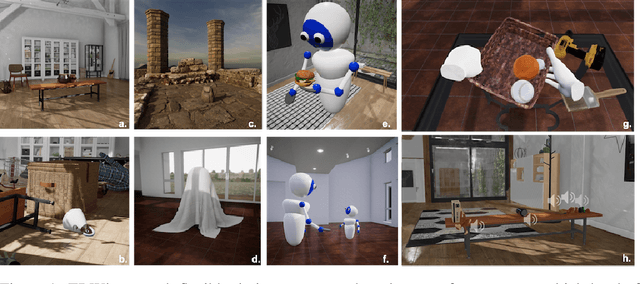
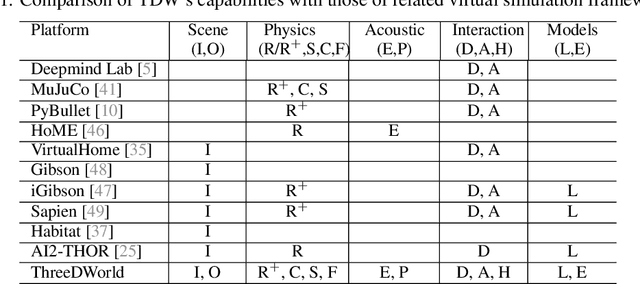

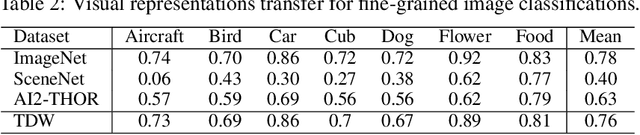
Abstract:We introduce ThreeDWorld (TDW), a platform for interactive multi-modal physical simulation. With TDW, users can simulate high-fidelity sensory data and physical interactions between mobile agents and objects in a wide variety of rich 3D environments. TDW has several unique properties: 1) realtime near photo-realistic image rendering quality; 2) a library of objects and environments with materials for high-quality rendering, and routines enabling user customization of the asset library; 3) generative procedures for efficiently building classes of new environments 4) high-fidelity audio rendering; 5) believable and realistic physical interactions for a wide variety of material types, including cloths, liquid, and deformable objects; 6) a range of "avatar" types that serve as embodiments of AI agents, with the option for user avatar customization; and 7) support for human interactions with VR devices. TDW also provides a rich API enabling multiple agents to interact within a simulation and return a range of sensor and physics data representing the state of the world. We present initial experiments enabled by the platform around emerging research directions in computer vision, machine learning, and cognitive science, including multi-modal physical scene understanding, multi-agent interactions, models that "learn like a child", and attention studies in humans and neural networks. The simulation platform will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge